RFID is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency Identification. Radio Frequency Identification is a contactless automatic identification technology that uses radio frequency electromagnetic waves through spatial coupling (alternating magnetic field or electromagnetic field) to achieve contactless information transmission between the reader and the mobile items to be identified, classified and tracked (RFID tags are attached to the items) and achieve identification through the transmitted information. RFID is an automatic identification and data capture technology that can provide unattended automatic monitoring and reporting operations.
The working principle of the RFID reader is as follows: the reader sends out a radio frequency signal of a certain frequency through the antenna. When the tag enters the magnetic field, an induced current is generated to obtain energy. The tag sends out its own code and related information, which is read and decoded by the reader and then sent back to the computer for relevant processing. The identification work does not require human intervention and can work in various harsh environments. High-performance RFID readers can identify multiple objects at the same time [1]. In agricultural production, the scope of RFID use is gradually expanding. With the increasingly stringent food inspection and quarantine systems in developed countries around the world, RFID technology has begun to be widely used in animal management abroad. In some domestic supermarkets, customers are also provided with basic additional functions such as using RFID tags to query the origin and date of high-end agricultural products such as clean vegetables. It can be foreseen that in the future, RFID will inevitably play a greater role in product traceability and quality monitoring. The design idea of this system is shown in Figure 1. It uses high-performance read-write modules and RFID tags that follow the RFIDGEN2 protocol to directly complete complex tag reading, tag anti-collision calculation, information extraction and data storage tasks locally, and only transmits valid information to the background server through the network. This greatly reduces the overhead of network communication and reduces the resource usage of the server, thereby improving the overall operation efficiency of the system, improving stability, and increasing business flexibility.

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of RFID technology applied to agricultural product packaging line
2. System Hardware Design

Figure 2 RF module and CPU interface
Considering high reliability and low cost, this system uses S344B0-based embedded CPU and WJ 6000 RF module as the basis, and cooperates with USB, Realtek network card, SDRAM and other chips to form the core system. The key RF module and CPU interface are shown in Figure 2.
3. Software system design of the system
The entire software system module relationship of the system is shown in Figure 3:

Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the overall system software module
The operating system uses uClinux system as the operating system to manage various hardware and provide a software operation platform. The driver layer provides drivers for various devices such as Ethernet, serial port, USB memory, status light and other devices. The network communication module is responsible for transmitting the processed tag information back to the background server, and can also control the main control module parameters according to the command of the background server to change the working mode. The embedded database control module is responsible for saving the system's work log and saving the read tags and related data to the local database for future inquiries. The protocol analysis module is responsible for protocol analysis of the received data communication packet, extracting valid tag data, and performing tag anti-collision operations, handling various interference problems, and ensuring the integrity of the received tag data. It is also the core part of the entire software system.
RFID reading system software workflow:
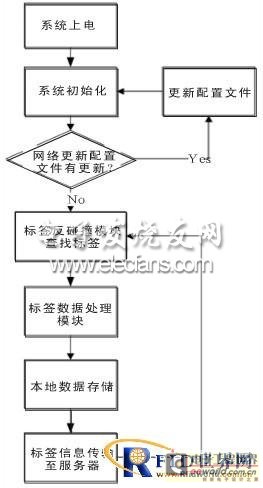
Figure 4 Software system workflow
1. Embedded database operation module
In this project, Sqlite3 is used as the embedded database of the system. The embedded database is an important part of the whole system. It is mainly responsible for the local storage of basic data, the preliminary storage and fast query of barcode reading information, and the preservation of work logs. It can also cooperate with the network communication module to realize the synchronization of network master/slave databases. In the case of the main server crash, most of the data can still be recovered by sorting out the data of all embedded databases, which increases the reliability of the system. This database adopts a single data file design, which can support most of the SQL 92 standard database operation statements and transaction functions. By extending the network operation interface function, it achieves the purpose of communicating and exchanging data with the background database.
2. Network communication module
The characteristic of this system is that it can transmit data to the background data server through multiple network transmission channels through the network bottom support of the embedded Linux operating system. In the network part design of this system, the TCP/IP protocol support provided by the Linux system is used in the local area network, and the method of dynamically establishing a connection with the server is adopted in programming. When the tag information is read and the valid information is decoded, the corresponding Socket request information is sent to the corresponding port of the server. After receiving the request, the server establishes a connection and creates a new Socket port to communicate with the terminal; only when reading data does the database and the terminal generate data transmission and occupy server resources, thereby reducing the network occupancy rate and the load on the server, and improving the efficiency of network communication.
3. RFID protocol analysis module
The protocol parsing module is responsible for adding the sent command parameters to the packet header and other information, and unpacking the information returned by the received tag. By unpacking the information, the relevant information of inventory or reading and writing can be obtained. The RFID Gen2 commands supported by MPR6000 include Read, Write, Kill, Erase, and Lock. The commands are composed of a string, and its structure is as follows:
which are composed of the start frame, node, total length, status, tag information, and CRC.
For example, the opcode of the Gen2 inventory command is 01h, and the operation will return all Gen2 tags that meet the read conditions in the read/write domain. After being processed by the anti-collision module, the resulting data frame consists of two parts: tag information and inventory summary:
That is,
For example, when using antenna B and the RF power is 22, read all Gen2 tags with SL as NOT SET and S3 flag as A. At this time, the starting Q is 1 (i.e. 2 time slots).
60 01 01 16 02 03 00 01If
the tag within the current RF range has a 64-bit Gen2 tag 1 with an ID of "0102 0304 0506 0708".
And there is a 96-bit Gen2 tag 2 with an ID of "1211 1009 08070605 0403 0201".
The read-write module may receive a packet like this, the complete content is as follows:
04 28 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 07 08 30 00 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 02 00 16 00 01 00 00 00 02 00 09Now
parse this packet. According to the protocol,
And
So we get
After extracting the tag information, the obtained tag information can be sent to the embedded database module for local temporary storage, and uploaded to the background server through the network module for recording. The interface function part in the middle will not be given in detail.
IV. Summary and Outlook
The embedded RFID terminal reader described in this article has been put into practical use in an agricultural product packaging production line. It basically meets the requirements of the production line RFID system for front-end RFID tag data collection, processing, and communication. It can replace dedicated RF readers in terms of functionality and stability. Because it uses the free open source Linux operating system and open source database Sqlite, the overall cost is greatly reduced. It is particularly suitable for use in the production and monitoring of agricultural products with high cost sensitivity.
Previous article:Application of RFID Technology in Logistics Management of Cigarette Factory
Next article:Application of RFID Technology in E-Government
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 21:03





- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
-
 Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) System Technology and Application (Written by Ci Xinxin, Wang Subin, and Wang Shuo)
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) System Technology and Application (Written by Ci Xinxin, Wang Subin, and Wang Shuo) -
 Introduction to Internet of Things Engineering 2nd Edition (Gongyi Wu)
Introduction to Internet of Things Engineering 2nd Edition (Gongyi Wu) -
 Detailed explanation and engineering practice of unmanned monitoring technology (Xie Jianbin, Li Peiqin, Yan Wei, Liu Tong, Lin Chenglong, Hong Quanyi, Zhou Hongfei, Cui Yibing)
Detailed explanation and engineering practice of unmanned monitoring technology (Xie Jianbin, Li Peiqin, Yan Wei, Liu Tong, Lin Chenglong, Hong Quanyi, Zhou Hongfei, Cui Yibing) -
 Introduction to Wireless Sensor Networks (Edited by Ma Sasa et al.)
Introduction to Wireless Sensor Networks (Edited by Ma Sasa et al.)
- High signal-to-noise ratio MEMS microphone drives artificial intelligence interaction
- Advantages of using a differential-to-single-ended RF amplifier in a transmit signal chain design
- ON Semiconductor CEO Appears at Munich Electronica Show and Launches Treo Platform
- ON Semiconductor Launches Industry-Leading Analog and Mixed-Signal Platform
- Analog Devices ADAQ7767-1 μModule DAQ Solution for Rapid Development of Precision Data Acquisition Systems Now Available at Mouser
- Domestic high-precision, high-speed ADC chips are on the rise
- Microcontrollers that combine Hi-Fi, intelligence and USB multi-channel features – ushering in a new era of digital audio
- Using capacitive PGA, Naxin Micro launches high-precision multi-channel 24/16-bit Δ-Σ ADC
- Fully Differential Amplifier Provides High Voltage, Low Noise Signals for Precision Data Acquisition Signal Chain
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Lazy voice-controlled lamp based on Gizwits Cloud
- Take the test on TI.com.cn and enjoy 10% off!
- How to measure the waveform capture rate of an oscilloscope and a tutorial
- Network port connector model help! (Except RJ45)
- 【NXP Rapid IoT Review】+ Review Summary
- This sentence was translated from Google Translate, and the final translation must be wrong. What does diode emulation mean?
- Examples of capacitor applications in power supply design (recommended for collection)
- Has anyone used Bosch's PM sensor?
- Detailed explanation | 4 main reasons for power module heating
- THGBMAG5A1JBAAR Where is this product used?

 Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) System Technology and Application (Written by Ci Xinxin, Wang Subin, and Wang Shuo)
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) System Technology and Application (Written by Ci Xinxin, Wang Subin, and Wang Shuo) Detailed explanation and engineering practice of unmanned monitoring technology (Xie Jianbin, Li Peiqin, Yan Wei, Liu Tong, Lin Chenglong, Hong Quanyi, Zhou Hongfei, Cui Yibing)
Detailed explanation and engineering practice of unmanned monitoring technology (Xie Jianbin, Li Peiqin, Yan Wei, Liu Tong, Lin Chenglong, Hong Quanyi, Zhou Hongfei, Cui Yibing)















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号