Zhineng will create a special column around Intelligent Driving, and systematically introduce intelligent driving technology to you in combination with the test environment.
By integrating advanced sensors , controllers , and actuators, vehicles can achieve partial or full autonomous driving . The functions and scenario systems of intelligent driving are the key to understanding and developing this technology, but some readers do not actually understand the functions and scenario systems of intelligent driving. This column will continue to introduce these functions and the relationship between them.
01 Functional system of intelligent driving
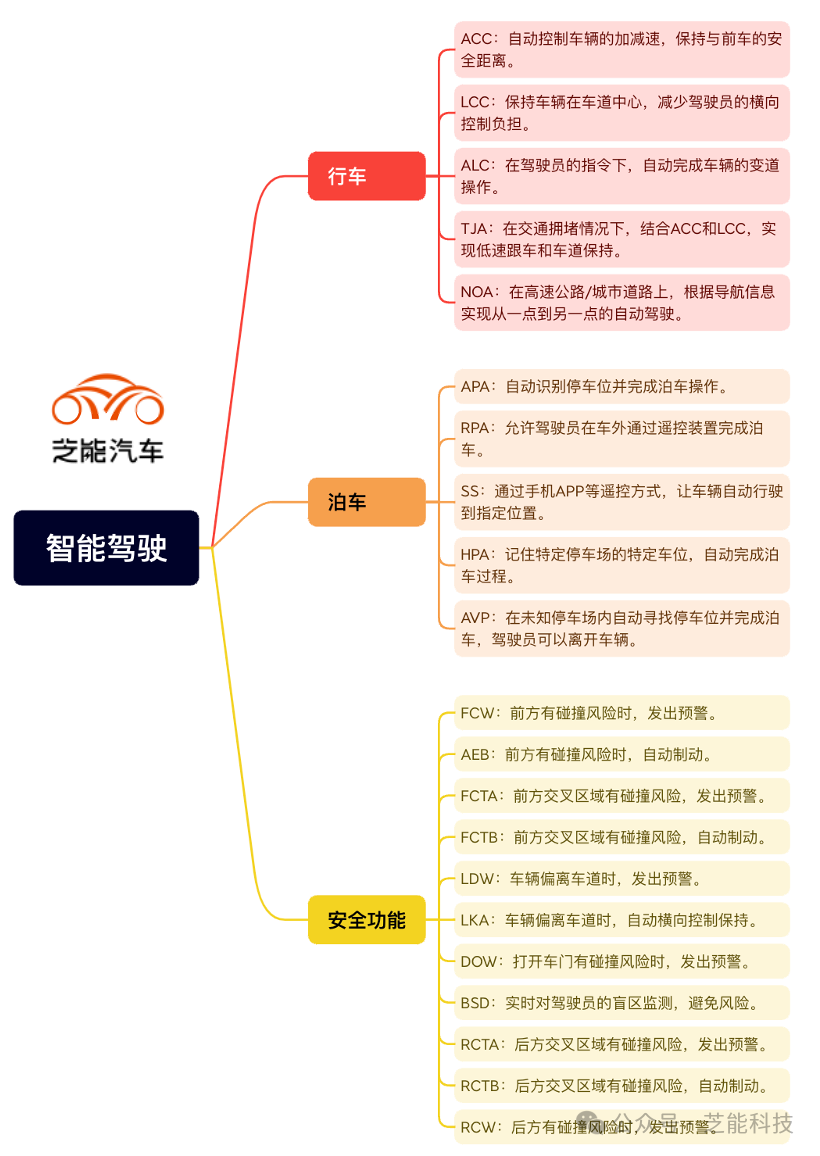
The functional system of intelligent driving is usually divided into two categories: driving functions and parking functions.
