When cars take advantage of the Internet, the concept of "big data" also flows into the traditional automotive industry. OEMs and suppliers of parts and aftermarket are developing more advanced driver assistance functions and in-car entertainment systems. Cars seem to have become the river god in Hayao Miyazaki's "Spirited Away" who never gets full, swallowing up a lot of user information and data. Therefore, the management of the flow and use of car user data is becoming more and more important.
On the one hand, from a safety perspective, drivers are easily distracted by too much information; on the other hand, the more information data a car receives, the more complicated the onboard electronic and electrical equipment will become. Just like a mother doting on her child, the uncontrolled development of the automotive industry over the past fifteen years has resulted in the current over-bloated onboard systems, but now the complicated onboard equipment has become a thorn in the eyes of manufacturers, which is painful to look at and painful to remove.
Bandwidth advancement: plastic optical fiber 1Gbit/s, coaxial cable 5Gbit/s, glass fiber 10Gbit/s
Faced with these challenges, engineers still have a lot of brushes in hand:
First, it is entirely possible to replace the existing unshielded twisted pair cables with optical fiber media that can transmit network data at high speeds;
Secondly, in terms of computing functions, the use of multi-core processors can not only assign different tasks to specific single-core processors for execution, but also upload some functions to the cloud or rely on mobile devices such as smartphones for processing.
Although luxury cars with multi-screen entertainment systems use a large number of computer processors to achieve rich and colorful functions, the advantage of multi-core technology is that it can reduce the number of data nodes in the car network, which means reducing the complexity of car control and design. In addition, multi-core technology can also solve the problem of increasing computing power requirements for computer chips as the number of ADAS increases.
For example, each core of a quad-core processor can control the entertainment system, cloud services, driver information, and ADAS. At the same time, different numbers of processor cores are configured for different operating system bases (Android, iOS, and Linux).
But as the number of ADAS systems increases, it becomes increasingly difficult to reduce the size of the physical network. In-vehicle entertainment systems, since the built-in sensors cannot be integrated, all basic equipment is greatly affected by these scattered sensors. For example, the rear-view camera can only be installed somewhere in the rear cabin of the car, and the front-view radar can only be placed in the front of the car.
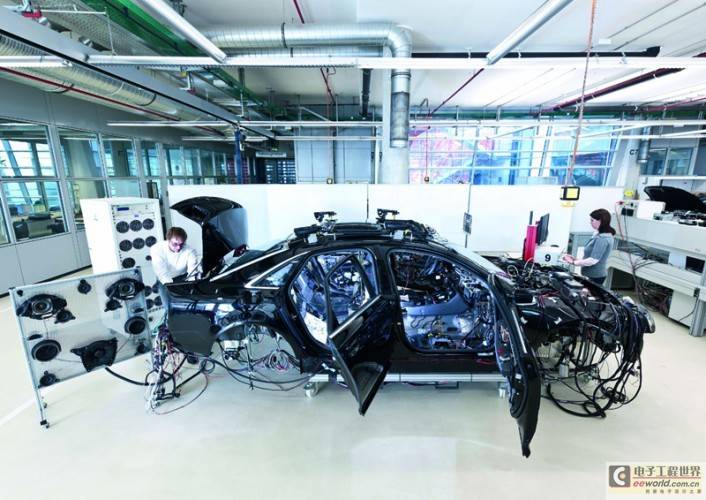

Using glass fiber optics can increase data transmission rates and reduce equipment complexity
The maximum transmission rate of plastic optical fiber can reach 1Gbit/s, while that of coaxial cable is 5Gbit/s. However, as the data transmission rate increases, the system will become more complex and the cost will continue to rise. The application of glass fiber optical cable in the future will solve the paradox of speed and cost. However, in addition to glass fiber optical cable, Ethernet, a communication network technology widely used in communication equipment, personal computers and home appliances, will also dominate the in-vehicle LAN. In addition to its inherent advantages such as openness and interconnection expansion, after it is introduced into the automotive environment, in addition to the original in-vehicle equipment, it will also become easier to link with a variety of devices such as smartphones and tablets.
