The advent of the Internet of Vehicles era has enabled the transformation of vehicles from human driving to autonomous driving, and has also promoted changes in vehicle management models. For example, commercial fleet management is rapidly moving towards intelligence and digitalization, and in-vehicle telematics technology, which helps improve operational efficiency and profitability, has ushered in a new period of development opportunities.
What is telematics?
On-board telematics, or the on-board intelligent device system, collects data on the vehicle, including driver status, vehicle location, speed and idling time, fuel consumption, tire pressure, etc., and uploads feedback through the wireless network, making it easier for fleet operators to monitor and control vehicles in motion in real time.
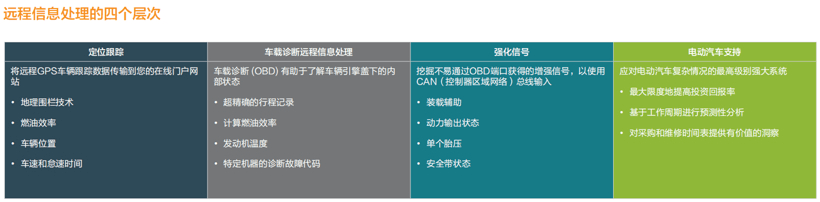
Image source: TE Connectivity
Its value is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Improve vehicle operation efficiency and profitability. First, through telematics monitoring, operators can timely learn about the location, route information, speed, loading and unloading process of the task vehicle, and monitor and adjust in real time to improve operation efficiency and customer satisfaction. In addition, the system monitors factors that affect fuel consumption, such as idling, driving style (aggressive), weather (low temperature), and accessory use (air conditioning), to reduce fuel costs.
2. Improve vehicle maintenance. Telematics can monitor vehicle battery voltage, tire pressure, brake status and other indicators. Once the car has problems or needs maintenance, the owner can respond in time, thus extending the service life of the car.
3. Improve driving safety. Telematics can remind the driver in time when the vehicle needs maintenance or slows down, issue a warning in time when the driver is in poor condition, and provide timely support when the vehicle is stolen or breaks down.
4. Fleet operators can make in-depth use of the collected data to facilitate business decision-making.
Based on the above factors, in countries with more developed fleet transportation industries, such as the United States (where large-scale freight companies account for up to 80%), vehicle telematics technology has been adopted earlier. As cars evolve towards intelligence, its market potential is further optimistic. According to relevant institutions, by 2025, the global fleet telematics service market is expected to grow to US$34 billion.
Domestic penetration rate is relatively low, but potential is being released
Compared with the United States, my country has a shorter history of freight transportation, with most of the users being individual users, supplemented by railway transportation, and the proportion of large-scale fleets is very low, about 10%. In the early days, for most small operators, it was not realistic to spend a lot of money to establish a real-time online monitoring system. Therefore, so far, the application of vehicle telematics management technology has only been in the initial stage, and is mostly concentrated in the aftermarket.
However, the advent of the Internet of Vehicles era has made the interconnection between cars and cars and between cars and people a matter of course. To achieve remote information management, it is nothing more than equipping vehicles with on-board intelligent devices. In addition, the intelligentization and networking of automobiles have become a general trend, especially in the Chinese market, which has made vehicle big data management inevitable, and vehicle information processing technology has entered a new development period.
Image source: TE Connectivity
In addition, the domestic commercial vehicle market has developed rapidly in recent years, thanks to the promotion of national infrastructure construction projects and the development of the trunk logistics and transportation industry. Data show that from 2017 to 2021, China's commercial vehicle stock market increased from 28.9 million vehicles to 33.4 million vehicles, with a compound annual growth rate of 3.68%. Behind this huge number, efficient operation management is imperative. In particular, with the advent of the COVID-19 epidemic, regional control has put forward higher requirements for fleet transportation security, which has made the industry more aware of the urgency and importance of digital and intelligent management of commercial fleets.