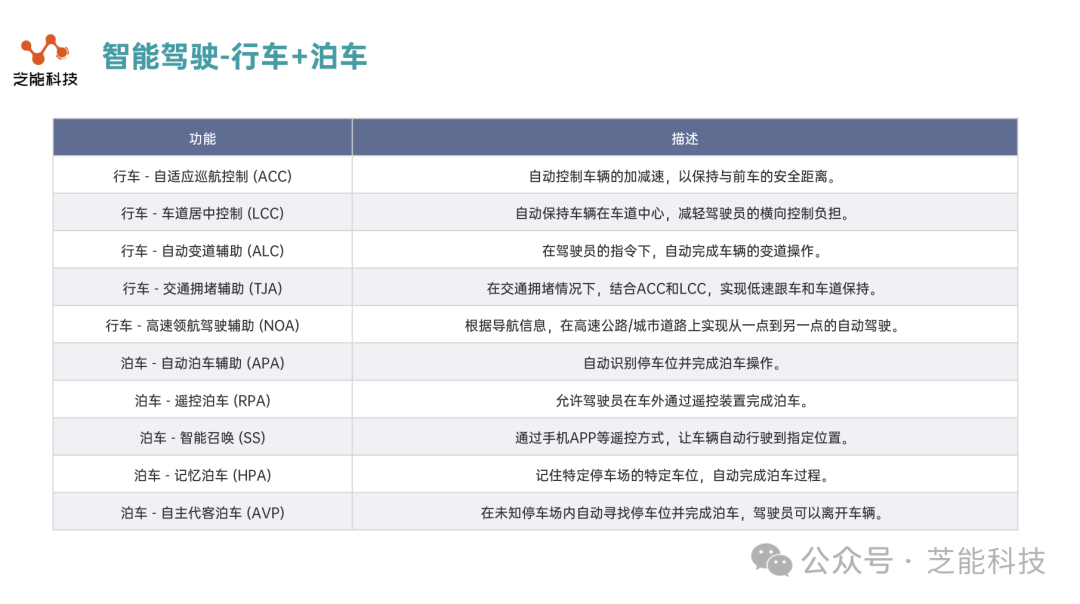
● Driving functions: including adaptive cruise control ( ACC ), lane centering control (LCC), automatic lane change assist (ALC), traffic jam assist (TJA) and highway pilot assist (NOA). These functions range from L1 to L3 according to SAE's intelligent driving classification standards, covering from simple longitudinal control to complex point-to-point autonomous driving.
◎ ACC: Automatically controls the acceleration and deceleration of the vehicle to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front.
◎ LCC: Keep the vehicle in the center of the lane and reduce the driver's lateral control burden.
◎ ALC: Automatically completes the vehicle's lane change operation under the driver's command.
◎ TJA: In traffic congestion, it combines ACC and LCC to achieve low-speed following and lane keeping.
◎ NOA: On highways/urban roads, autonomous driving from one point to another is achieved based on navigation information .
● Parking functions: including automatic parking assistance (APA), remote parking (RPA), smart summon (SS), memory parking (HPA) and autonomous valet parking (AVP). These functions range from L2 to L4 levels, providing solutions from assisted parking to fully automatic parking.
◎ APA: Automatically identify parking spaces and complete parking operations.
◎ RPA: Allows the driver to complete parking through a remote control device outside the car.
◎ SS: Through remote control methods such as mobile phone APP, the vehicle can automatically drive to the designated location.
HPA: Remembers specific parking spaces in specific parking lots and automatically completes the parking process.
◎ AVP: Automatically searches for a parking space in an unknown parking lot and completes parking, allowing the driver to leave the vehicle.
In addition to the two major functions of intelligent driving and parking, intelligent driving also covers a series of active safety functions.
These features include forward collision warning (FCW), automatic emergency braking (AEB), front cross traffic area alert (FCTA), front cross traffic area assist (FCTB), lane departure warning (LDW), lane keeping assist (LKA), door opening warning (DOW), blind spot monitoring (BSD ) , rear cross traffic area alert (RCTA), rear cross traffic area assist (RCTB), and rear collision warning (RCW).
