Chip design companies (Fabless) are the fastest growing group in the domestic semiconductor industry in recent years. Industry data show that as of 2020, there are 2,218 IC design companies in China, 438 more than the 1,780 in 2019, a 24.6% increase. Although domestic strength in IC design capabilities is constantly improving, and some are even on par with leading international companies, in terms of scale, most companies are still small and weak. In addition, when it comes to data analysis, IT maintenance, and mass production, most domestic IC design companies are significantly behind mature foreign companies.
Recently, Jia Jun, Vice President of Marketing for China Region of Pudifei Semiconductor, said in an exclusive interview with Jiwei.com that they found in their conversations with more than a dozen chip design companies that only by maintaining a high yield rate can the production capacity be fully utilized and a higher profit conversion rate be achieved. This is especially critical in the current environment of tight production capacity. The challenge of big data analysis has become a hurdle that IC design companies must overcome when facing the problem of improving yield rate, and more and more companies are beginning to pay attention to yield data analysis.
Domestic chip design companies are growing rapidly
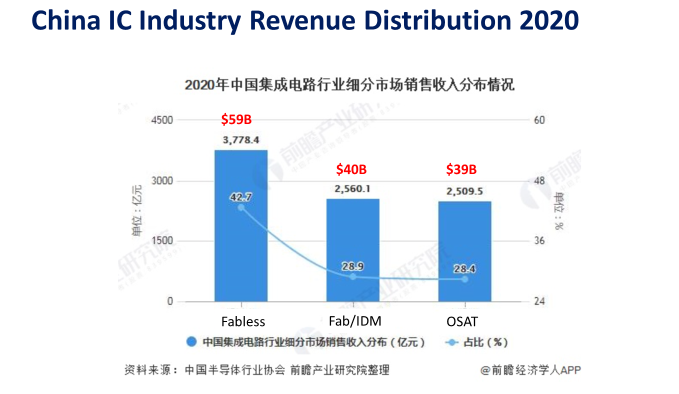
The domestic IC design industry has been booming in recent years. According to statistics from the Prospective Industry Research Institute, in 2020, the sales revenue of China's integrated circuit industry segment market: IC design reached US$59 billion, far exceeding wafer manufacturing (US$40 billion) and packaging and testing (US$39 billion); from 2015 to 2020, the sales revenue of the domestic integrated circuit design market increased year by year from 132.5 billion yuan to 377.84 billion yuan, almost tripling; from 2011 to 2020, the number of domestic integrated circuit design companies increased year by year from 534 to 2,218, quadrupling.
However, if compared with mature foreign manufacturers, the scale of China's IC design industry is still relatively small. Jia Jun gave an example, Intel's revenue in 2020 alone (US$79 billion) exceeded the total revenue of China's IC design industry last year (US$59 billion), and Qualcomm's revenue in 2020 (US$23.5 billion) was equivalent to half of China's IC industry.
However, he also pointed out that high-end chips do not represent everything, and starting with mid- and low-end chips is not without prospects. "In the United States, there are also a large number of companies that focus on semiconductor devices based on mature processes, such as power semiconductors. These companies will focus more on the design of the product itself. Factors such as reliability, cost reduction and efficiency improvement are very critical, and advanced technology is only one of the links. Companies must clarify their own strategies and have a clear understanding of product goals. This is also a process of constantly accumulating experience."
Fabless needs to pay more attention to yield issues
With the continuous development of integrated circuits, the feature size continues to shrink, the number of transistors grows rapidly, and the performance continues to improve. At the same time, the process difficulty increases sharply and the cost continues to rise. According to Gartner statistics, the average IC design cost of 16nm/14nm chips is about 80 million US dollars, and the design of 7nm chips requires 271 million US dollars.
The high cost issue means that the yield rate is regarded as the criterion by all chip manufacturers. How to further improve the yield rate is also the ultimate question that all semiconductor industry chain manufacturers cannot get rid of. For IC design companies, in the future, while continuing to improve their design capabilities, they must further fight to improve the yield rate.
Jia Jun pointed out that, on the one hand, in the context of tight production capacity, chip design companies have fewer opportunities for trial and error, and only by maintaining a high yield rate can they fully utilize production capacity and achieve a higher profit conversion rate. More importantly, as semiconductor advanced processes continue to advance, the yield problem is no longer just a problem of the technical capabilities of wafer fabs.

As the number of process steps increases, if the yield per step remains at the 28nm level, the predicted cumulative yield for advanced nodes will decrease.
Source: https://sst.semiconductor-digest.com/2016/02/yield-and-cost-challenges-at-16nm-and-beyond/
When the semiconductor process technology reaches 7nm and 5nm, the process complexity increases sharply. Many defects are not on the surface but buried inside. When designing products, Fabless buries the monitoring structure inside the product, and locates problems quickly and accurately by capturing feature data and performing efficient analysis, thereby improving product yield.
In addition, Fabless also collects various data from packaging and testing plants and manufacturing plants. In order to ensure product quality or yield, it is necessary to analyze these data so that feedback can be provided to product design, and the experience can be passed on to the next generation of product design, further improving the yield efficiently.
However, when it comes to data analysis, many young fabless companies in China still encounter many practical operational difficulties.
How to solve the big data challenge: What can the yield management system do?
According to Jia Jun, when it comes to data analysis, the lack of effective data analysis experience and methods is a difficulty faced by domestic fabless companies. "After obtaining the data, which data should be integrated and aligned? Which analysis can help them identify the problem? Many design companies are often easily confused."
The huge amount of data is one thing, but the data format varies in different factories and even different machines. In order to analyze this data, engineers need to spend a lot of time preprocessing and cleaning it. "At this stage, engineers need to spend 80% of their time preprocessing the data, and only 20% of the time is actually spent on analysis," he said.

