1. Definition of the two
The frequency converter is an electric energy control device that uses the on-off function of power semiconductor devices to convert the industrial frequency power supply into another frequency. It can realize the functions of soft starting, variable frequency speed regulation, improving operation accuracy, changing power factor, etc. for AC asynchronous motors. The frequency converter can drive variable frequency motors and ordinary AC motors, and mainly plays the role of regulating motor speed. The frequency converter usually consists of four parts: rectifier unit, intermediate circuit, inverter and controller.

The servo system is an automatic control system that enables the output controlled quantities such as the position, orientation, and state of an object to follow any changes in the input target (or given value). The main task is to amplify, transform, and regulate the power according to the requirements of the control command, so that the torque, speed, and position control of the drive device output are very flexible and convenient.
A servo system is a feedback control system used to accurately follow or reproduce a process. It is also called a follow-up system. In many cases, a servo system specifically refers to a feedback control system in which the controlled quantity (the output of the system) is a mechanical displacement or displacement velocity or acceleration. Its function is to make the output mechanical displacement (or rotation angle) accurately track the input displacement (or rotation angle). The structural composition of a servo system is not fundamentally different from other forms of feedback control systems.
Servo systems can be divided into electromechanical servo systems, hydraulic servo systems and pneumatic servo systems according to the type of driving components used. The most basic servo system includes servo actuators (motors, hydraulic cylinders), feedback components and servo drivers. If you want the servo system to run smoothly, you also need a host mechanism, PLC, and a special motion control card, industrial computer + PCI card, to send instructions to the servo driver.
2. Working Principles of the Two
The speed regulation principle of the frequency converter is mainly subject to four factors: the speed n of the asynchronous motor, the frequency f of the asynchronous motor, the motor slip rate s, and the number of motor pole pairs p. The speed n is proportional to the frequency f. The speed of the motor can be changed by changing the frequency f. When the frequency f changes within the range of 0-50Hz, the motor speed adjustment range is very wide.
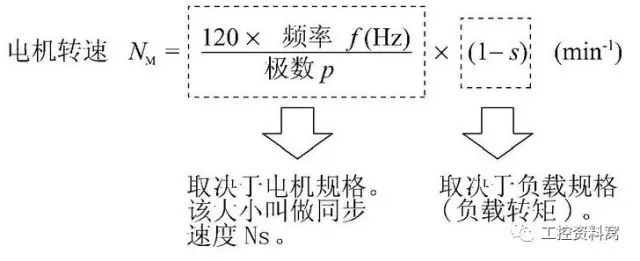
Frequency conversion speed regulation is to achieve speed regulation by changing the power frequency of the motor. It mainly adopts the AC-DC-AC method. The industrial frequency AC power is first converted into a DC power supply through a rectifier, and then the DC power supply is converted into an AC power supply with controllable frequency and voltage to supply the motor. The circuit of the inverter generally consists of four parts: rectification, intermediate DC link, inversion and control. The rectification part is a three-phase bridge uncontrolled rectifier, the inversion part is an IGBT three-phase bridge inverter, and the output is a PWM waveform. The intermediate DC link is filtering, DC energy storage and buffering reactive power.
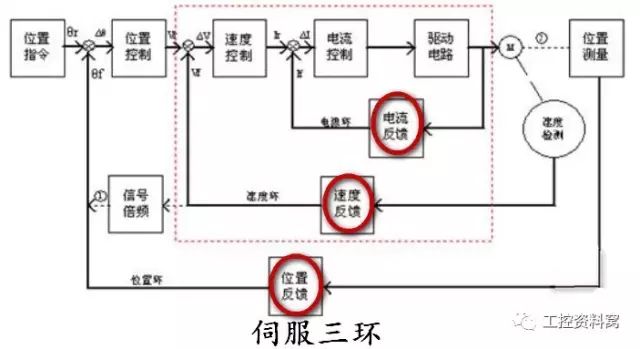
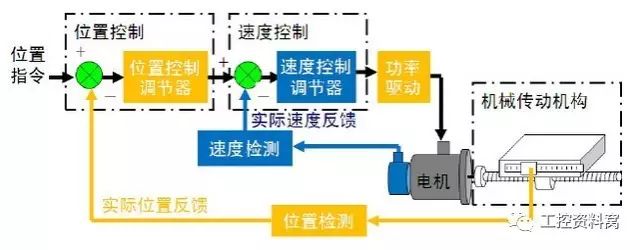
The working principle of the servo system is to feed back the speed and position signals to the driver through rotary encoders, resolvers, etc. for closed-loop negative feedback PID control based on the open-loop controlled AC and DC motors. In addition, the current closed loop inside the driver is adjusted through these three closed loops to greatly improve the accuracy and time response characteristics of the motor output to the set value. The servo system is a dynamic follow-up system, and the steady-state balance achieved is also a dynamic balance.
