USB Type-C, with its powerful functions and the strong promotion of Apple, Intel, Google and other manufacturers, will quickly lead to a revolution in USB interfaces and will have a positive impact on all aspects of our daily lives. This article discusses an important professional issue: Do USB Type-C devices need CC logic detection and control chips?
Keywords:USB
Reference address:Do USB Type-C devices require CC logic chips?
To answer this question, we have to start with the basic concepts.
DFP (Downstream Facing Port) : Downstream port, which can be understood as Host, DFP provides VBUS and can also provide data. The typical DFP device is a power adapter because it always only provides power.
UFP (Upstream Facing Port) : Upstream port, which can be understood as Device, draws power from VBUS and can provide data. Typical devices are USB flash drives and mobile hard drives, because they always read data and draw power from VBUS. Of course, it is not ruled out that USB flash drives that can be used as hosts may appear in the future.
DRP (Dual Role Port) : Dual role port, DRP can be used as DFP (Host) or UFP (Device), and can also switch between DFP and UFP dynamically. Typical DRP devices are computers (computers can be used as USB hosts or as charged devices (Apple's new MAC Book Air)), mobile phones with OTG function (mobile phones can be used as devices to be charged and read data, or as hosts to provide power to other devices or read data from USB flash drives), and mobile power supplies (discharging and charging can be done through a USB Type-C port, that is, this port can discharge and charge).
CC (Configuration Channel) : Configuration channel, which is a new key channel in USB Type-C. Its functions include detecting USB connection, detecting forward and reverse insertion, establishing and managing the connection between data and VBUS between USB devices, etc.
USB PD (USB Power Delivery) : PD is a communication protocol. It is a new power and communication connection method. It allows USB devices to transmit up to 100W (20V/5A) of power. At the same time, it can change the properties of the port and switch the port between DFP and UFP. It can also communicate with the cable to obtain the properties of the cable.
Electronically Marked Cable : A USB Type-C active cable encapsulated with an E-Marker chip. DFP and UFP can use the PD protocol to read the properties of the cable: power transmission capability, data transmission capability, ID and other information. All full-featured Type-C cables should be encapsulated with an E-Marker, but USB2.0 Type-C cables do not need to be encapsulated with an E-Marker.
The USB Type-C device DFP-to-UFP configuration process and VBUS management have the following main processes:
Device connection and separation detection: DFP needs to detect a certain voltage on the CC pin to determine whether the UFP device has been inserted or unplugged to provide and manage VBUS. When no UFP device is inserted, VBUS must be turned off. Therefore, all DFP devices require CC logic detection and control chips.
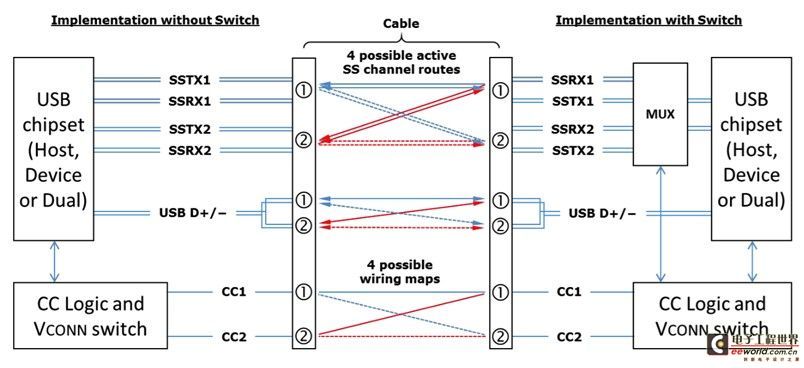
Insertion direction detection: As shown in Figure 1, although the two rows of pins of the USB Type-C socket and plug are symmetrical, and the USB data signal has two sets of repeated channels, the main control chip usually has only one set of TX/RX and D+/- channels. Since the data rate of USB2.0 is only 480Mbps at most, the impedance continuity of the signal routing can be ignored to obtain better data transmission quality. Therefore, the D+/- signal of USB2.0 can be directly connected to the two sets of D+/- pins of the USB Type-C socket from the main control chip without being controlled by the MUX. However, the data rate of USB3.0 or USB3.1 is as high as 5Gbps or 10Gbps. If the signal line is still simply divided into two, the discontinuous signal line impedance will seriously damage the data transmission quality. Therefore, the MUX must be switched to ensure the consistency of the signal path impedance to ensure the signal transmission quality. The MUX shown on the right side of the figure below selects one from TX1/RX1 and TX2/RX2 to connect to the main control chip, and this MUX must be controlled by CC Logic.
Therefore, in USB2.0 applications, there is no need to consider the direction detection problem, but in USB3.0 or USB3.1 applications, the direction detection problem must be considered.