Jia Jun further pointed out that the yield analysis methods used by fabless companies at different stages of development are different. Startups do not have high requirements for data analysis and usually use "Excel + drawing software" to process data. Although the entry threshold is low and it is easy to get started, the disadvantage is that once the yield problem needs to be discovered, the work of data cleaning will increase exponentially, making data analysis time-consuming and even forcing them to give up some analysis.
Companies with growing data volumes will turn to scripts (R, Python, etc.) for data cleaning and mapping analysis, which can significantly reduce data cleaning and statistical time. However, they do not have a database and cannot implement system upgrades, and they also require high personal programming skills from employees. Each analysis requires separate program debugging for different data types.
If more efficient yield management is desired, the Yield Management System (YMS) has begun to enter the field of vision of some Fabless companies.
It is understood that YMS is a system that integrates data management, data analysis and professional tools. It can collect data for analysis during chip design, wafer manufacturing, packaging testing and other processes, helping engineers quickly find key points to improve yield.
For semiconductor design companies, YMS can help engineers significantly improve data analysis efficiency and conduct more and more efficient data analysis in the same amount of time. The key link is the database management system (DBMS), which can greatly shorten the time engineers spend cleaning and processing data. Specifically, after certain settings, the database can automatically load data, and automatically pre-process and align the data to ensure that the data is correct, complete and valid. At the same time, YMS can process semiconductor data in various formats and links, and allows a lot of calculations to quickly obtain summary level data.
Regarding how to establish an effective yield data analysis platform and how to choose the appropriate data analysis software, Jia Jun suggested that it should be considered in combination with the stage the company is in. "Enterprises should have a basic understanding of their own situation, whether they are developing new products that have not yet entered the mass production stage, or have already been mass-produced and have a large amount of data to analyze, or whether the process is already quite mature and needs to monitor mass production and understand the various factors that affect the yield rate, etc." Jia Jun said, "Enterprises should clearly define what kind of analysis to do, what kind of automated reports to generate, and what new analysis to do for future new products."
Jiwei.com learned that Pudifei Semiconductor, which has been deeply engaged in the field of semiconductor big data analysis for more than 30 years, has maintained close cooperation with world-class wafer foundries and design companies, helping advanced Fab, Fabless, IDM/System and other international leading semiconductor companies to complete many advanced process mass production improvement projects. Pudifei also pays attention to the data analysis needs of semiconductor startups and small and medium-sized enterprises, and launches corresponding data analysis modules for semiconductor companies of different growth stages and sizes to meet personalized needs.

Among them, the free cloud-based platform Exensio Fabless Quick Start can meet the basic needs of small and medium-sized design companies. The system is maintained by Pudifei and does not require additional hardware or resources, which can more effectively help chip design companies in the early stages of data analysis. For larger chip design companies, they can choose the standard version or the big data architecture version of the Exensio platform according to their size, which has higher performance and more flexible functions to achieve in-depth data tracking and mining.
Previous article:Honor Watch GS 3 review: Lightweight, stylish and a health assistant
Next article:Ningxia Chuxin integrated circuit R&D project was put into production in Yinchuan Zhongguancun Innovation Park
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Apple and Samsung reportedly failed to develop ultra-thin high-density batteries, iPhone 17 Air and Galaxy S25 Slim phones became thicker
- Micron will appear at the 2024 CIIE, continue to deepen its presence in the Chinese market and lead sustainable development
- Qorvo: Innovative technologies lead the next generation of mobile industry
- BOE exclusively supplies Nubia and Red Magic flagship new products with a new generation of under-screen display technology, leading the industry into the era of true full-screen
- OPPO and Hong Kong Polytechnic University renew cooperation to upgrade innovation research center and expand new boundaries of AI imaging
- Gurman: Vision Pro will upgrade the chip, Apple is also considering launching glasses connected to the iPhone
- OnePlus 13 officially released: the first flagship of the new decade is "Super Pro in every aspect"
- Goodix Technology helps iQOO 13 create a new flagship experience for e-sports performance
- BOE's new generation of light-emitting devices empowers iQOO 13 to fully lead the flexible display industry to a new level of performance
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- CGD and Qorvo to jointly revolutionize motor control solutions
- CGD and Qorvo to jointly revolutionize motor control solutions
- Keysight Technologies FieldFox handheld analyzer with VDI spread spectrum module to achieve millimeter wave analysis function
- Infineon's PASCO2V15 XENSIV PAS CO2 5V Sensor Now Available at Mouser for Accurate CO2 Level Measurement
- Advanced gameplay, Harting takes your PCB board connection to a new level!
- Advanced gameplay, Harting takes your PCB board connection to a new level!
- A new chapter in Great Wall Motors R&D: solid-state battery technology leads the future
- Naxin Micro provides full-scenario GaN driver IC solutions
- Interpreting Huawei’s new solid-state battery patent, will it challenge CATL in 2030?
- Are pure electric/plug-in hybrid vehicles going crazy? A Chinese company has launched the world's first -40℃ dischargeable hybrid battery that is not afraid of cold
- Can anyone help me figure out what chip model this is?
- 【Beetle ESP32-C3】8. OLED clock and weather assistant (Arduino)
- PWM wave problem
- Typical uses of voltage followers
- How does ADR1399 perform?
- Electric energy measurement solution based on C2000 built-in 12-bit ADC
- How many memory wafers are used in STM32F0 and STM32F1 series?
- The stm32f103c8t6 core board is powered by two USB cables, and the program cannot start automatically
- Beijing Excellence Communication is recruiting embedded developers with high salary!!!
- How to assign initial values to a continuous RAM range in C2000 chip



 UPC393HA-A
UPC393HA-A











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号