3. Common characteristics of the two The technology of AC servo itself is based on and applies the technology of frequency conversion. It is realized by imitating the control method of DC motor through frequency conversion PWM method on the basis of servo control of DC motor. That is to say, AC servo motor must have this link of frequency conversion: frequency conversion is to rectify the industrial frequency 50, 60HZ AC power into DC power first, and then invert it into frequency-adjustable waveform similar to sine and cosine pulsating electricity through various transistors with controllable gates (IGBT, IGCT, etc.) through carrier frequency and PWM adjustment. Since the frequency is adjustable, the speed of AC motor can be adjusted (n=60f/p, n speed, f frequency, p pole pair number).
4. The difference between the two
1. Different overload capacity. Servo drives generally have a 3-fold overload capacity, which can be used to overcome the inertia moment of the inertial load at the moment of startup, while frequency converters generally allow 1.5-fold overload.
2. Control accuracy. The control accuracy of the servo system is much higher than that of the frequency conversion. Usually, the control accuracy of the servo motor is guaranteed by the rotary encoder at the rear end of the motor shaft. The control accuracy of some servo systems can even reach 1:1000.
3. Different application occasions. Frequency conversion control and servo control are two categories of control. The former belongs to the field of transmission control, and the latter belongs to the field of motion control. One is to meet the requirements of general industrial applications, and the application occasions with low requirements for performance indicators pursue low cost. The other pursues high precision, high performance, and high response.
4. Different acceleration and deceleration performance. Under no-load conditions, the servo motor takes less than 20ms to accelerate from a stationary state to 2000r/min. The acceleration time of the motor is related to the inertia of the motor shaft and the load. Generally, the greater the inertia, the longer the acceleration time.
5. Market competition between the two
Due to the differences in performance and functions between inverters and servos, their applications are also quite different. The main competition focuses on:
Competition in technical content. In the same field, if the purchaser has high and complex technical requirements for machinery, they will choose servo systems. Otherwise, they will choose inverter products. For example, some high-tech machinery such as CNC machine tools and electronic special equipment will first choose servo products.
Price competition. Most buyers are concerned about cost and often ignore technology and prefer lower-priced inverters. As we all know, the price of a servo system is several times that of an inverter product.
Previous article:Features and composition of electric compressors
Next article:Under what circumstances will the servo motor vibrate?
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- Rambus Launches Industry's First HBM 4 Controller IP: What Are the Technical Details Behind It?
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- Changes in car rear lighting design
- A collection of essential basic knowledge for electronic engineers
- Last day! Live broadcast with prizes | RSL15 - ON Semiconductor's more efficient, smarter and safer BLE 5.2 Bluetooth chip
- Studying the road to electric motor driving-1
- TI blog post: The principle of BLDC square wave sensorless control using ADC sampling and integration
- EEWORLD University - Tektronix will teach you the oscilloscope usage skills you don't know
- LM2776 charge pump cannot start
- Help, IAR for msp430 encountered this warning, what happened
- The dispute between China and the United States over wireless LAN standards: WAPI Alliance strikes back
- [Problem Feedback] Error and warning message issues in TangDynasty ChipWatcher

 Key technologies for inverter control of new energy access to smart grids
Key technologies for inverter control of new energy access to smart grids
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号