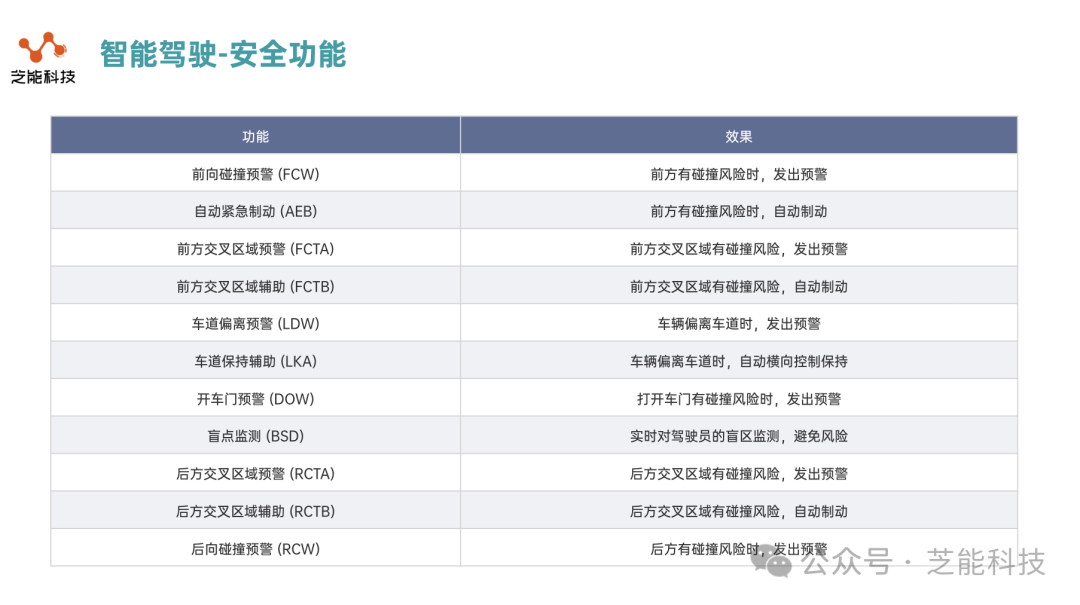
● These functions are related to the danger sources in the relative position of the vehicle:
◎ FCW: Issues a warning when there is a risk of collision ahead.
◎ AEB: Automatic braking when there is a risk of collision ahead.
◎ FCTA: There is a risk of collision in the intersection area ahead, and a warning is issued.
◎ FCTB: There is a risk of collision in the front intersection area, automatic braking.
◎ LDW: Issues a warning when the vehicle deviates from the lane.
◎ LKA: Automatic lateral control is maintained when the vehicle deviates from the lane.
◎ DOW: When there is a risk of collision when opening the door, a warning is issued.
◎ BSD: Real-time monitoring of the driver’s blind spots to avoid risks.
◎ RCTA: There is a risk of collision in the rear cross-traffic area and a warning is issued.
◎ RCTB: There is a risk of collision in the rear cross traffic zone, and automatic braking is applied.
◎ RCW: Issues a warning when there is a risk of rear collision.
These features provide a variety of safety effects, helping drivers to be alerted and take action in a timely manner to reduce the risk of accidents.
02 Intelligent Driving Scenario System
The scenario system of intelligent driving is based on the user's travel experience, and mainly includes three areas: highways, urban areas and parking lots.
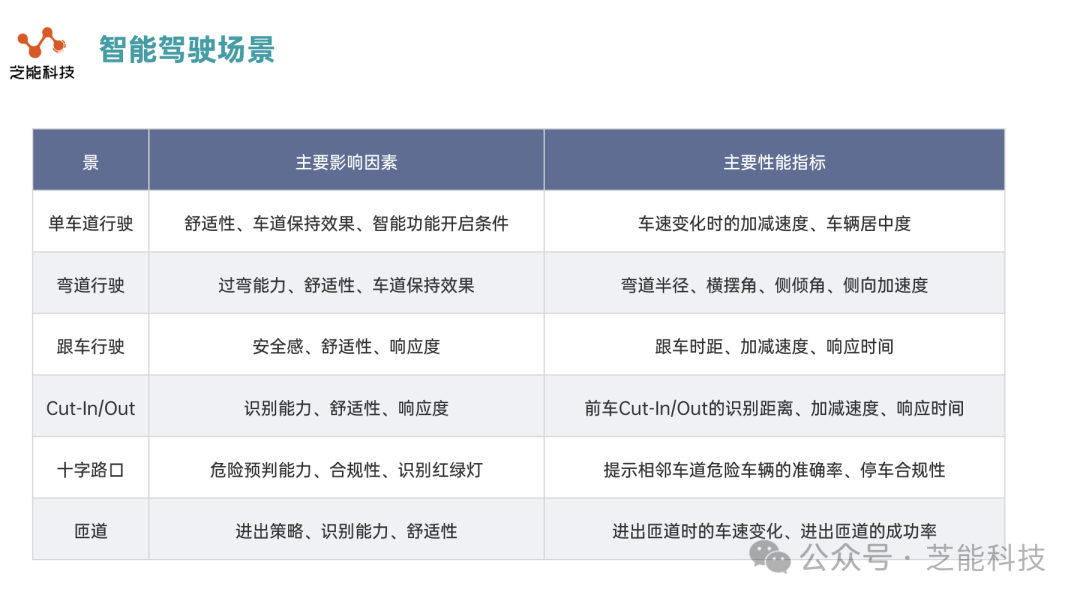
● Driving scenarios: including driving in the same lane, changing lanes, intersections, ramps, etc. In these scenarios, the intelligent driving system needs to consider factors such as comfort, safety, responsiveness, and recognition capabilities to provide a smooth and safe driving experience.
