1. Become more familiar with the HNIST-2 single-chip microcomputer system
Related hardware circuits;
2. Master the application of microcontroller interrupts and the writing method of interrupt handling programs;
3. Master the use and programming methods of the internal timer/counter of the microcontroller
。
2. Preparation before the experiment
1. Complete homework 4
2. Write relevant programs according to the experimental content and perform Proteus simulation.
3. Experimental Content
There are three experimental items, of which the first and second items are required.
1. Basic traffic lights.
According to the circuit in Figure 3.2, the IO port of the microcontroller controls 4 groups of red, green and yellow light-emitting diodes, totaling 12, so that the light-emitting diodes emit and flash according to certain rules and orders to realize the function of simulating traffic lights. Assume that the initial state is: (north-south traffic state) north-south green light, east-west red light (25s); then turn to the transition state: north-south yellow light, east-west red light (5s); then turn to the east-west traffic state: east-west green light, north-south red light 25 (s). Then turn to the transition state: east-west yellow light, north-south red light (5s), and then cycle back and forth.
It is required to use a timer to achieve the required timing.
2. Key-controlled traffic lights.
Press the K1 key
, keep the north-south traffic status; press the K2 key
, keep the east-west traffic status; press the K3 key
, maintain normal traffic lights.
Requires keystroke processing to be performed in an interrupt.
3. With flashing traffic lights.
Increase on the basis of 2, the green light flashes for the last 5 seconds, that is, on for 0.5 seconds and off for 0.5 seconds.
4. Experimental Schematic Diagram
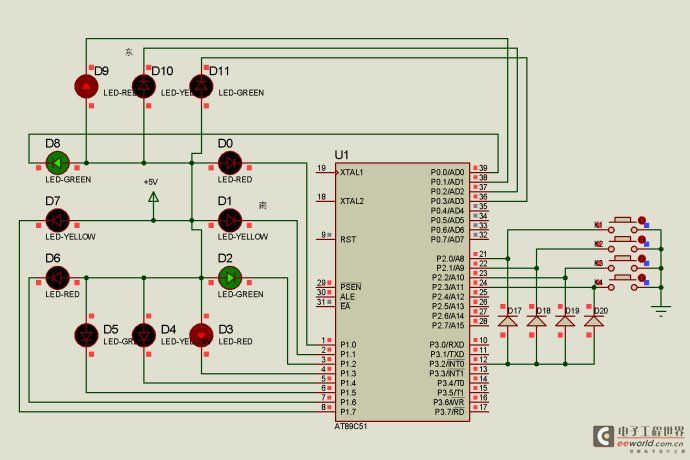 Figure 3.2 Traffic light experimental circuit schematic
Figure 3.2 Traffic light experimental circuit schematic
Figure 3.2 shows a total of four buttons K1, K2, K3, and K4, which are connected to the microcontroller P2.0, P2.1, P2.2, and P2.3 pins respectively. After the button is pressed, the corresponding pin is at a low level, and is connected to P3.2 (external interrupt 0) through four diodes D17, D18, D19, and D20. This is an AND circuit composed of diodes, that is, pressing any key can generate a low level or drop on P3.2, which serves as an interrupt trigger signal.
5. Software Design Concept
1. Regular thinking.
Use timer T0 or T1 to set the timing to 500ms, interrupt and count every 500ms, count 10 times for 0.5s, count 20 times for 1s, and achieve the required timing time for the second counting.
2. Turn on the light to control your thoughts.
The microcontroller controls the lamp pins and the lamp corresponds as follows, 0 lights up.
There are four states: S0, S1, S2, and S3.
a. North-south traffic S0 state:
Green light for north-south direction, red light for east-west direction, P0= 11110111=0xf7, P1=10011110=0x9e;
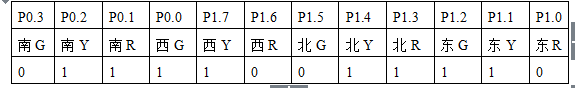
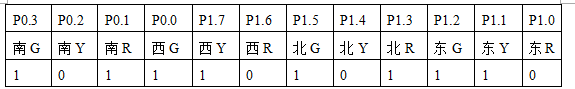 Transition state S1
Transition state S1
c. East-West Traffic Status S2:
East-west green light, north-south red light, P0=11111100=0xfc, P1=11110011=0xf3;
Set a second counting unit SEC to +1 per second, and set two control value variables a and b.