In view of the above, in recent years, some domestic automakers and equipment integrators have begun to exert their efforts in this field. For example, automakers such as SAIC Iveco Hongyan and China National Heavy Duty Truck Corporation have started to try to build intelligent vehicle management systems early. For example, SAIC Iveco Hongyan released the Hongyan Jieshida GEN-Star vehicle network system at the 2015 Shanghai Auto Show. This is an intelligent control integrated network system that integrates production commissioning, transportation management, fleet management, and after-sales service built by the company in combination with the needs of truck users. With the rapid development of the Internet of Vehicles and the intensification of industry competitiveness, vehicle telematics management technology will be increasingly used in the original equipment market.
Technical challenges behind opportunities
From the perspective of architecture, the fleet telematics service system is mainly composed of vehicle-mounted devices, data, cellular networks, security services and fleet management software. Among them, the vehicle-mounted device is the core carrier, mainly composed of MCU main control and information processing unit (GNSS receiver, antenna, connector, SIM card, expansion port, etc.).
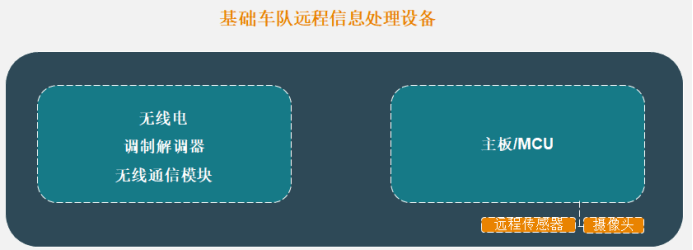
Image source: TE Connectivity
Nowadays, as cars move towards electrification and intelligence, the complexity of vehicle electronic and electrical architecture increases, the number of electronic devices continues to increase, and the information interconnected between the car and the outside world becomes more and more complex, which poses a great challenge to the reliability and integration of the core components of the equipment. This is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Increased complexity of data collection and transmission. Nowadays, in order to improve competitiveness, new cars are equipped with more and more intelligent devices, such as DMS (driver monitoring system), ADAS assisted driving system, etc., which puts forward higher requirements on the comprehensiveness and anti-interference of vehicle-mounted equipment information collection. In addition, the complexity of vehicle electrical and electronic architecture has increased, which poses a great challenge to high-quality data transmission.
2. Safety requirements have been upgraded. In addition to reliable information collection and transportation, the safety of equipment is another important concern of the industry, including reliability in extreme environments, stability in the event of collisions, and whether it is fireproof and corrosion-resistant.
3. The layout inside the equipment is becoming more complex and the integration is increasing. As technology continues to upgrade, the layout of components in the equipment will become more and more complex, and the number will increase. This requires technology providers to reduce the size as much as possible to save space while ensuring the high performance of the components, and make installation more convenient. In addition, an integrated solution is needed to reduce the complexity of the system and improve cost efficiency.
4. Diversified demands and accelerated technological changes. With the rapid development of in-vehicle information processing technology, the diversified demands of the market will increase, and the technological changes will also accelerate, which poses a great challenge to the technological innovation of equipment suppliers and the responsiveness of R&D teams.
In general, while the market potential of in-vehicle telematics technology has been released, it has also brought new challenges to the technical reliability, safety, and innovation of equipment and related component providers.
Meeting the challenge, TE helps the industry accelerate
Faced with numerous market opportunities and technical challenges, TE Connectivity (TE), a leading global connector provider, has laid out a comprehensive product portfolio. In addition to covering the basic core components of vehicle-mounted telematics equipment, its rich product series and advanced technical concepts have greatly met the diverse needs of equipment integrators and automakers, helping them shorten the development cycle of new products.
