The original intention of establishing AEC was to solve the problem of electronic component qualification certification. If a universal certification specification can be established, each electronic component company can use universal qualification certification to replace the various qualification certification methods used by each company. In this way, the AEC certification test standard was created. The universal qualification certificate promotes the universalization of automotive electronic devices. For example, if a device meets the qualification certificate, the device is qualified for all three companies (Chrysler, Delco Electronics and Ford). We now see this matter as commonplace, but at that time, and in a longer time dimension, this universal qualification recognition is extremely significant, no less than the FDA certification in the pharmaceutical industry, just like once the FDA approves a drug, it can be used globally because everyone recognizes the FDA.
In the automotive industry, everyone recognizes 16949 and AEC. The AEC standard has greatly promoted the universalization of automotive electronic device qualifications, reduced the device selection, use and change costs of component companies and OEMs, greatly improved the reliability of electronic components and vehicles, and improved the universalization level of electronic devices, which is beneficial to the present and future generations. With the development of vehicle technology and the emergence of new demands, more and more electronic devices/components will be included in the coverage of AEC, thereby promoting the development of the entire automotive industry.
Industry insiders look at "automotive grade" standards
For people in the industry, "automotive grade" is like water to fish and air to humans. It is a default, a habit, and a basic understanding deeply rooted in the consciousness. Just like you have never seen Bosch or Conti advertise that the components used in their products are "automotive grade" certified. It seems abnormal to say so, because it is the most basic, so people in the industry usually don't talk about it.
Increasingly complex and demanding automotive electronics
Many articles talk about "automotive grade", but they usually only compare it from the perspective of temperature range, saying that non-automotive grade devices "cannot meet the temperature range and will have problems when installed in the car." I guess everyone has seen the comparison picture below.

We have talked a lot about "automotive grade" before, and everyone has understood it a little. The real "automotive grade" is of course far more than just the temperature range, although the temperature range is also a very important consideration in automotive electronics design.
The earliest time when the words "car" and "electronics" were combined together can be traced back to 1968, more than half a century ago. At that time, with the emergence of emission regulations, Volkswagen mass-produced the world's first car that used ECU to control engine fuel injection. At that time, it was advertised as "electronic brain", which seems exaggerated now. Everyone knows what happened later. Now there should be no car engine without ECU (except for walk-behind tractors).
With the development of technology, designing a car has become an extremely complicated matter. There may be as many as 100 ECUs and more than 100 million lines of code. At the same time, with the development of autonomous driving technology, vehicles will become more and more complex. The automotive industry has surpassed computers and communications to become the fastest growing field for electronic systems and chips.
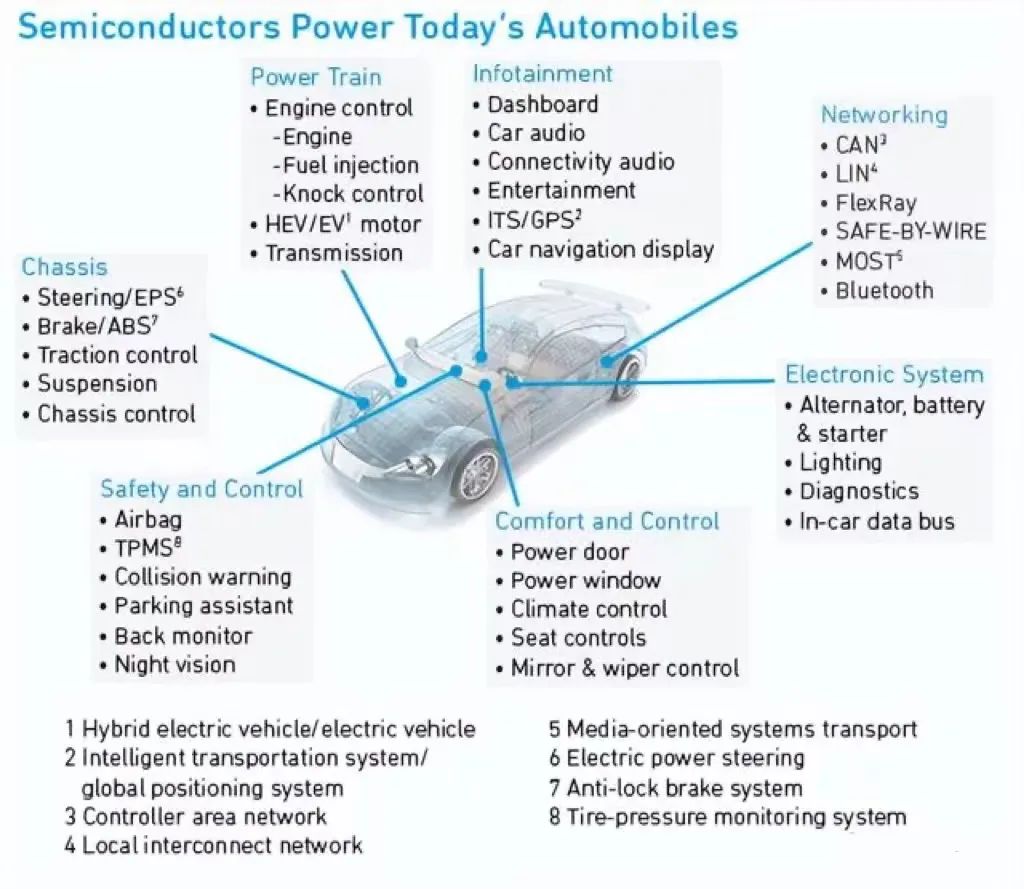
For automotive electronic components, the core key factors are actually the following two points:
Reliability: Components must be able to withstand the harsh and extreme temperatures, humidity, mechanical vibration, shock, and complex electrical and electromagnetic environments of daily use.
Longevity: Consumers expect their cars to last longer than other electronic devices such as mobile phones, typically 10 years or longer, with actual design lifespans exceeding 15 years.
In order to ensure the reliability of everything from electronic components to parts and components to the entire vehicle, the automotive industry has established strict quality standards for parts manufacturing and testing, which are the IATF16949, AEC-Q, ISO16750 and other related standards we mentioned earlier.
Previous article:The relationship and difference between FG, CHAR, PAT, SBA and ED in AEC Q100 automotive chip certification
Next article:Automotive Electronics PPTC Resettable Fuse Protection Application
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications

 【TI】16-bit and 32-bit RISC flash microcontroller tms570lc4357
【TI】16-bit and 32-bit RISC flash microcontroller tms570lc4357
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号