As a liquid level measuring instrument with intuitive observation, simple installation and convenient maintenance, the magnetic flap level gauge has been widely used in the measurement of tank areas. Because the magnetic flap level gauge can directly reflect the actual state of the liquid level in the tank without using other means, this simple, clear, stable and intuitive measurement advantage has been recognized by more and more users. In the actual manufacturing process of the instrument, the manufacturer can also expand the functions of the level gauge by adding some additional technical means, so that it can be used in actual production control. The
1. The practical significance of on-site calibration
(1) The density range of the medium measured by the level gauge is often wide, generally 0.8 to 1.2 g/cm3. How to correct the influence of density on the measurement error of the level gauge;
(2) The installation of the magnetic flap level gauge storage tank cannot be absolutely vertical, so how to choose the measurement standard and how to measure will be very important.
(3) The on-site storage tank is like a black box. How to determine the liquid level reference point for calibration is a key issue;
This article takes the side-mounted magnetic flap level gauge with (4-20mA) electrical remote transmission signal as an example to explore a simple and effective on-site calibration method, in order to achieve the purpose of measuring the liquid level error and its uncertainty of the entire system under on-site installation conditions, which has practical significance.
2. Structural principle of the instrument
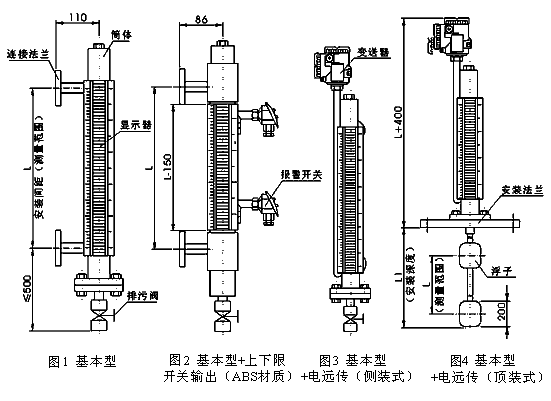
The magnetic flap level gauge is developed based on the principle of buoyancy and magnetic coupling. When the liquid level in the measured container rises or falls, the magnetic float in the main tube of the level gauge also rises or falls. The permanent magnet in the float is transmitted to the magnetic flip column indicator through magnetic coupling, driving the red and white flip columns to flip, thereby achieving clear indication of the liquid level. The transmission of current or voltage signals is achieved by opening and closing the built-in reed switch contacts. The magnetic flap level gauge is generally calibrated by simulation method (this method is not specified in the regulations) before leaving the factory to ensure that it matches the actual medium at the time of delivery.
3. Specific on-site calibration steps of the level gauge
(1) First, determine the density of the measured medium
(2) Secondly, the reference zero point should be determined.
a) Use a vernier caliper to measure the inner diameter D of the connecting pipe. The magnetic flap level gauge determines a lower scale point of the standard liquid level on the upper part of the tank body. If conditions permit, it is best to grind it into a groove to prevent the depth gauge from swinging, and make a mark;
b) Manually fill the tank with water without pressure in the tank. When the water level is slightly higher than the water inlet pipe of the level gauge, stop filling the water. The magnetic flap level gauge opens the manual ball valve E at the lower connecting flange and loosens the connecting flange F between the tank body and the calibrated level gauge (do not remove it to prevent water from over-rushing). When there is no surging flow in the pipeline, close E, remove the flange, and open E when the liquid in the tank is stable. Wait until it is in a dripping state and stabilize for 1 minute (drain water through the drain valve when necessary to improve detection efficiency);
c) The magnetic flap level gauge uses a depth measuring steel tape to measure the distance ha from the measuring point to the water surface. The actual zero position height h0=ha-D/2. This state is the measurement zero point of the level gauge.
(3) Calibration of each liquid point
a) Install the flange, close E, continue to fill the tank with water until the flap indicates the main scale of the liquid level to be calibrated. After the water surface stabilizes, measure the output current Ii and the water level height hi. The actual liquid level is: H0= h0-hi= ha- D /2 - hi;
b) Continue to measure other points of the magnetic flap level gauge until the full scale.
(4) Adjustment of liquid level zero point and full scale
4. Summary
The instruments and related devices used for on-site calibration of magnetic flap level gauges are simple and practical, with strong operability. They solve the problem that large-scale liquid level instruments cannot be detected in laboratories and have high practical value. If there is no direct contact with the liquid medium, if the magnetic flap level gauge has a slight inclination of the tank and the surface of the measuring point is horizontal, it is recommended to use a laser rangefinder instead of a depth measuring tape. However, the on-site detection methods introduced above still have certain limitations and are not suitable for level calibration of pressurized containers or volatile media. The level calibration methods for pressurized containers and volatile media will be explained in subsequent articles. If you encounter problems using the magnetic flap level gauge, you can call us or visit our corporate website for technical support.
Reference address:Detailed explanation of the on-site calibration method using a magnetic flap level gauge

1. The practical significance of on-site calibration
(1) The density range of the medium measured by the level gauge is often wide, generally 0.8 to 1.2 g/cm3. How to correct the influence of density on the measurement error of the level gauge;
(2) The installation of the magnetic flap level gauge storage tank cannot be absolutely vertical, so how to choose the measurement standard and how to measure will be very important.
