Principle analysis of 62.4V/10A charger
Source: InternetPublisher:抄写员 Updated: 2012/08/08
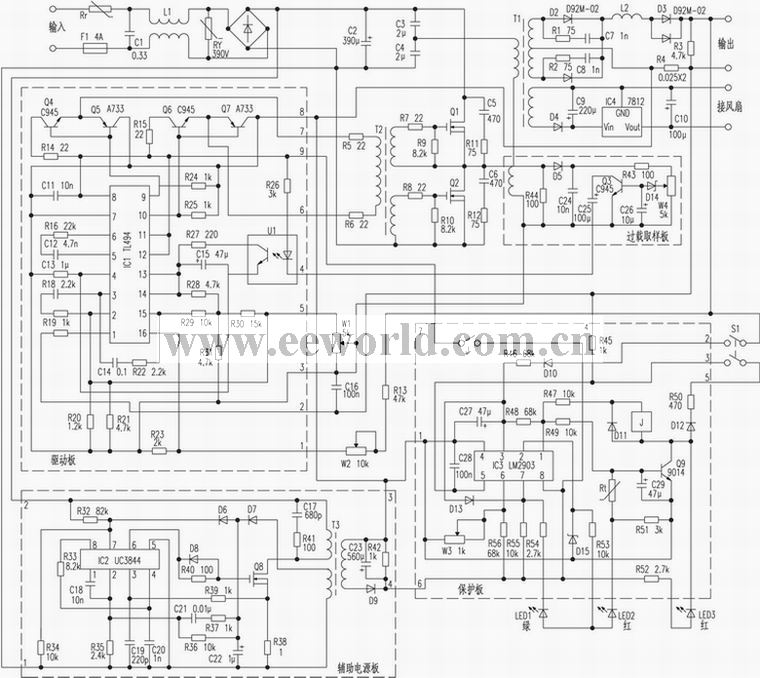
High-frequency switching chargers are becoming popular in the market due to their small size and high efficiency. Not long ago, the author purchased a 62.4V, 10A high-frequency switch-type charging movement from Xiangqiao Electronics Company. It also comes with a cooling fan. I think the price of more than 100 yuan is worth the money. In order to facilitate maintenance and adjustment, the author drew a schematic diagram based on the actual object. The introduction is as follows: The movement is composed of the main board and four modules of drive, auxiliary power supply, protection and overload sampling. The main board contains mains rectifier, power conversion, high-frequency rectifier and other components. The mains power is input from the main board and is used as the main power supply of the machine after rectification and filtering. Transformers T1, T2, Q1, Q2, etc. constitute a high-frequency power conversion circuit. D2, D3, and L2 are high-frequency rectification and output isolation components, and D4, IC4, etc. provide 12V power for the cooling fan. The auxiliary power module provides 12V DC working power for the whole machine. It uses UC3844 as pulse width modulation, Q8 (K1204), T3, etc. to form power conversion. After being rectified and filtered by D9 and C23, 12V DC power is output from the ③ and ④ pins of the board. R33 and C20 determine the operating frequency of UC3844. The operating frequency of this circuit is about 200kHz. R38 is the current sampling resistor of the power supply. Its voltage drop is fed to the ③ pin of IC2 through R39. When it exceeds 1V, the power supply will be turned off. Pin ⑦ of IC2 is the power terminal. When starting up, +300V provides power to IC2 through R32. After the circuit is working, D6, D7 and C22 provide working power. The ⑨ pin of the driver board is the power input, the ⑧ pin is the common ground, the ⑥ and ⑦ pins are the high-frequency push output terminals, the ⑤ pin is the constant current adjustment terminal, the ④ pin is the overload protection input, and the ① pin is the charging voltage limit adjustment terminal. This board uses the PWM dedicated IC TL494 as the core. Its principle has been introduced in many newspapers and periodicals, so it is omitted here. This board has multiple protection functions such as overload protection, automatic constant current, and voltage limiting. Overload protection is detected by L2 and then input through the ④ pin after adjustment and processing by the load sampling board. When overloaded, D14 and Q3 are turned on, the driver board U1 is turned on, and the 5V reference voltage of the IC1{14} pin is passed through U1 to make the ④ pin present a high level. , to maximize the dead time, thereby turning off the output of IC1. The automatic constant current is fed to the IC1① pin through the change of R4 voltage drop through the board's ② pin. Adjusting W1 can make the IC1 ② pin voltage between 0 and 0.5V. If the output current Io is determined to be 10A, then the voltage of pin ② should be adjusted to 0.25V. The automatic overvoltage protection divides the output voltage through R13, W2, and R23 and then supplies it to pin {16} of IC1. Since pin {15} is approximately 2.2V after being divided by R28, R29, R30, and R31, W2 should be adjusted. After the battery is fully charged, the IC1{16} pin voltage is 2.2V. Changing R23 and W2 can change the maximum charging voltage value. This function seems to be of little significance to the maintenance industry. The protection board of this machine has a manual start function. Its unique design prevents the charger from starting when it is unloaded or the battery is connected reversely. It is realized by the dual voltage comparator LM2903 and related components. After starting up, if the output terminal is not connected to the battery or the polarity is reversed, and the start button S1 is pressed, the IC3 pin ③ is still low level, the output terminal pin ① is also low level, and the relay J does not operate and cannot provide work to the driver board. power supply. Only after correctly connecting the battery and pressing S1, the voltage of the battery passes through S1, D10 and R46 so that pin 3 of IC3 is at high level, pin 1 outputs high level, Q9 is turned on, J is pulled in, and the 12V voltage can pass The ⑦ pin of the board is added to the ⑨ pin of the drive board so that the drive board can work. When the battery is fully charged, the charging current gradually decreases, and the voltage drop of this current on R4 is sent to pin 5 of IC3 from R45. Therefore, adjusting W3 can change the minimum current automatic shutdown critical point. Set the termination current to 2A, and adjust W3 to make ⑥ The pin voltage is 0.05V. The numbering order of the module pins in this article is from left to right facing the components, and all component codes are self-numbered. This article aims to provide the circuit to facilitate readers' adjustment and maintenance. If there are any inaccuracies, please ask the factory to correct them.

Latest Control Circuits Circuits
- Model rocket launch controller circuit
- Build a Smart Garage Door Opener Using a Raspberry Pi
- An automated model railroad layout project using a microcontroller
- How to set up a cheap beam break sensor control distance scene using a reflector
- Controlling stepper motors with wireless remote control transceiver and PE-51 board
- Motor self-starting circuit
- Simple phase failure protection circuit composed of intermediate relay
- IGBT modules block overcurrent by controlling the gate
- Infrared detection alarm
- Multi-channel laser anti-theft alarm circuit
Popular Circuits
- Homemade disinfectant circuit
- Multi-channel patrol detection control circuit a
- Assembly line outage monitoring circuit
- Haier KFR-25GW air conditioner control circuit schematic diagram
- Galanz rice cooker control circuit
- Range hood detection control circuit
- Small power electric heater temperature detection control circuit
- Electric heater temperature detection control circuit
- Voltage servo motor and control circuit
- Wide input range non-synchronous voltage mode control circuit







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号