First, set SEC=0, a=0xfd, b=0x75, in S0 state;
SEC==25, a=0xfc, b=0xf3, in S1 state;
SEC==30, a=0xfb, b=0xae, in S2 state;
SEC==55, a=0xf7, b=0x9e, in S3 state;
SEC==60, SEC=0, a=0xfd, b=0x75, in S0 state;
P0=a,P1=b。
3. Traffic light keying
After pressing the button, external interrupt 0 is entered, and the external interrupt 0 interrupt program is judged: if the K1 key is pressed, the north-south traffic state is controlled, and the timer T0 is turned off to maintain the north-south traffic state; if the K2 key is pressed, the east-west traffic state is controlled, and the timer T0 interrupt is turned off to maintain the east-west traffic state; if the K3 key is pressed, the timer T0 interrupt is turned on to restore the normal traffic light.
4. Flicker control
When flashing is required, 0.5s is displayed normally, and 0.5s is completely off, which is the flashing effect. The implementation method is: when = 0.5s, and in the last 5s (19) of north-south traffic or the last 5s (49) of east-west traffic, turn off the green light: P0 = 0xf9, P1 == 0x24, when = 1s, display normally.
6. Experimental source code
#include //Basic traffic light program
#define uint unsigned int
uint flag = 20; // define the timer flag
uint second=0; //define the second sign
void main()
{
TMOD=0x01; //Select T0 timer working mode 1
TH0=(65536-50000)/256; //Initial value of TH0 is 50000us
TL0=(65536-50000)%6; //Install the initial value for TH1
TR0=1; //T0 timer in SCON is turned on
ET0=1; //Open the timer counter T0 interrupt
EA=1; //Open the general interrupt
P2=0xf7; // Initialize the traffic light
P3=0x9e;
while(1) //Wait for time and react
{
if(second==25)
{ P2=0xf7;P3=0x9e; }
if(second==30)
{ P2=0xfb;P3=0xae; }
if(second==55)
{ P2=0xfc; P3=0xf3; }
if(second==60)
{ P2=0xfd; P3=0x75; }
if(second>60) second=second`;
}
}
void T0_int(void) interrupt 1
{
TH0=(65536-50000)/256;
TL0=(65536-50000)%6;
flag--;
if(flag==0)
{
second++; //second mark plus 1
flag=20; //Reset timer flag
}
}
#include //Basic traffic light program
#define uint unsigned int
sbit k1=P2^0;
sbit k2=P2^1;
sbit k3=P2^2;
uint flag = 5; // define the timer flag
uint second=0; //define the second sign
uint key; //A flag to determine whether a key is pressed
void main()
{
TMOD=0x01; //Select T0 timer working mode 1
TH0=(65536-5000)/256; //Install the initial value of TH0 to 50000us
TL0=(65536-5000)%6; //Install the initial value for TH1
TR0=1; //T0 timer in SCON is turned on
ET0=1; //Open the timer counter T0 interrupt
EX0=1; //Open external interrupt 0
IT0=1; //External interrupt 0 trigger mode is edge trigger
PX0=1; //Set external interrupt 0 priority to 1
EA=1; //Open the general interrupt
P1=0xf7; // Initialize the traffic light
P3=0x9e;
while(1) //Wait for time and react
{
if(second==10)
{ P1=0xf7;P3=0x9e; }
if(second==20)
{ P1=0xfb;P3=0xae; }
if(second==30)
{ P1=0xfc; P3=0xf3; }
if(second==40)
{ P1=0xfd; P3=0x75; }
if(second>40) second=second`;
if(key==1) { TR0=0; P1=0xf7;P3=0x9e; } //If k1 is pressed, north-south traffic
if(key==2) { TR0=0; P1=0xfc; P3=0xf3; } //If k2 is pressed, east and west pass
if(key==3) //If k3 is pressed, normal traffic light
{
TR0=1;
TH0=(65536-5000)/256;
TL0=(65536-5000)%6;
}
}
}
void T0_int(void) interrupt 1 //Interrupt subroutine of timer counter
{
TH0=(65536-5000)/256;
TL0=(65536-5000)%6;
flag--;
if(flag==0)
{
second++; //second mark plus 1
flag=5; //Reset timer flag
}
}
void X0_int(void) interrupt 0 //interrupt subroutine for external interrupt 0
{
if(k1==0) key=1; //Set key flags according to each key situation
if(k2==0) key=2;
if(k3==0) key=3;
}
Previous article:Single chip microcomputer--electronic clock (C51)
Next article:MCU Experiment--Marquee
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Download from the Internet--ARM Getting Started Notes
- Learn ARM development(22)
- Learn ARM development(21)
- Learn ARM development(20)
- Learn ARM development(19)
- Learn ARM development(14)
- Learn ARM development(15)
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method



 ADCMP573BCPZ-R2
ADCMP573BCPZ-R2
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号