For people who study electronics, setting test points on circuit boards is a natural thing, especially when there are too many electronic components to test one by one. But for people who study mechanics, what is a test point? You may still not understand its function.
I remember when I first started working in a PCBA factory as a process engineer, I had to ask many people about this test point before I understood it. Basically, the purpose of setting test points is to test whether the components on the circuit board meet the specifications and solderability. For example, if you want to check whether there is a problem with the resistor on a circuit board, the easiest way is to use a multimeter to measure both ends to find out.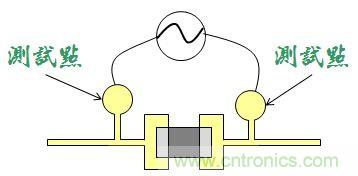
However, in a mass production factory, there is no way for you to use an electric meter to slowly measure whether each resistor, capacitor, inductor, or even IC circuit on each board is correct, so there is the so-called ICT (In-Circuit-Test) automated test machine, which uses multiple probes (generally called "Bed-Of-Nails" fixtures) to contact all the parts circuits on the board that need to be measured at the same time, and then sequentially measure the characteristics of these electronic parts through program control in a sequence-based, parallel-assisted manner. Usually, it only takes about 1 to 2 minutes to test all the parts of a general board, depending on the number of parts on the circuit board. The more parts, the longer the time.
However, if these probes are allowed to directly contact the electronic parts or their solder pins on the board, it is very likely that some electronic parts will be crushed, which is counterproductive. Therefore, smart engineers invented the "test point", which leads to a pair of small circular dots at both ends of the parts. There is no solder mask on them, which allows the test probes to contact these small dots without directly contacting the electronic parts being measured.
In the early days when traditional plug-ins (DIP) were still used on circuit boards, the solder pins of parts were indeed used as test points, because the solder pins of traditional parts were strong enough and not afraid of needle piercing. However, there were often misjudgments of poor probe contact. Because after general electronic parts are tinned by wave soldering or SMT, a layer of residual film of solder paste flux is usually formed on the surface of the solder. The impedance of this film is very high, which often causes poor probe contact. Therefore, it was often seen that test operators on the production line often used air spray guns to blow desperately, or wiped these places that needed to be tested with alcohol.
In fact, the test points after wave soldering will also have the problem of poor probe contact. Later, after the prevalence of SMT, the situation of test misjudgment was greatly improved, and the application of test points was also greatly given an important task. Because SMT parts are usually very fragile and cannot withstand the direct contact pressure of the test probe, the use of test points can prevent the probe from directly contacting the parts and their solder pins, which not only protects the parts from damage, but also indirectly greatly improves the reliability of the test, because the misjudgment situation has been reduced.
However, with the development of technology, the size of circuit boards is getting smaller and smaller. It is already a bit difficult to squeeze so many electronic components on a small circuit board. Therefore, the problem of test points occupying circuit board space is often a tug-of-war between the design end and the manufacturing end. However, this topic will be discussed later. The appearance of the test point is usually round, because the probe is also round, which is easier to produce and easier to make adjacent probes closer, so as to increase the density of needle bed. There are some inherent limitations in the mechanism when
using a needle bed for circuit testing. For example, there is a certain limit to the minimum diameter of the probe. The needle with a diameter that is too small is easy to break and damage.
There is also a certain limit to the distance between needles, because each needle must come out of a hole, and a flat cable must be welded to the back end of each needle. If the adjacent holes are too small, in addition to the problem of contact short circuit between needles, the interference of flat cables is also a major problem.
It is impossible to implant needles next to some high parts. If the probe is too close to the high part, there is a risk of collision with the high part and damage. In addition, because the part is high, it is usually necessary to open a hole on the needle bed seat of the test fixture to avoid it, which indirectly causes the inability to implant needles. It is becoming increasingly difficult to accommodate the test points of all components on a circuit board. As boards become smaller and smaller, the number of test points has been repeatedly discussed. Now there are some methods to reduce the number of test points, such as Net test, Test Jet, Boundary Scan, JTAG, etc. There are also other test methods that want to replace the original bed of nails test, such as AOI and X-Ray, but currently each test seems unable to replace ICT 100%.
Regarding the needle implantation capability of ICT, you should ask the cooperating fixture manufacturer, that is, the minimum diameter of the test point and the minimum distance between adjacent test points. Usually there is a desired minimum value and a minimum value that can be achieved by the capability, but large-scale manufacturers will require that the distance between the minimum test point and the minimum test point should not exceed a certain number of points, otherwise the fixture will be easily damaged.
Reference address:Check specifications and solderability, the role of test points on PCB circuit boards
I remember when I first started working in a PCBA factory as a process engineer, I had to ask many people about this test point before I understood it. Basically, the purpose of setting test points is to test whether the components on the circuit board meet the specifications and solderability. For example, if you want to check whether there is a problem with the resistor on a circuit board, the easiest way is to use a multimeter to measure both ends to find out.