After using glass fiber optical cables as the transmission medium, the network bandwidth can be increased to 10Gbit/s, and the system needs fewer optical cables to transmit the same amount of data, but it will not affect the durability of the network. The construction of the above-mentioned in-vehicle Ethernet, on the one hand, meets the requirements of high-speed data transmission in the future; on the other hand, Ethernet can also help streamline the network and reduce costs.
Smart terminals: connecting cars to “external brains”
Of course, it is also possible to offload the load on embedded systems by using handheld devices to provide the required computing power, which would also make entertainment systems in low-end cars more affordable and avoid the phenomenon of redundant equipment caused by overdeveloped consumer electronics.
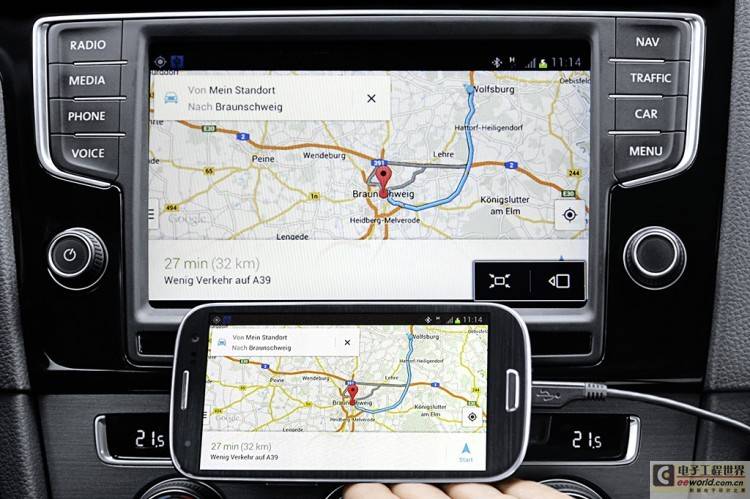
Smart devices as external processors: Reducing the load on the in-vehicle entertainment system processor
Every time a new smartphone is launched, it uses the latest chip technology, not only equipped with a multi-core processor, but also with a larger memory. But for cars, it is impossible to achieve the same speed of replacement as consumer electronics. In addition, due to the cost of various technologies, the automotive industry cannot rely too much on silicon technology even in order to adapt to the competition of future performance requirements.
For this problem, the initial idea of parts supplier Johnson Controls is to integrate tuners, signal amplifiers and network connection devices (such as Wi-Fi) into a system, and then install it on the smart devices currently on the market. In this way, the complex electronic devices in some small cars can be replaced by this reintegrated smart device. Harald Schöpp, engineering director of Johnson Controls in-vehicle entertainment systems, said: "Our goal is to make these smart things in your pocket an extension of the functions of the in-vehicle system."
Therefore, using mobile devices as an aid for additional computing power will help these classic cars look less outdated, and the in-vehicle system will be more compatible. Future mobile applications will be able to build a bridge between the rapidly developing consumer electronics and automotive hardware. But for those high-end luxury cars that are not short of money, fully built-in in-car entertainment systems are still retained because cost is not a major issue for them.
Cloud computing, a castle in the air
In the future, in-vehicle systems will show a trend of rapid development, especially as voice recognition functions become more intelligent and information processing algorithms become more complex. Cloud computing technology can effectively reduce the burden on embedded systems.
