Mainly the writing of adc.h and adc.c files (written as add.h and add.c during the experiment)
After debugging for a whole morning, I found that the clock was set wrongly. RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC|RCC_APB2Periph_ADC1,ENABLE);
It is set to APB1, so only 0v can appear. Beware! ! !
The add.h code is as follows:
#ifndef _ADD_H
#define _ADD_H
#include "stm32f10x.h"
void ADC_Configure();
#endif
The add.c code is as follows:
#include "add.h"
#define ADC1_DR_Address ((u32)0x40012400 + 0x4C)
__IO uint16_t ADC_ConvertedValue;
static void ADC_GPIO_Config()
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
RCC_AHBPeriphClockCmd(RCC_AHBPeriph_DMA1 ,ENABLE);
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC|RCC_APB2Periph_ADC1,ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_1;
GPIO_Init(GPIOC,&GPIO_InitStructure);
}
static void ADC_DMA_Config()
{
ADC_InitTypeDef ADC_InitStructure;
DMA_InitTypeDef DMA_InitStructure;
DMA_DeInit(DMA1_Channel1);
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_BufferSize = 1;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_DIR = DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_M2M = DMA_M2M_Disable;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryBaseAddr = (u32)&ADC_ConvertedValue;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryDataSize = DMA_MemoryDataSize_HalfWord;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryInc = DMA_MemoryInc_Disable;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Mode = DMA_Mode_Circular;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralBaseAddr = ADC1_DR_Address;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralDataSize = DMA_PeripheralDataSize_HalfWord;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralInc = DMA_PeripheralInc_Disable;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Priority = DMA_Priority_High;
DMA_Init(DMA1_Channel1,&DMA_InitStructure);
DMA_Cmd(DMA1_Channel1, ENABLE);
ADC_InitStructure.ADC_ContinuousConvMode = ENABLE;
ADC_InitStructure.ADC_DataAlign = ADC_DataAlign_Right;
ADC_InitStructure.ADC_ExternalTrigConv = ADC_ExternalTrigConv_None;
ADC_InitStructure.ADC_Mode = ADC_Mode_Independent;
ADC_InitStructure.ADC_NbrOfChannel = 1;
ADC_InitStructure.ADC_ScanConvMode = DISABLE;
ADC_Init(ADC1,&ADC_InitStructure);
RCC_ADCCLKConfig(RCC_PCLK2_Div8);
ADC_RegularChannelConfig(ADC1,ADC_Channel_11,1,ADC_SampleTime_55Cycles5);
ADC_DMACmd(ADC1,ENABLE);
ADC_Cmd(ADC1,ENABLE);
ADC_ResetCalibration(ADC1);
while(ADC_GetResetCalibrationStatus(ADC1));
ADC_StartCalibration(ADC1);
while(ADC_GetCalibrationStatus(ADC1));
ADC_SoftwareStartConvCmd(ADC1,ENABLE);
}
void ADC_Configure()
{
ADC_GPIO_Config();
ADC_DMA_Config();
}
The usart.h code is as follows:
#ifndef _USART_H
#define _USAET_H
#include
void Usart_GPIO_Config(void);
int fputc(int ch,FILE *f);
#endif
The usart.c code is as follows:
#include "usart.h"
#include "stm32f10x.h"
void Usart_GPIO_Config()
{
USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA|RCC_APB2Periph_USART1,ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_9;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA,&GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_10;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA,&GPIO_InitStructure); //Note that this must be added for unclear reasons
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = 115200;
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Tx|USART_Mode_Rx;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;
USART_Init(USART1,&USART_InitStructure);
USART_Cmd(USART1,ENABLE);
}
int fputc(int ch,FILE *f)
{
USART_SendData(USART1,(unsigned char)ch);
while(!(USART1->SR & USART_FLAG_TXE));
return ch;
}
The main.c code is as follows:
/******************** (C) COPYRIGHT 2013 ******************************
* File name: main.c
* Description: Project template built with version 3.5.0.
* Experimental platform: WildFire STM32 development board
* Library version: ST3.5.0
*
* Version: v1.0
**********************************************************************************/
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "add.h"
#include "usart.h"
void delay(__IO uint32_t count);
extern __IO uint16_t ADC_ConvertedValue;
float ADC_ConvertedValueLocal;
/*
* Function name: main
* Description: Main function
* Input: None
* Output: None
*/
int main(void)
{
Usart_GPIO_Config();
ADC_Configure();
while(1)
{
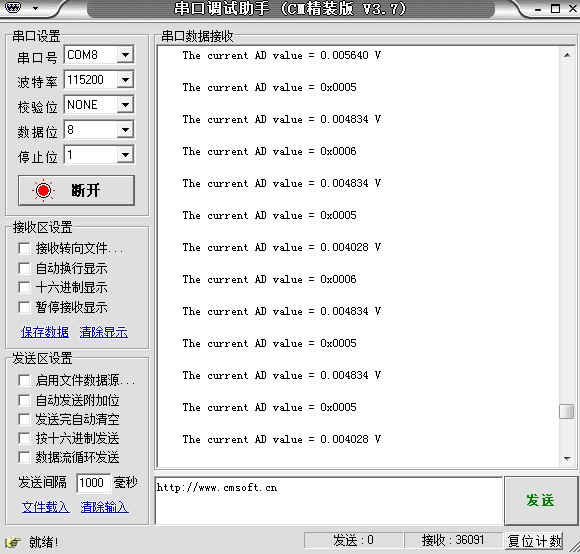
ADC_ConvertedValueLocal =(float) ADC_ConvertedValue/4096*3.3; // Read the converted AD value
printf("\r\n The current AD value = 0x%04X \r\n", ADC_ConvertedValue);
printf("\r\n The current AD value = %f V \r\n",ADC_ConvertedValueLocal);
delay(0x01fffff0);
}
// add your code here ^_^。
}
/******************* (C) COPYRIGHT 2013 *****END OF FILE************/
void delay(__IO uint32_t count)
{
for(;count>0;count--);
}
Previous article:stm32 learning ten
Next article:STM32 learning six
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-15 23:56





- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications

 usb_host_device_code
usb_host_device_code Transplantation of real-time operating system RT-ThreadSmart on STM32MP1
Transplantation of real-time operating system RT-ThreadSmart on STM32MP1















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号