what is reset
The function of the microcontroller reset circuit is to restore the microcontroller to the starting state, allow the microcontroller program to be executed from the beginning, the running clock is in a stable state, various registers, ports are in the initialization state, etc. The purpose is to enable the microcontroller to execute the program stably and correctly from scratch.
Why add reset?
The default state and data of registers and RAM in digital circuits after power-on are uncertain. If there is a reset, we can reset the register to the initial state, and the RAM data can trigger RAM initialization through reset.
If the program logic enters the wrong state, all logic states can be restored to their initial values through reset. If there is no reset, the logic may always run in the wrong state. (Some simple IC chips do not have a watchdog circuit and require an external reset)
Okay, through the above two paragraphs, you understand the role of the reset circuit and why it is necessary to add a reset circuit
Normal microcontrollers and IC chip resets have a Reset pin. Reset can be achieved by passing the high/low level to the reset pin for a certain period of time.
A typical 51 microcontroller will reset when the RST reset pin remains high for more than two machine cycles.
Like our commonly used STM32F1 series, check the manual and find out that the reset pin needs to be at a low level for more than 20us to complete the reset.
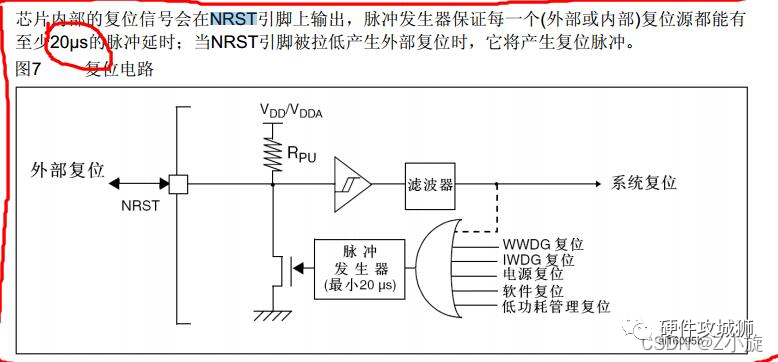
So how to design the reset circuit specifically, and how many types are there? We generally divide it into:
high reset
low reset
Button reset circuit
Power on reset circuit
A circuit device that restores a circuit to its original state
High level power on reset

Let's take a look at the high-level power-on reset, which is essentially an RC series charging circuit. At the moment of power-on, since the voltage across the capacitor cannot change suddenly, the capacitor is equivalent to a short circuit at the moment after power-on. Capacitor C11 is charged, and the charging current The voltage formed on the resistor is high level; the microcontroller is reset. After a few milliseconds, the capacitor is fully charged, the circuit is open, the current is 0, and the voltage across the resistor is approximately 0V. At this time, RST is low level. The microcontroller will enter normal working state.
Capacitor charging time T/reset duration:
T=(1/9)*R*C
1
Low level power on reset

Low-level power-on reset. Due to the characteristic that the voltage across the capacitor cannot mutate suddenly, the potential of the RST terminal is approximately GND at the moment of power-on. The C11 capacitor is charged through the 10K resistor. At this time, the RST reset pin voltage is low level; The microcontroller is reset. After a few milliseconds, the capacitor is full, the circuit below is open, the current is 0, the current flows into the RST reset pin through the resistor, and the pin is high. At this time, the microcontroller will enter the normal working state.
Capacitor charging time T/reset duration:
T= 9*R*C
1
High level key reset

High level button reset, when VCC is powered on, capacitor C is charged. At this time, the circuit is turned on, voltage appears on the 10K resistor, and the RST pin is high level, causing the microcontroller to reset; after a few milliseconds, C is full, and at this time The circuit is open, the current on the 10K resistor drops to 0, the voltage is also 0, and the RST pin is low level, causing the microcontroller to enter the working state. During operation, when the button Key is pressed, both ends of the capacitor are equivalent to a short circuit, the capacitor C is discharged, and the RST pin is high, causing the microcontroller to reset. Release the key, and the capacitor C is charged again. After a few milliseconds, the charging is completed, the circuit is open, and the microcontroller enters the working state.
Low level key reset

Low level button reset, when VCC is powered on, capacitor C is charged. At this time, the circuit is turned on, and the RST pin is low level, causing the microcontroller to reset; after a few milliseconds, capacitor C is full, and the circuit is open at this time, and the current is The 10K resistor flows into the RST reset pin, and the RST pin is high level, causing the microcontroller to enter the working state. During operation, when the button Key is pressed, the RST reset pin is directly connected to GND, which is low level, and the capacitor C is discharged, causing the microcontroller to reset. Release the key, and the capacitor C is charged again. After a few milliseconds, the charging is completed, the circuit is open, and the microcontroller enters the working state.
Previous article:High level reset and low level reset of microcontroller
Next article:A few tips to teach you how to solve the endless problems of microcontroller reset
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Learn ARM development(16)
- Learn ARM development(17)
- Learn ARM development(18)
- Embedded system debugging simulation tool
- A small question that has been bothering me recently has finally been solved~~
- Learn ARM development (1)
- Learn ARM development (2)
- Learn ARM development (4)
- Learn ARM development (6)
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Detailed explanation of intelligent car body perception system
- How to solve the problem that the servo drive is not enabled
- Why does the servo drive not power on?
- What point should I connect to when the servo is turned on?
- How to turn on the internal enable of Panasonic servo drive?
- What is the rigidity setting of Panasonic servo drive?
- How to change the inertia ratio of Panasonic servo drive
- What is the inertia ratio of the servo motor?
- Is it better for the motor to have a large or small moment of inertia?
- What is the difference between low inertia and high inertia of servo motors?
- [Synopsys IP Resources] EDA on the cloud makes chip innovation "fast, accurate and stable"
- Internet of Vehicles testing and verification of automotive CAN bus network data
- [Raspberry Pi Pico Review] - Start compiling the program 2
- USB2.0 Transactions
- Characteristics of voltage-type electrostatic breakdown of MOS tubes
- Share: How to convert C program from floating point to fixed point
- Hello, second half of 2020
- Basic knowledge of 5G standards
- How to Reduce Waveform Noise When Measuring with an Oscilloscope
- What do the 8 defense zones represent in the building intercom system?

 LMH6646MA
LMH6646MA















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号