◎ For driving in this lane, users are very concerned about comfort and the effect of the vehicle staying in the lane. Comfort is reflected in the acceleration and deceleration of the vehicle speed, while the lane keeping effect is evaluated by the distance between the vehicle and the lane line.
◎ For curved roads, the system's ability to negotiate corners directly affects the user's trust, while the sense of safety and comfort when following a car are equally important. At intersections, the system's recognition ability and understanding of traffic lights affect the driver's sense of safety. Ramps test the system's entry and exit strategies and speed change control capabilities.
● Parking scenarios: involve automatic driving, searching for parking spaces, parking in and out of parking spaces in the parking lot. In these scenarios, the system's parking capability and comfort are key user experience factors. When driving in the parking lot, the system needs to accurately identify various static and dynamic obstacles to ensure safe driving. When searching for parking spaces, the system's parking space recognition capability directly determines the user's parking efficiency and experience.
By deeply understanding the relationship between functions and scenarios, developers can better plan the performance indicators of intelligent driving and ensure that user experience and function development proceed in parallel. This will not only help improve the market competitiveness of products , but also ensure that intelligent driving technology is safer, more reliable and more user-friendly.
There is a close relationship between the functions and scenarios of intelligent driving. For example, ACC and LCC are mainly applicable to driving in the same lane, while ALC is applicable to lane changing scenarios. TJA and NOA involve more complex scenarios, including driving in the same lane, lane changing, and ramps. Parking functions such as APA and RPA are mainly used in parking scenarios in parking lots.
summary
The development of intelligent driving technology is constantly driving the automotive industry forward. By establishing a complete functional system and scenario system and understanding the inherent connection between them, we can better develop and optimize the intelligent driving system and provide users with a safer, more convenient and more enjoyable driving experience. With the continuous advancement of technology and the improvement of regulations, intelligent driving will play an increasingly important role in future travel.
Previous article:Definition of basic concepts of intelligent driving Analysis of China's intelligent driving landscape
Next article:Research on the technology of small three-electric system (PDU+DC+OBC) for new energy vehicles
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Next-generation automotive microcontrollers: STMicroelectronics technology analysis
- WPG World Peace Group launches automotive headlight solution based on easy-to-charge semiconductor products
- What is the car ZCU that we talk about every day?
- An article reviews the "no-map" intelligent driving solutions of various car companies
- Renesas takes the lead in launching multi-domain fusion SoC using automotive-grade 3nm process
- BYD and Huawei have made another big move!
- V2X technology accelerates, paving the way for advanced autonomous driving
- Rimac and Ceer to supply fully integrated electric drive systems for electric vehicles
- Huawei's all-solid-state battery has surfaced, achieving a major technological breakthrough!
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Red Hat announces definitive agreement to acquire Neural Magic
- 5G network speed is faster than 4G, but the perception is poor! Wu Hequan: 6G standard formulation should focus on user needs
- SEMI report: Global silicon wafer shipments increased by 6% in the third quarter of 2024
- OpenAI calls for a "North American Artificial Intelligence Alliance" to compete with China
- OpenAI is rumored to be launching a new intelligent body that can automatically perform tasks for users
- Nidec Intelligent Motion is the first to launch an electric clutch ECU for two-wheeled vehicles
- Nidec Intelligent Motion is the first to launch an electric clutch ECU for two-wheeled vehicles
- ASML provides update on market opportunities at 2024 Investor Day
- Arm: Focusing on efficient computing platforms, we work together to build a sustainable future
- AMD to cut 4% of its workforce to gain a stronger position in artificial intelligence chips

 LM8261M5X/NOPB
LM8261M5X/NOPB











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号