However, in a mass production factory, there is no way for you to use an electric meter to slowly measure whether each resistor, capacitor, inductor, or even IC circuit on each board is correct, so there is the so-called ICT (In-Circuit-Test) automated test machine, which uses multiple probes (generally called "Bed-Of-Nails" fixtures) to contact all the parts circuits on the board that need to be measured at the same time, and then sequentially measure the characteristics of these electronic parts through program control in a sequence-based, parallel-assisted manner. Usually, it only takes about 1 to 2 minutes to test all the parts of a general board, depending on the number of parts on the circuit board. The more parts, the longer the time.
However, if these probes are allowed to directly contact the electronic parts or their solder pins on the board, it is very likely that some electronic parts will be crushed, which is counterproductive. Therefore, smart engineers invented the "test point", which leads to a pair of small circular dots at both ends of the parts. There is no solder mask on them, which allows the test probes to contact these small dots without directly contacting the electronic parts being measured.
In the early days when traditional plug-ins (DIP) were still used on circuit boards, the solder pins of parts were indeed used as test points, because the solder pins of traditional parts were strong enough and not afraid of needle piercing. However, there were often misjudgments of poor probe contact. Because after general electronic parts are tinned by wave soldering or SMT, a layer of residual film of solder paste flux is usually formed on the surface of the solder. The impedance of this film is very high, which often causes poor probe contact. Therefore, it was often seen that test operators on the production line often used air spray guns to blow desperately, or wiped these places that needed to be tested with alcohol.
In fact, the test points after wave soldering will also have the problem of poor probe contact. Later, after the prevalence of SMT, the situation of test misjudgment was greatly improved, and the application of test points was also greatly given an important task. Because SMT parts are usually very fragile and cannot withstand the direct contact pressure of the test probe, the use of test points can prevent the probe from directly contacting the parts and their solder pins, which not only protects the parts from damage, but also indirectly greatly improves the reliability of the test, because the misjudgment situation has been reduced.
However, with the development of technology, the size of circuit boards is getting smaller and smaller. It is already a bit difficult to squeeze so many electronic components on a small circuit board. Therefore, the problem of test points occupying circuit board space is often a tug-of-war between the design end and the manufacturing end. However, this topic will be discussed later. The appearance of the test point is usually round, because the probe is also round, which is easier to produce and easier to make adjacent probes closer, so as to increase the density of needle bed. There are some inherent limitations in the mechanism when
using a needle bed for circuit testing. For example, there is a certain limit to the minimum diameter of the probe. The needle with a diameter that is too small is easy to break and damage.
There is also a certain limit to the distance between needles, because each needle must come out of a hole, and a flat cable must be welded to the back end of each needle. If the adjacent holes are too small, in addition to the problem of contact short circuit between needles, the interference of flat cables is also a major problem.
It is impossible to implant needles next to some high parts. If the probe is too close to the high part, there is a risk of collision with the high part and damage. In addition, because the part is high, it is usually necessary to open a hole on the needle bed seat of the test fixture to avoid it, which indirectly causes the inability to implant needles. It is becoming increasingly difficult to accommodate the test points of all components on a circuit board. As boards become smaller and smaller, the number of test points has been repeatedly discussed. Now there are some methods to reduce the number of test points, such as Net test, Test Jet, Boundary Scan, JTAG, etc. There are also other test methods that want to replace the original bed of nails test, such as AOI and X-Ray, but currently each test seems unable to replace ICT 100%.
Regarding the needle implantation capability of ICT, you should ask the cooperating fixture manufacturer, that is, the minimum diameter of the test point and the minimum distance between adjacent test points. Usually there is a desired minimum value and a minimum value that can be achieved by the capability, but large-scale manufacturers will require that the distance between the minimum test point and the minimum test point should not exceed a certain number of points, otherwise the fixture will be easily damaged.
Previous article:Application of current detection in vehicle systems
Next article:Introducing 2 easy-to-understand methods of testing capacitors with a multimeter
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
Recommended Content
Latest Test Measurement Articles
- Seizing the Opportunities in the Chinese Application Market: NI's Challenges and Answers
- Tektronix Launches Breakthrough Power Measurement Tools to Accelerate Innovation as Global Electrification Accelerates
- Not all oscilloscopes are created equal: Why ADCs and low noise floor matter
- Enable TekHSI high-speed interface function to accelerate the remote transmission of waveform data
- How to measure the quality of soft start thyristor
- How to use a multimeter to judge whether a soft starter is good or bad
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of non-contact temperature sensors?
- In what situations are non-contact temperature sensors widely used?
- How non-contact temperature sensors measure internal temperature
MoreSelected Circuit Diagrams
MorePopular Articles
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
MoreDaily News
- CGD and Qorvo to jointly revolutionize motor control solutions
- CGD and Qorvo to jointly revolutionize motor control solutions
- Keysight Technologies FieldFox handheld analyzer with VDI spread spectrum module to achieve millimeter wave analysis function
- Infineon's PASCO2V15 XENSIV PAS CO2 5V Sensor Now Available at Mouser for Accurate CO2 Level Measurement
- Advanced gameplay, Harting takes your PCB board connection to a new level!
- Advanced gameplay, Harting takes your PCB board connection to a new level!
- A new chapter in Great Wall Motors R&D: solid-state battery technology leads the future
- Naxin Micro provides full-scenario GaN driver IC solutions
- Interpreting Huawei’s new solid-state battery patent, will it challenge CATL in 2030?
- Are pure electric/plug-in hybrid vehicles going crazy? A Chinese company has launched the world's first -40℃ dischargeable hybrid battery that is not afraid of cold
Guess you like
- Interface ov5640_camera
- 51 MCU 16_16 dot matrix example
- [NXP Rapid IoT Review] + How to import the project downloaded from WEB IDE into MCUXpresso IDE and debug it?
- EEWORLD University Hall----Engineering is smarter, industrial design is more powerful-field transmitter and smart meter design solution
- Startup interface kernel code modification
- DC regulated power supply to charge the battery
- AWR1843BOOST mmw demo operation guide (Part 1)
- [NXP Rapid IoT Review] Offline Compilation and Testing Summary
- How to determine whether the power supply needs a PFC circuit?
- RFMD and Qorvo prototype boards vs. honeycomb heat sinks

 LM711AMW/883
LM711AMW/883















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号