(3) The on-site storage tank is like a black box. How to determine the liquid level reference point for calibration is a key issue;
This article takes the side-mounted magnetic flap level gauge with (4-20mA) electrical remote transmission signal as an example to explore a simple and effective on-site calibration method, in order to achieve the purpose of measuring the liquid level error and its uncertainty of the entire system under on-site installation conditions, which has practical significance.
2. Structural principle of the instrument
The magnetic flap level gauge is developed based on the principle of buoyancy and magnetic coupling. When the liquid level in the measured container rises or falls, the magnetic float in the main tube of the level gauge also rises or falls. The permanent magnet in the float is transmitted to the magnetic flip column indicator through magnetic coupling, driving the red and white flip columns to flip, thereby achieving clear indication of the liquid level. The transmission of current or voltage signals is achieved by opening and closing the built-in reed switch contacts. The magnetic flap level gauge is generally calibrated by simulation method (this method is not specified in the regulations) before leaving the factory to ensure that it matches the actual medium at the time of delivery.
3. Specific on-site calibration steps of the level gauge
(1) First, determine the density of the measured medium
(2) Secondly, the reference zero point should be determined.
a) Use a vernier caliper to measure the inner diameter D of the connecting pipe. The magnetic flap level gauge determines a lower scale point of the standard liquid level on the upper part of the tank body. If conditions permit, it is best to grind it into a groove to prevent the depth gauge from swinging, and make a mark;
b) Manually fill the tank with water without pressure in the tank. When the water level is slightly higher than the water inlet pipe of the level gauge, stop filling the water. The magnetic flap level gauge opens the manual ball valve E at the lower connecting flange and loosens the connecting flange F between the tank body and the calibrated level gauge (do not remove it to prevent water from over-rushing). When there is no surging flow in the pipeline, close E, remove the flange, and open E when the liquid in the tank is stable. Wait until it is in a dripping state and stabilize for 1 minute (drain water through the drain valve when necessary to improve detection efficiency);
c) The magnetic flap level gauge uses a depth measuring steel tape to measure the distance ha from the measuring point to the water surface. The actual zero position height h0=ha-D/2. This state is the measurement zero point of the level gauge.
(3) Calibration of each liquid point
a) Install the flange, close E, continue to fill the tank with water until the flap indicates the main scale of the liquid level to be calibrated. After the water surface stabilizes, measure the output current Ii and the water level height hi. The actual liquid level is: H0= h0-hi= ha- D /2 - hi;
b) Continue to measure other points of the magnetic flap level gauge until the full scale.
(4) Adjustment of liquid level zero point and full scale
4. Summary
The instruments and related devices used for on-site calibration of magnetic flap level gauges are simple and practical, with strong operability. They solve the problem that large-scale liquid level instruments cannot be detected in laboratories and have high practical value. If there is no direct contact with the liquid medium, if the magnetic flap level gauge has a slight inclination of the tank and the surface of the measuring point is horizontal, it is recommended to use a laser rangefinder instead of a depth measuring tape. However, the on-site detection methods introduced above still have certain limitations and are not suitable for level calibration of pressurized containers or volatile media. The level calibration methods for pressurized containers and volatile media will be explained in subsequent articles. If you encounter problems using the magnetic flap level gauge, you can call us or visit our corporate website for technical support.
Previous article:What are the special tests related to the use of integrated electromagnetic flowmeter?
Next article:Key points for solving the problem of intelligent electromagnetic flowmeter signal being easily interfered
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
Recommended Content
Latest Test Measurement Articles
- Keysight Technologies Helps Samsung Electronics Successfully Validate FiRa® 2.0 Safe Distance Measurement Test Case
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- Seizing the Opportunities in the Chinese Application Market: NI's Challenges and Answers
- Tektronix Launches Breakthrough Power Measurement Tools to Accelerate Innovation as Global Electrification Accelerates
- Not all oscilloscopes are created equal: Why ADCs and low noise floor matter
- Enable TekHSI high-speed interface function to accelerate the remote transmission of waveform data
- How to measure the quality of soft start thyristor
- How to use a multimeter to judge whether a soft starter is good or bad
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of non-contact temperature sensors?
MoreSelected Circuit Diagrams
MorePopular Articles
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
MoreDaily News
- Keysight Technologies Helps Samsung Electronics Successfully Validate FiRa® 2.0 Safe Distance Measurement Test Case
- Innovation is not limited to Meizhi, Welling will appear at the 2024 China Home Appliance Technology Conference
- Innovation is not limited to Meizhi, Welling will appear at the 2024 China Home Appliance Technology Conference
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Download from the Internet--ARM Getting Started Notes
- Learn ARM development(22)
- Learn ARM development(21)
- Learn ARM development(20)
- Learn ARM development(19)
- Learn ARM development(14)
Guess you like
- A Complete List of "English Abbreviations" in Hardware Schematics
- A little skill can satisfy high return income. Let's share a product repair with super high click rate
- Why use ultrasonic testing for flow meters?
- How KiCAD schematics and PCB interact
- About Power
- Usage of $test$plusargs
- Amplifier Expert Design Experience
- Flathead RVB2601 board-web playback
- After magnifying the CPU internals 10,000 times
- [Modification] Both the boost board and the purifier are troublesome in voltage

 LT1214CS16
LT1214CS16
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号