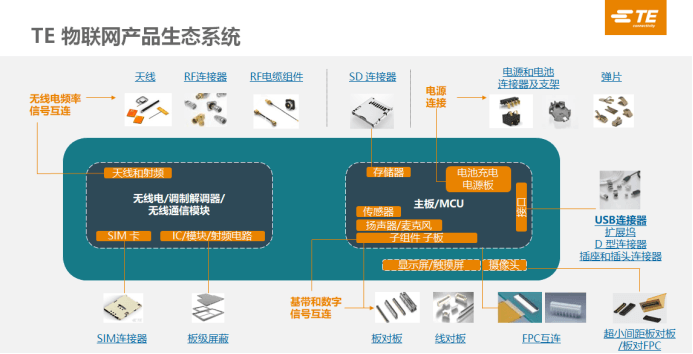
Image source: TE Connectivity
Analysis of some products:
antenna:
TE's antenna solutions can provide high-quality data transmission in wireless devices at various frequencies, including but not limited to Bluetooth, WLAN, cellular and ZigBee.
Among them, TE's latest Barracuda vehicle-mounted six-port antenna can support 5G, Wi-Fi/BT, GNSS global navigation services, and 300/400MHz radio cluster communications. This product can transform the vehicle into a communication hub and is configured for ESN and FirstNet operations. In addition, the Barracuda antenna also supports single-hole installation, which can reduce the risk of vehicle damage and installation costs. In the future, TE will also launch configurations that support higher-speed 4X4 and 8X8 MIMO.

Image source: TE Connectivity
In addition, the Trigger series antenna is another breakthrough of TE. Usually, the traditional multi-functional (wifi+cellular+GNSS) vehicle-mounted antenna is usually installed flat on the roof, and the cellular antenna is inevitably designed as a single horizontal polarization, which has a certain performance impact. To overcome this problem, TE designed the Trigger series antenna, which uses both horizontal and vertical polarization antenna elements. This combination shows excellent performance advantages:
Previous article:Nvidia's new AI model turns static images into 3D models for training self-driving cars
Next article:GKN Automotive launches next-generation inverter to support 800V electric vehicle technology
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- A new chapter in Great Wall Motors R&D: solid-state battery technology leads the future
- Naxin Micro provides full-scenario GaN driver IC solutions
- Interpreting Huawei’s new solid-state battery patent, will it challenge CATL in 2030?
- Are pure electric/plug-in hybrid vehicles going crazy? A Chinese company has launched the world's first -40℃ dischargeable hybrid battery that is not afraid of cold
- How much do you know about intelligent driving domain control: low-end and mid-end models are accelerating their introduction, with integrated driving and parking solutions accounting for the majority
- Foresight Launches Six Advanced Stereo Sensor Suite to Revolutionize Industrial and Automotive 3D Perception
- OPTIMA launches new ORANGETOP QH6 lithium battery to adapt to extreme temperature conditions
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions
- TDK launches second generation 6-axis IMU for automotive safety applications
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
- Brief Analysis of Automotive Ethernet Test Content and Test Methods
- How haptic technology can enhance driving safety
- Let’s talk about the “Three Musketeers” of radar in autonomous driving
- Why software-defined vehicles transform cars from tools into living spaces
- How Lucid is overtaking Tesla with smaller motors
- Wi-Fi 8 specification is on the way: 2.4/5/6GHz triple-band operation
- Research and development of supercapacitor urban public transportation electric vehicles
- [Raspberry Pi Pico Review] Serial communication function and its test
- How to choose the appropriate main circuit topology for power supply?
- The diameter of the four holes on the EK140 base plate
- This circuit is called a "lawn mower"
- CC3200-LAUNCHXL
- In a single-chip computer, writing 1 clears it to 0, and writing 0 clears it to 0. What is the difference?
- How to monitor battery voltage with Arduino
- Image Algorithm Transplantation to DSP and Its Optimization Steps
- To advance in technology to a certain level, you just need to read more datasheets!



 LM1877M-9X/NOPB
LM1877M-9X/NOPB











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号