Figure 1 USB Type-C data routing logic model
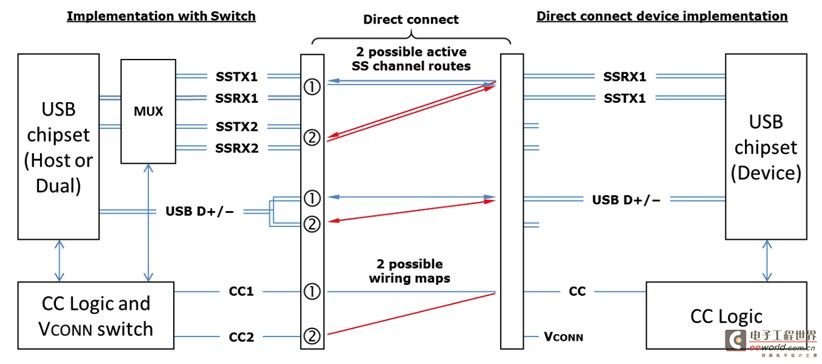
However, it must be noted that in the application of USB3.0/USB3.1, there is a situation where MUX is not required, that is, direction detection is not required. As shown in Figure 2, whether it is forward or reverse insertion, the left host can switch MUX according to the status of the CC pin to connect the USB3.0/USB3.1 signal. This scenario occurs when the right device is always UFP, such as a USB flash drive, mobile hard disk, etc.
Therefore, in USB3.0/USB3.1 applications, all devices except UFP devices require CC logic detection and control chips.

Figure 2 USB Type-C direct connection data routing logic model
Establishing DFP-to-UFP and VBUS management and detection
DRP switches between DFP and UFP every 50ms in standby mode. When switching to DFP, the CC pin must have a resistor Rp pulled up to VBUS or output a current source. When switching to UFP, the CC pin must have a resistor Rd pulled down to GND. This switching action must be completed by the CC Logic chip.
DFP can output VBUS only after it detects that UFP is inserted, and VBUS must be turned off when UFP is unplugged. This action must be completed by CC Logic chip.
USB Type-C VBUS current detection and use
USB Type-C adds current detection and usage functions, and adds three new current modes: the default USB power mode (500mA/900mA), 1.5A, and 3.0A. The three current modes are transmitted and detected by the CC pin. For DFPs that need to broadcast current output capabilities, they need to be implemented through CC pull-up resistors Rp of different values; for UFPs, it is necessary to detect the voltage value on the CC pin to obtain the current output capability of the other DFP.
USB PD Communication
USB PD seems to be just a protocol for power transmission and management. In fact, it can change the role of the port, communicate with active cables, allow DFP to become a powered device and many other advanced functions. Therefore, devices that support PD must use CC Logic chips.
Discover and configure other peripherals (Audio, Debug)
USB Type-C supports voice attachments and debug mode. If the headset with USB Type-C interface is only used as UFP and does not need to detect the power supply capability of DFP because of its low power consumption, CC Logic chip is not required.
In summary, all DFPs (such as power adapters), all DRPs (such as computers, mobile phones, tablets, mobile power supplies), all UFPs that need to detect the current output capability of DFPs, and all devices that support PDs require CC logic detection and port control chips. In other words, only UFPs (U disks, headphones, mice, etc.) that do not need to detect current capabilities due to low power consumption do not need CC logic detection port control chips.
The author is Wu Hao , a senior expert at Chsemi. Chsemi is a local high-performance analog and mixed-signal company that now provides complete USB Type-C solutions and reference designs. For more information, please email sales@chsemi.com or visit www.chsemi.com.
Previous article:Mobile Magnetic Stripe Card Reader Reference Design Application Report
Next article:Texas Instruments teaches you how to navigate with touch
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 14:40
USB to RS232 communication interface principle

I. Introduction USB, as a new PC interconnection protocol, makes the connection of peripherals to computers more efficient and convenient. This interface is suitable for a variety of devices. It is not only fast, plug-and-play, and supports hot plugging, but also can connect up to 127 devices at the same time, solving
[Analog Electronics]

Introduction to the S3C2440 USB Host Driver protocol based on OHCI protocol (Part 2)

1 HCD's responsibilities: 1.HCD is responsible for the operation of HC. HCD can directly communicate with the operable registers of HC and establish the interrupt ED table header pointer in HCCA. HCD maintains the status of HC, table processing pointer, table processing enable, and interrupt enable. 2. Bandwidth
[Microcontroller]

[Free trial of Letuo USB oscilloscope] Comparison test of Letuo USB oscilloscope
![[Free trial of Letuo USB oscilloscope] Comparison test of Letuo USB oscilloscope](https://6.eewimg.cn/news/statics/images/loading.gif)
1. Driver installation After unpacking, I was ready to try it out. My computer was installed with WIN7 system. I followed the instructions of the LOTO driver installation guide and installed it successfully at one time. The installation guide is very detailed, so I won't repeat it here. 2. TeKtronix TDS210 digital os
[Test Measurement]
![[Free trial of Letuo USB oscilloscope] Comparison test of Letuo USB oscilloscope](https://6.eewimg.cn/news/statics/images/loading.gif)
GRL expands Dongguan laboratory and continues to accelerate its layout in China

