Principles, characteristics and parameters of power field effect tubes
Power field effect transistor is also called power field controlled transistor.
1.
Power Field Effect Transistor
Principle
:
Semiconductor structure analysis is omitted. This lecture note is attached with relevant information for interested colleagues to refer to.
In fact, power field effect transistors are also divided into junction type and insulated gate type. But it usually refers to the MOS tube in the latter, that is, MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor).
It is divided into two types: N-channel and P-channel. The device symbols are as follows:

N-channel P-channel
Figure 1-3: Graphical symbol of MOSFET
The electrodes of MOS device are gate G, drain D, and source S.
Like ordinary MOS tubes, it also has:
Depletion type: When the gate voltage is zero, there is a conductive channel. Whether VGS is positive or negative, it plays a controlling role.
Enhancement type: A positive bias gate voltage is required to generate a conductive channel. Before reaching saturation, the greater the positive bias of VGS, the greater the IDS.
Most of the power MOSFETs used in general are N-channel enhancement type. Moreover, unlike the lateral conductive structure of ordinary low-power MOS tubes, a vertical conductive structure is used, thereby improving the withstand voltage and current capabilities, so it is also called VMOSFET.
2.
Features
of power field effect tube
:
This device is characterized by large input insulation resistance (more than 10,000 megohms) and basically zero gate current.
Low drive power, high speed, and wide safe operating area. However, at high voltage, the on-resistance is proportional to the square of the voltage, so it is difficult to increase the withstand voltage and reduce the high voltage impedance.
It is suitable for low voltages below 100V and is a relatively ideal device.
The current research and development level is around 1000V/65A (reference).
Its speed can reach several hundred KHz, and can reach the mega level using resonance technology.
3.
Parameters and device characteristics
of power field effect tube
:
No carrier injection, the speed depends on the device's capacitance charge and discharge time, and has little to do with the operating temperature, so the thermal stability is good.
(1) Transfer characteristics:
The curve of ID changing with UGS is called transfer characteristics. As can be seen from the figure below, as UGS increases, the transconductance will become higher and higher.

Figure 1-4: Transfer characteristics of MOSFET
(2) Output characteristics (drain characteristics):
The output characteristics reflect the law of drain current changing with VDS.
This characteristic is related to VGS. The figure below reflects this law.
In the figure, the climbing section is the unsaturated region, the horizontal section is the saturated region, and the area near the horizontal axis is the cut-off region, which is different from GTR.

Figure 1-5: Output characteristics of MOSFET
The saturation current when VGS=0 is called saturation leakage current IDSS.
(3) On-resistance Ron:
On-resistance is an important parameter of the device, which determines the output voltage amplitude and loss of the circuit.
This parameter increases linearly with the increase of temperature. Moreover, as VGS increases, the on-resistance decreases.
(4) Transconductance:
The gain characteristic of MOSFET is called transconductance. It is defined as:
Gfs=ΔID/ΔVGS.
Obviously, the larger this value is, the better it is. It reflects the gate control ability of the tube.
(5) Gate threshold voltage
The gate threshold voltage VGS refers to the lowest gate voltage when the specified drain current (1mA) starts. It has a negative temperature coefficient. For every 45 degrees increase in junction temperature, the threshold voltage decreases by 10%.
(6) Capacitor
An obvious feature of MOSFET is that there are relatively obvious parasitic capacitances between the three poles. These capacitors have a certain effect on the switching speed. When the bias voltage is high, the capacitance effect also increases, so it will have a certain impact on high-voltage electronic systems.
Some data give gate charge characteristic diagrams, which can be used to estimate the impact of capacitance. Taking the gate-source as an example, its characteristics are as follows:
It can be seen that: during the device turn-on delay time, the charge accumulates slowly. As the voltage increases, the charge rises rapidly, corresponding to the tube turn-on time. Finally, when the voltage increases to a certain level, the charge increase slows down again, and the tube is already turned on.

Figure 1-6: Gate charge characteristics
(8) Forward bias safe operating area and main parameters
MOSFET, like bipolar transistors, also has its safe operating area. The difference is that its safe operating area is surrounded by four lines.
Maximum drain current IDM: This parameter reflects the current driving capability of the device. Maximum
drain-source voltage VDSM: It is determined by the reverse breakdown voltage of the device.
Maximum drain power consumption PDM: It is determined by the temperature rise allowed by the tube.
Drain-source on-resistance Ron: This is a parameter that must be considered for MOSFET. If the on-resistance is too high, it will affect the output efficiency and increase the loss. Therefore, it should be limited according to the requirements of use.
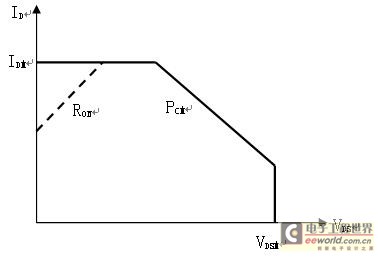
Figure 1-7: Forward bias safe operating area
Previous article:Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Principles, Characteristics and Parameters
Next article:Darlington tube, Darlington tube principle
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- High signal-to-noise ratio MEMS microphone drives artificial intelligence interaction
- Advantages of using a differential-to-single-ended RF amplifier in a transmit signal chain design
- ON Semiconductor CEO Appears at Munich Electronica Show and Launches Treo Platform
- ON Semiconductor Launches Industry-Leading Analog and Mixed-Signal Platform
- Analog Devices ADAQ7767-1 μModule DAQ Solution for Rapid Development of Precision Data Acquisition Systems Now Available at Mouser
- Domestic high-precision, high-speed ADC chips are on the rise
- Microcontrollers that combine Hi-Fi, intelligence and USB multi-channel features – ushering in a new era of digital audio
- Using capacitive PGA, Naxin Micro launches high-precision multi-channel 24/16-bit Δ-Σ ADC
- Fully Differential Amplifier Provides High Voltage, Low Noise Signals for Precision Data Acquisition Signal Chain
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Do you know the two technologies that help the Internet of Things during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Play board + simple TMS320F28035 development board
- Principle of the hardware debounce circuit for buttons
- Prize-winning live broadcast: TI low-power MCU products and Zigbee wireless solutions video playback summary!
- How to add Fourier algorithm to measure body temperature and pulse in stc89c52? How to use algorithm to analyze the results after getting it?
- [TI recommended course] #THS6222 broadband PLC line driver overview#
- Bluetooth 5 CC2640R2F
- ESP-C3 series module products
- Support the e-sports competition and get gifts for grabbing the building~~
- 【MicroPython】ESP32 starts to support hardware I2C method

 82036022X
82036022X











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号