1 Introduction
The robot hearing system mainly recognizes and judges human voices, and then outputs corresponding action commands to control the movements of the head and arms. The traditional robot hearing system generally uses a PC as a platform to control the robot. Its characteristic is that a computer is used as the information processing core of the robot to control the robot through an interface circuit. Although the processing power is relatively strong, the voice library is relatively complete, and the system update and function expansion are relatively easy, it is relatively bulky, which is not conducive to the miniaturization of the robot and working under complex conditions. In addition, it consumes a lot of power and is costly.
This design uses the digital signal processing chip TMS320VC5509 with a high cost performance as the voice recognition processor. It has a fast processing speed, which enables the robot to independently complete complex voice signal processing and action command control in an offline state. The development of the FPGA system reduces the area occupied by the timing control circuit and the logic circuit on the PCB board, making the voice processing part of the robot's "brain" miniaturized and low-power. The development of a robot system with a small size, low power consumption, high speed, and the ability to complete voice recognition and action commands in a specific range has great practical significance.
2 Overall design of system hardware
The hardware function of the system is to realize the collection of voice commands and the drive control of the stepper motor, and provide a development and debugging platform for the system software, as shown in Figure 1.
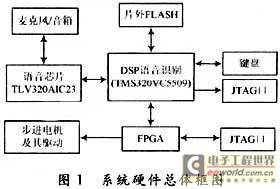
The system hardware is divided into several parts: voice signal acquisition and playback, DSP-based voice recognition, FPGA action command control, stepper motor and its driver, DSP external flash memory chip, JTAG port simulation debugging and keyboard control. The workflow is that the microphone converts the human voice signal into an analog signal, which is then quantized by the audio chip TLV320AIC23 and converted into a digital signal for input into the DSP. After the DSP completes the recognition, it outputs the action command.
FPGA generates correct forward and reverse signals and accurate pulses to the stepper motor driver chip according to the action instructions input by DSP. The driver chip provides the driving signal of the stepper motor to control the rotation of the stepper motor. The off-chip FLASH is used to store system programs and voice libraries and complete the power-on loading of the system. The JTAG port is used for online simulation with the PC, and the keyboard is used for parameter adjustment and function switching.
3 Speech Recognition System Design
3.1 Characteristics of speech signals
The frequency components of speech signals are mainly distributed between 300 and 3400 Hz. According to the sampling theorem, the sampling rate of the signal is selected to be 8 kHz. One characteristic of speech signals is their "short-term nature". Sometimes they show the characteristics of random noise in a short period of time, while in another period they show the characteristics of periodic signals, or both. The characteristics of speech signals change with time. Only within a period of time can the signal show stable and consistent characteristics. Generally speaking, the short period of time can be 5 to 50 ms. Therefore, the processing of speech signals must be based on their "short-term nature" [2]. The system sets the speech signal frame length to 20 ms and the frame shift to 10 ms, so each frame of data is 160×16 bits.
3.2 Collection and playback of speech signals
The voice collection and playback chip used is TLV320AIC23B produced by TI. The analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) and digital-to-analog conversion (DAC) components of TLV320AIC23B are highly integrated inside the chip. The chip uses an 8 k sampling rate, single-channel analog signal input, and dual-channel output. TLV320AIC23 has programmable characteristics. DSP can edit the control register of the device through the control interface, and can compile SPI and I2C interfaces. The circuit connection between TLV320AIC23B and DSP5509 is shown in Figure 2.
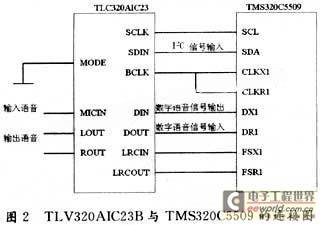
DSP uses I2C port to set the register of TLV320AIC23. When MODE=O, it is an I2C interface. DSP uses master transmission mode to initialize 11 registers with addresses of 0000000 to 0001111 through I2C port. In I2C mode, data is written in three 8-bits. TLV320AIC23 has 7-bit address and 9-bit data, that is, the highest bit of the data item needs to be supplemented to the last bit of the second 8-bit.
