Chapter 4 Integrated Triggers
Contents
4.1 Overview
1. The concept of triggers
Triggers have three basic characteristics:
2. Two stable states of triggers
1 state:
0 state:
3. Description of the logical function of triggers:
4. Classification of triggers:
4.2 Basic forms of triggers
4.2.1 Basic RS triggers
1. Basic RS triggers composed of NAND gates
1. Circuit structure
2. Logical function
3. Characteristic table
2. Basic RS triggers composed of NOR gates
4.2.2 Synchronous triggers
1. Synchronous RS triggers
1. Circuit structure
2. Logical function
3. Drive table
4. Characteristic equation
5. State transition diagram
Chapter 4 Integrated Triggers
Contents
Trigger: A basic logic unit with memory function.
The circuit structure, working principle, and logic function of the basic RS trigger.
The logic function and triggering mode of various triggers.
A brief introduction to the application of triggers.
4.1 Overview
I. The concept of triggers
Review: What is the definition of a combinational circuit? What are the characteristics of the gate circuits that constitute its circuit? The difference between a combinational circuit and a sequential circuit?
Gate circuit: The output signal at a certain moment depends entirely on the input signal at that moment and has no memory function.
Trigger: A basic logic circuit with memory function that can store binary information (digital information).
Triggers have three basic characteristics:
(1) There are two stable states, which can represent binary digits 0 and 1 respectively, and the stable state can be maintained without external triggering;
(2) Under external triggering, the two stable states can be converted to each other (called flip-flop), and the converted stable state can be maintained for a long time, which enables the trigger to memorize binary information and is often used as a binary storage unit.

3. Description of the logical function of the trigger:
characteristic table, excitation table (also known as drive table), characteristic equation, state transition diagram and waveform diagram (also known as timing diagram)
4. Classification of triggers: According to
Different logical functions: RS trigger, D trigger, JK trigger, T trigger and trigger, etc.
Different triggering methods: level trigger, edge trigger and master-slave trigger, etc.
Different circuit structures: basic RS trigger, synchronous trigger, hold blocking trigger, master-slave trigger and edge trigger, etc.
4.2 Basic forms of triggers
4.2.1 Basic RS trigger
1. Basic RS trigger composed of NAND gates
1. Circuit structure
Circuit composition: two NAND gates with cross-coupling input and output (feedback delay). As shown in Figure 4.2.1 (a).
Logic symbol: as shown in Figure (b).

2. Logical function
Review: What is the logical function of the NAND gate?
Use DLCCAI or EWB to demonstrate the logical function of the basic RS flip-flop. (10 minutes)
Working principle. (List the characteristic table while analyzing. The following text is not written on the blackboard.)



Table 4.2.1 Characteristics of basic RS flip-flops composed of NAND gates
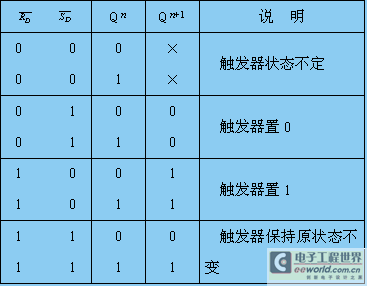
2. Basic RS flip-flops composed of NOR gates
Circuit structure: The input and output of two NOR gates are cross-coupled, as shown in Figure 4.2.2 (a).
Logic symbol: as shown in Figure (b).

Question: What is the logical function of the NOR gate?
Working Principle
A slight change is made to the basic RS flip-flop implemented by the NAND gate.
Characteristics table of basic RS flip-flop composed of NOR gate

4.2.2 Synchronous trigger
Why use synchronous trigger?
The triggering mode of basic RS trigger:
![]() directly controlled by the input signal of the terminal. (Level direct trigger)
directly controlled by the input signal of the terminal. (Level direct trigger)
In actual work, the trigger is required to flip at a certain beat.
Measures: Add the clock control terminal CP, and the state flipping of the trigger is in accordance with the CP beat.
Synchronous trigger (clock trigger or clock-controlled trigger): a trigger controlled by the clock pulse CP.
CP: a pulse signal with a fixed frequency that controls the working rhythm of the timing circuit, generally a rectangular wave.
Synchronous: because the change of the trigger state is synchronized with the clock pulse.
The flipping moment of the synchronous trigger: controlled by CP
The state to which the trigger flips: determined by the input signal
I. Synchronous RS trigger
1. Circuit structure
Basic RS trigger + two clock gates G3 and G4, as shown in Figure 4.2.3 (a).
Logical symbol: as shown in Figure (b).
Clock control terminal (CP terminal): clock pulse input terminal.

2. Logical function
Working principle. (List the characteristics table while analyzing. The following text is not written on the blackboard.)
When CP = 0, G3 and G4 are blocked and both output 1, and the state of the trigger remains unchanged.

Table 4.2.2 Characteristics of synchronous RS flip-flop

3. Driver table

4. Characteristic equation

5. State transition diagram
The requirements for the input signal (R, S) when the trigger changes from one state to another or remains unchanged.
The state transition diagram can be drawn based on the drive table.

Circle: stable state of trigger
Arrow: state transition under CP
The marked R and S values: conditions for trigger state transition.
Previous article:Synchronous trigger
Next article:CMOS integrated logic gate circuit
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- High signal-to-noise ratio MEMS microphone drives artificial intelligence interaction
- Advantages of using a differential-to-single-ended RF amplifier in a transmit signal chain design
- ON Semiconductor CEO Appears at Munich Electronica Show and Launches Treo Platform
- ON Semiconductor Launches Industry-Leading Analog and Mixed-Signal Platform
- Analog Devices ADAQ7767-1 μModule DAQ Solution for Rapid Development of Precision Data Acquisition Systems Now Available at Mouser
- Domestic high-precision, high-speed ADC chips are on the rise
- Microcontrollers that combine Hi-Fi, intelligence and USB multi-channel features – ushering in a new era of digital audio
- Using capacitive PGA, Naxin Micro launches high-precision multi-channel 24/16-bit Δ-Σ ADC
- Fully Differential Amplifier Provides High Voltage, Low Noise Signals for Precision Data Acquisition Signal Chain
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- [Factory Visit Live Replay] Arrived at the destination - TE Qingdao Factory
- Useful tutorial | How to quickly splice PCB data at unconventional angles?
- Class AB Audio Amplifier
- Max30102 heart rate blood oxygen sensor measures heart rate problem 2
- Xunwei IMX6 development board non-device tree source code compilation environment construction (I)
- Execution process before keil main
- I need help from a great God to look at this circuit diagram, thank you very much
- FPGA Global Clock Constraints (Xilinx)
- The 2020-2021 ON Semiconductor and Avnet IoT Innovation Design Competition awards have been announced!
- How to measure BLE power consumption (one of the most viewed app reports)

 LM158AFK
LM158AFK











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号