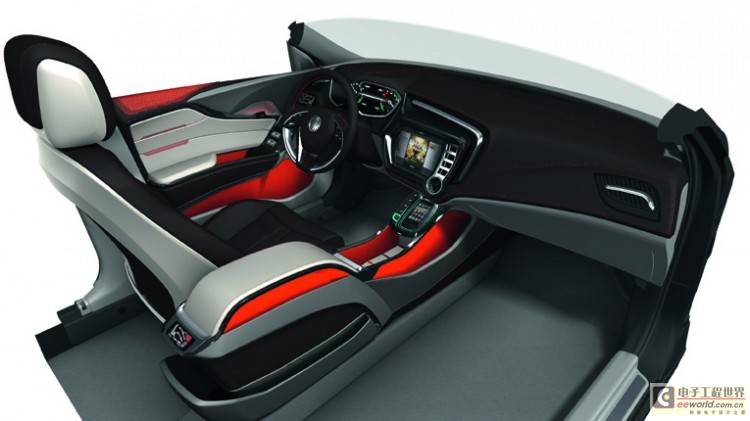

Transferring functions to the cloud can streamline system equipment
Transferring the system to the cloud can significantly improve the operation quality and recognition rate. When the language command you send is received by the corresponding receivers in English, German, French and Spanish with the help of cloud technology, they can process all the data in parallel and then output it synchronously.
However, more advanced cloud technology requires high-speed network connections such as 4G or Wi-Fi. However, in some areas, stable 3G or even GSM communication technology is a problem, so there is still a long way to go to achieve highly developed cloud technology.
At present, the screens of in-vehicle systems seem to be getting bigger and bigger. Whether it is streaming media content such as DVDs for passengers to watch or 3D navigation data for drivers, the in-vehicle system needs to have strong enough processing power in the process of video encoding/decoding. But don't forget that in addition to vision, drivers also have hearing and touch. Now the lane departure warning system will vibrate the steering wheel, which is the result of research on touch. In the future, we should focus on developing more in-vehicle technologies that can mobilize the driver's full body senses.
Previous article:Toyota develops gasoline fractionation system to improve fuel efficiency by 10%
Next article:Japan develops new heat-resistant technology for electric vehicle batteries
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- A new chapter in Great Wall Motors R&D: solid-state battery technology leads the future
- Naxin Micro provides full-scenario GaN driver IC solutions
- Interpreting Huawei’s new solid-state battery patent, will it challenge CATL in 2030?
- Are pure electric/plug-in hybrid vehicles going crazy? A Chinese company has launched the world's first -40℃ dischargeable hybrid battery that is not afraid of cold
- How much do you know about intelligent driving domain control: low-end and mid-end models are accelerating their introduction, with integrated driving and parking solutions accounting for the majority
- Foresight Launches Six Advanced Stereo Sensor Suite to Revolutionize Industrial and Automotive 3D Perception
- OPTIMA launches new ORANGETOP QH6 lithium battery to adapt to extreme temperature conditions
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions
- TDK launches second generation 6-axis IMU for automotive safety applications
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Detailed explanation of intelligent car body perception system
- How to solve the problem that the servo drive is not enabled
- Why does the servo drive not power on?
- What point should I connect to when the servo is turned on?
- How to turn on the internal enable of Panasonic servo drive?
- What is the rigidity setting of Panasonic servo drive?
- How to change the inertia ratio of Panasonic servo drive
- What is the inertia ratio of the servo motor?
- Is it better for the motor to have a large or small moment of inertia?
- What is the difference between low inertia and high inertia of servo motors?
- How does a drone know its position? How accurate is its hovering?
- EEWORLD University Hall -- Animation analysis of the working principles of various motors
- Xunwei-iMX6ULL development board--C program calls shell
- MSP430F5529 Beginner Programming Example - Button Lighting
- Pull-up and pull-down issues on SWCLK and SWDIO.
- [Rawpixel RVB2601 Development Board Trial Experience] Part 2: Recording and Playback
- EEWORLD University - Mechanics in Electronic Packaging
- Nandflash mass production burning mine clearance strategy
- Apply for free! Samples of ADI Chronous TM Ethernet PHY solutions for reliable industrial networks
- 【GD32E503 Review】 Simple Oscilloscope Experiment

 5962-8757802PX
5962-8757802PX











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号