The MCBSP serial port is connected to the TLV320AIC23 through six pins: CLKX, CLKR, FSX, FSR, DR and CX. Data is transmitted through the MCBSP serial port to communicate with peripherals through the DR and DX pins, and the control synchronization signal is realized by the four pins CLKX, CLKR, FSX and FSR. Set the MCBSP serial port to DSP Mode, then synchronize the receiver and transmitter of the serial port, and start the serial port transmission by the frame synchronization signal LRCIN and LRCOUT of the TLV320AIC23, and set the data word length of the transmission and reception to 32b (16b for the left channel and 16b for the right channel) single frame mode.
3.3 Design of speech recognition program module
In order to realize the robot's recognition of non-specific voice commands, the system adopts a non-specific isolated word recognition system. Non-specific voice recognition means that the voice model is trained by people of different ages, genders, and accents, and the speaker's voice can be recognized without training [2]. The system is divided into pre-emphasis and windowing, short point detection, feature extraction, pattern matching with the voice library, and training.
3.3.1 Pre-emphasis and windowing of speech signals
The pre-emphasis processing is mainly to remove the influence of glottal excitation and oral and nasal radiation. The pre-emphasis digital filter H(Z)=1-KZ-1, where is the pre-emphasis coefficient, close to 1. In this system, k is 0.95. Pre-emphasize the speech sequence X(n) to obtain the pre-emphasized speech sequence
x(n):x(n)=X(n)-kX(n-1) (1)
The system uses a finite-length Hamming window to slide on the speech sequence to intercept the speech signal with a frame length of 20 ms and a frame shift of 10 ms. The use of the Hamming window can effectively reduce the loss of signal features.
3.3.2 Endpoint Detection
Endpoint detection detects the beginning and end of a word when there is enough time gap between words. It usually detects short-time energy distribution. The equation is:
![]()
Among them, x(n) is the speech sequence intercepted by the Hamming window, and the sequence length is 160, so N is 160. For a silent signal, E(n) is very small, but for a sound signal, E(n) will quickly increase to a certain value, thereby distinguishing the starting point and the ending point of the word.
3.3.3 Feature vector extraction
The feature vector is to extract effective information from the speech signal for further analysis and processing. Currently, the commonly used feature parameters include linear prediction cepstrum coefficients LPCC, Mel cepstrum coefficients MFCC, etc. The speech signal feature vector is extracted using the Mel Frequency Cepstrum Coeficient MFCC. The MFCC parameter is based on the human auditory characteristics. It uses the critical band effect of human hearing and uses the MEL cepstrum analysis technology to process the speech signal to obtain the MEL cepstrum coefficient vector sequence. The MEL cepstrum coefficients are used to represent the spectrum of the input speech. Several bandpass filters with triangular or sinusoidal filtering characteristics are set within the speech spectrum range, and then the speech energy spectrum is passed through the filter group. The output of each filter is calculated, the logarithm is taken, and a discrete cosine transform (DCT) is performed to obtain the MFCC coefficient. The transformation formula of the MFCC coefficient can be simplified as follows:
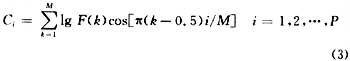
Among them, i is the number of triangular filters, this system selects P as 16, F(k) is the output data of each filter, and M is the data length.
3.3.4 Pattern Matching and Training of Speech Signals
Model training is to train the feature vector to establish a template, and pattern matching is to match the current feature vector with the template in the speech library to obtain the result. The pattern matching and training of the speech library adopts the Hidden Markov Model HMM (Hidden Markov Models), which is a probability model of the statistical characteristics of a statistical random process and a double random process. Because the Hidden Markov Model can well describe the non-stationarity and variability of speech signals, it is widely used.
There are three basic algorithms for HMM: Viterbi algorithm, forward-backward algorithm, and Baum-Welch algorithm. This design uses the Viterbi algorithm for state discrimination and matches the feature vector of the collected speech with the model of the speech library. The Baum-Welch algorithm is used to solve the training of speech signals. Since the observation features of the model are independent between frames, the Baum-Welch algorithm can be used to train the HMM model.
3.4 DSP Development of Speech Recognition Program
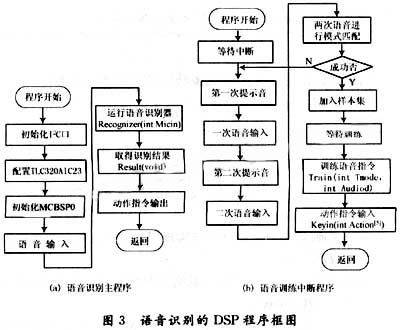
The development environment of DSP is CCS3.1 and DSP/BIOS. The speech recognition and training programs are made into modules respectively, defined as different functions, and called in the program. The speech recognition function is defined as int Recognizer (int Micin), the recognition result output function is int Result (void), the speech training function is int Train (int Tmode, int Audiod), and the action command input function is int Keyin (int Action).