Recently, GRL Technology Information Technology (hereinafter referred to as "GRL") announced that it would triple the physical size of its Dongguan laboratory and add new testing capabilities as an important sign of its development in mainland China. At this important moment, Holger, President of GRL Global Services,
[Test Measurement]

USB port data acquisition and analysis system based on DSP

As DSP chips become more powerful
,
faster, more cost-effective and development tools become more sophisticated, they are widely used in communications, radar, sonar, remote sensing, biomedicine, robotics, control, precision machinery, voice and image processing and other fields. As one of the computer int
[Microcontroller]

When developing USB CDC class, it is not possible to send data in multiples of 64

1 Introduction This article will introduce how to use the USB CDC class for development based on the STM32F4DISCOVERY board, as well as the analysis and solution of the problem of failure when sending 64 integer multiples of data during the development process. 2 Hardware Introduction Before creating a project, we fi
[Microcontroller]

LPC1768 USB usage--macro definition
#ifndef __USBREG_H #define __USBREG_H /* usb device interrupt definition usb_devintst usb_devinten usb_devintclr usb_devintdet*/ #define FRAME_INT 0x00000001 //Generate a frame interrupt every 1MS. This interrupt is used in the transmission of synchronous packets. #define EP_FAST_INT 0x00000002 //Endpoint fast inter
[Microcontroller]
STM32 USB slave HID analysis
Overview Initialize the STM32 USB as a USB slave and use the standard HID protocol. The control board comes with VBUS power supply, so VBUS and GND pins are not required. Just connect 2 data cables to the computer. Source code analysis When connected to the computer via USB cable, a USB reset packet is receive
[Microcontroller]
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
-
 Virtualization Technology Practice Guide - High-efficiency and low-cost solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (Wang Chunhai)
Virtualization Technology Practice Guide - High-efficiency and low-cost solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (Wang Chunhai) -
 usb_host_device_code
usb_host_device_code -
 Image acquisition and processing system for panoramic map applications
Image acquisition and processing system for panoramic map applications -
 Teach you to learn 51 single chip microcomputer-C language version (Second Edition) (Song Xuefeng)
Teach you to learn 51 single chip microcomputer-C language version (Second Edition) (Song Xuefeng)
Recommended Content
Latest Mobile phone portable Articles
- Apple faces class action lawsuit from 40 million UK iCloud users, faces $27.6 billion in claims
- Apple and Samsung reportedly failed to develop ultra-thin high-density batteries, iPhone 17 Air and Galaxy S25 Slim phones became thicker
- Micron will appear at the 2024 CIIE, continue to deepen its presence in the Chinese market and lead sustainable development
- Qorvo: Innovative technologies lead the next generation of mobile industry
- BOE exclusively supplies Nubia and Red Magic flagship new products with a new generation of under-screen display technology, leading the industry into the era of true full-screen
- OPPO and Hong Kong Polytechnic University renew cooperation to upgrade innovation research center and expand new boundaries of AI imaging
- Gurman: Vision Pro will upgrade the chip, Apple is also considering launching glasses connected to the iPhone
- OnePlus 13 officially released: the first flagship of the new decade is "Super Pro in every aspect"
- Goodix Technology helps iQOO 13 create a new flagship experience for e-sports performance
MoreSelected Circuit Diagrams
MorePopular Articles
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
MoreDaily News
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
Guess you like
- The power supply cannot be completely turned off. There is a leakage of 4~5MA. I hope an expert can give me some advice.
- About the memory mode of TMS320C2X/C5X
- EEWORLD University Hall----Live Replay: When intelligence meets industry, how can technology be implemented?
- catkin_make does not compile all packages
- [Zero-knowledge ESP8266 tutorial] Quick start 22 Re-exploration of OLED module
- How to amplify the sound as much as possible when the sound source size is unknown
- Line regulation and load regulation
- Some cases of DSP program crash (flying away) - hardware reasons
- [Social Recruitment] [Campus Recruitment] China Electronics Technology Group Corporation Recruitment for Embedded Software Development
- EEWORLD University Hall----Live Replay: ON Semiconductor and Avnet IoT Innovation Design Competition Award Ceremony

 Virtualization Technology Practice Guide - High-efficiency and low-cost solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (Wang Chunhai)
Virtualization Technology Practice Guide - High-efficiency and low-cost solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (Wang Chunhai) usb_host_device_code
usb_host_device_code Image acquisition and processing system for panoramic map applications
Image acquisition and processing system for panoramic map applications
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号