sliding mean filter algorithm
Various sensors are used in the embedded development process, such as pressure sensors, light sensors, acceleration sensors, temperature and humidity sensors, angular rate sensors, etc. The data collection process of these sensors is mixed with noise, which makes the sensor measurement accuracy error too large [sensor data fluctuates greatly]. The source of sensor data output noise may be caused by many factors such as vibration, temperature changes, electromagnetic interference, etc. Often we use digital signal processing methods to eliminate or suppress this noise. Commonly used mathematical methods include FFT filtering algorithm, DFT filtering algorithm, Kalman algorithm, median filtering algorithm, average filtering algorithm, sliding mean filtering, least squares method, sorting algorithm, limiting filtering algorithm, high-pass filtering, low-pass filtering, etc. Each algorithm has its own characteristics and application scenarios. Making good use of these mathematical tools can make your products or works more soulful.
This series of articles mainly explains the above various algorithms and application scenarios. The text first introduces the sliding mean filter algorithm.
Take the multi-channel voltage acquisition system project in the practical entry-level STM32 software project as an example to describe sliding mean filtering. Before that, we must clarify why sliding mean filtering is used in ADC acquisition. First, the analog quantity of the acquisition port may be mixed with interference signals of different frequency bands and different peaks. Then the amount of data collected by the ADC will deviate from the original real result. Then the acquisition error can be greatly reduced and the accuracy improved through two means: hardware and digital filtering. Software methods include arithmetic average (which is the sum of N values and then divided by the number of values.), sliding average filter, Kalman, FFT, etc.
The steps to implement the sliding mean filter algorithm are as follows: The first is to acquire sensor data. The ADC + cyclic DMA method is used to collect voltage data, with 5 data as a group, and these data are queued in sequence, that is, the following array. The first entry The data to the queue is flushed continuously, and the purpose of data sliding can be achieved in turn.

Code
The picture shows the sliding mean filtering of the 5-channel ADC sampling values. Every five channels are sequentially averaged. Because the data in ADC_ConvertedValue[] is continuously refreshed by DMA, the sliding of the data is realized.
The picture below shows how MATLAB is used to process the collected data with sliding mean filtering. Blue is the original signal with noise, and red is the processed signal. It can be seen that sliding mean filtering can filter out a large amount of noise [burr].
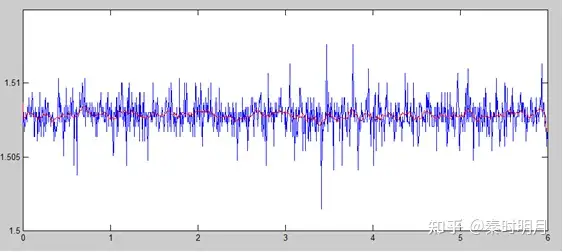
Simulation renderings
The characteristics of sliding mean filter when used are as follows: it has good suppression effect on periodic interference signals, has high smoothness, is suitable for high-rate signal acquisition, and the algorithm is simple and easy to calculate. Because the ADC acquisition is above 100KHz, this algorithm is suitable for this application scenario.
A large N value will result in low sensitivity. This algorithm is not suitable for large interference signals, that is, when the signal-to-noise ratio is small.
Previous article:C language programming suggestions and techniques are also applicable to the learning of microcontrollers.
Next article:What are the tips and tricks about learning and finding a job with microcontrollers?
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Learn ARM development(16)
- Learn ARM development(17)
- Learn ARM development(18)
- Embedded system debugging simulation tool
- A small question that has been bothering me recently has finally been solved~~
- Learn ARM development (1)
- Learn ARM development (2)
- Learn ARM development (4)
- Learn ARM development (6)
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- CGD and Qorvo to jointly revolutionize motor control solutions
- CGD and Qorvo to jointly revolutionize motor control solutions
- Keysight Technologies FieldFox handheld analyzer with VDI spread spectrum module to achieve millimeter wave analysis function
- Infineon's PASCO2V15 XENSIV PAS CO2 5V Sensor Now Available at Mouser for Accurate CO2 Level Measurement
- Advanced gameplay, Harting takes your PCB board connection to a new level!
- Advanced gameplay, Harting takes your PCB board connection to a new level!
- A new chapter in Great Wall Motors R&D: solid-state battery technology leads the future
- Naxin Micro provides full-scenario GaN driver IC solutions
- Interpreting Huawei’s new solid-state battery patent, will it challenge CATL in 2030?
- Are pure electric/plug-in hybrid vehicles going crazy? A Chinese company has launched the world's first -40℃ dischargeable hybrid battery that is not afraid of cold
- EEWORLD University Hall ---- Signal and System Analysis Tsinghua University Zhuo Qing
- [Live broadcast has ended] TI's new generation of high-performance, low-power Zigbee solutions
- Will you use ESP32-C2 to replace ESP8266?
- Solve the hidden BUG problem of the HX711 chip of the weight scale
- User Guide:TI LAUNCHXL-F28027 C2000 Piccolo LaunchPad
- [Raspberry Pico Review] -- Just received the sample today
- The six lies of open source. Are they true?
- 【ST NUCLEO-H743ZI Review】Testing SPI+TFT (3)
- MSP430 uses timer to measure frequency
- STEVAL-MKI109V3 FSM Experience Analysis

 TLC081CDGNR
TLC081CDGNR
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号