The function of the speech recognizer is to transform the current speech input into a speech feature vector, match the template of the speech library and output the result. The speech response output function outputs the speech response corresponding to the acquired speech recognition result. Speech training is to convert the speech command input of multiple people of different ages, genders and accents into the template of the training library. In order to prevent sample errors, each person's speech command needs to be trained twice. For the two inputs, the Euclidean distance is used for pattern matching. If the similarity of the two inputs reaches 95%, they are added to the sample set. The speech response input function is to input the opposite speech output for each template in the speech library to achieve the purpose of language response. The system working state is to execute the language recognition subroutine, execute external interrupts during training, execute the training function, obtain the database template, and return after training. The program flowchart is shown in Figure 3.
4. Design of robot motion control system
4.1 FPGA Logic Design
The system controls the robot's head movements through voice. The head movements are divided into two degrees of freedom: up and down and left and right. Two stepper motors are required for control. After the DSF completes voice recognition, it outputs the corresponding action instructions. After the action is executed, the DSP issues a zeroing instruction and the head returns to the initial state. The role of the FPGA is to provide DSP interface logic, set the RAM block to store DSP instructions, and generate stepper motor drive pulses to control the rotation direction and angle of the stepper motor.
The FPGA device is the action command control unit. The design uses the FLEXlOKE chip. After receiving the DSP data, it controls two stepper motors in parallel. The internal structure logic of the FPGA is shown in Figure 4. Two components are set inside the FPGA as motor pulse generators to control the working pulses and forward and reverse rotation of the motor. AO~A7 are DSP data input ports, WR is the data write port, P1 and P2 are the pulse input ports of the two stepper motor driver chips, L1 and L2 are the motor forward and reverse control ports, and ENABLE is the enable signal.
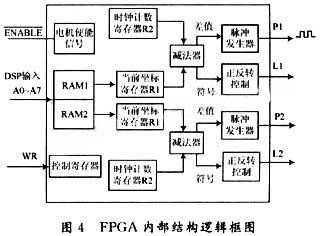
RAM1 and RAM2 are the command registers of the two stepper motors respectively. The motor pulse generator sends out square wave pulses corresponding to the number in RAM. DSP outputs 8-bit instructions through DO~D8 data terminal, where D8 is RAM selection. When it is 1, RAM1 is selected, and when it is 0, RAM0 is selected. DO~D7 is the output motor angle. The electrode rotation angle is 120° up and down and left and right, with an accuracy of 1°. The initial value is 60°. The range of DO~D7 is 00000000~11111000, and the initial value is 00111100. FPGA acts as a stepper pulse generator, controls the motor speed through clock cycle configuration, and the coordinates corresponding to the initial value determine the forward and reverse rotation. The system action instruction program is shown in Figure 5.
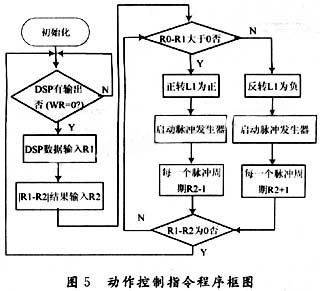
Among them, R1 is the DSP instruction register, and R2 is the current coordinate register. The rotation direction and angle of the stepper motor are determined by performing a difference operation between the output coordinates of the DSP and the current coordinates of the FPGA. The advantage is that the current action can be ended to run new instructions according to the changes in the new input instructions. After the instruction is executed, the system is reset and the stepper motor returns to the initial state.
4.2 FPGA Logic Simulation
FPGA uses MAX-PLUSⅡ development platform and VHDL language to design the above logic functions, and debugs them through JTAG interface. FLEXl0KE chip can output correct positive and negative reverse signals and pulse waveforms according to DSP output instructions.
4.3 Stepper Motor Drive Design
FPGA controls the stepper motor driver chip through P1, L1, P2, and L2 outputs. The stepper motor driver uses the single-chip sinusoidal subdivision two-phase stepper motor driver dedicated chip TA8435H produced by Toshiba. The circuit connection between FPGA and TA8435H is shown in Figure 6.
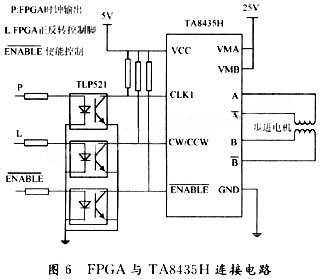
Since the operating voltage of FLEX1OKE and TMS320VC5509 is 3.3 V, while that of TA8435H is 5 V and 25 V, the pin connection uses the optocoupler device TLP521 to isolate the voltage on both sides. CLK1 is the clock input pin, CW/CCW is the forward and reverse control pin, and A, A, B, B are the two-phase stepper motor input.
5 Conclusion
The system makes full use of the high processing speed of DSP and the expandable off-chip storage space. It has the characteristics of high speed, real-time, high recognition rate and supports a large voice library. The use of FPGA simplifies the system circuit. One FLEX10KE chip can complete the timing control of 2 stepper motors. Although there is a certain gap between the processing speed and the storage capacity of the voice library and the PC system, the embedded system with DSP and FPGA as the core undoubtedly has a broad prospect in the miniaturization, low power consumption and specific function realization of the robot.
Previous article:Design of communication software for a certain aircraft bus system based on FPGA and DSP technology
Next article:Discussion on the selection strategy of ASIC, FPGA and DSP in software radio design
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-23 10:23







- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- "Cross-chip" quantum entanglement helps build more powerful quantum computing capabilities
- Why is the vehicle operating system (Vehicle OS) becoming more and more important?
- Car Sensors - A detailed explanation of LiDAR
- Simple differences between automotive (ultrasonic, millimeter wave, laser) radars
- Comprehensive knowledge about automobile circuits
- Introduction of domestic automotive-grade bipolar latch Hall chip CHA44X
- Infineon Technologies and Magneti Marelli to Drive Regional Control Unit Innovation with AURIX™ TC4x MCU Family
- Power of E-band millimeter-wave radar
- Hardware design of power supply system for automobile controller
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Intel promotes AI with multi-dimensional efforts in technology, application, and ecology
- ChinaJoy Qualcomm Snapdragon Theme Pavilion takes you to experience the new changes in digital entertainment in the 5G era
- Infineon's latest generation IGBT technology platform enables precise control of speed and position
- Two test methods for LED lighting life
- Don't Let Lightning Induced Surges Scare You
- Application of brushless motor controller ML4425/4426
- Easy identification of LED power supply quality
- World's first integrated photovoltaic solar system completed in Israel
- Sliding window mean filter for avr microcontroller AD conversion
- What does call mean in the detailed explanation of ABB robot programming instructions?
- STMicroelectronics discloses its 2027-2028 financial model and path to achieve its 2030 goals
- 2024 China Automotive Charging and Battery Swapping Ecosystem Conference held in Taiyuan
- State-owned enterprises team up to invest in solid-state battery giant
- The evolution of electronic and electrical architecture is accelerating
- The first! National Automotive Chip Quality Inspection Center established
- BYD releases self-developed automotive chip using 4nm process, with a running score of up to 1.15 million
- GEODNET launches GEO-PULSE, a car GPS navigation device
- Should Chinese car companies develop their own high-computing chips?
- Infineon and Siemens combine embedded automotive software platform with microcontrollers to provide the necessary functions for next-generation SDVs
- Continental launches invisible biometric sensor display to monitor passengers' vital signs
- How to measure the resistance of a capacitor with a fully automatic multimeter
- Knowledge of using precision resistors
- Xiaobai made InMoov robot arm without any obstacles
- How to collect the analog signal 4-20mA input and input it to the ADC pin of STM32?
- Toshiba Photorelay TLP3547 Trial
- Capacitive touch MSP430FR2676 MCU motherboard
- ③、Drive SSD1306
- How to deal with two ground networks
- TWS headset hardware design pictures
- New Technology Development of Satellite Transponders

 FPGA implementation of FIR filter
FPGA implementation of FIR filter Analysis and Implementation of MAC Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks (by Yang Zhijun, Xie Xianjie, and Ding Hongwei)
Analysis and Implementation of MAC Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks (by Yang Zhijun, Xie Xianjie, and Ding Hongwei)
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号