There are two excitation methods for induction synchronizers: one is to excite the slider (or stator) to extract the induced potential from the fixed-size (or rotor) winding; the other is to excite the fixed-size (or rotor) to extract the induced potential from the slider (or stator) winding. The first excitation method is usually used in practice.
From the working principle of the induction synchronizer, it can be seen that the output signal of the induction synchronizer is an alternating induced potential that can reflect the relative displacement between the fixed-size and the slider. When the excitation frequency is constant, the amplitude and phase can be used to describe the characteristics of the alternating induced potential. Therefore, the output signal processing methods of the induction synchronizer include phase detection method, amplitude detection method, pulse width modulation method, etc.
1. Phase detection method
The so-called phase detection method is a signal processing method that identifies the displacement according to the phase of the induced potential. Sinusoidal excitation voltages with the same frequency and amplitude but a phase difference of 90° are applied to the sine and cosine windings of the slider, that is,
 (12.2.4).
(12.2.4).
At this time, the total induced potential output by the fixed scale is
![]()
![]() (12.2.5)
(12.2.5)
where
![]() ——the amplitude of the induced potential of the fixed scale winding;
——the amplitude of the induced potential of the fixed scale winding;
θ——the displacement phase angle,
![]() .
.
The above formula is the theoretical basis of the phase detection method. It can be seen that the phase difference θ between the induced potential e of the fixed scale and the sine winding excitation voltage Us is proportional to the relative displacement
x
between the fixed scale and the slider
, so the mechanical displacement can be measured by the phase of the induced potential e.
The induction synchronizer is equivalent to a phase modulator. The induced potential e is input into the digital phase detection circuit, and the displacement can be measured by the phase change. AD2S90 is a dedicated integrated chip for phase detection induction synchronizer signal processing produced by AD Company of the United States. It has the advantages of low cost, low power consumption, multiple functions, and few peripheral components required. The chip uses differential input and completes the digital conversion of the induction synchronizer output signal by phase detection. Figure 12.2.6 shows the connection between AD2S90 and the induction synchronizer.
AD2S90 uses a fixed-length excitation working mode. A sine wave signal of about 10kHz generated by a sine wave generator and a power amplifier circuit is used as the excitation signal for the fixed length of the induction synchronizer. As the slider moves, the two sine wave signals induced and output by the two independent windings on the slider will be phase-modulated by the mechanical angle θ corresponding to the slider position. These two signals and the reference sine signal of the sine wave generator are sent to the SIN, COS and REF ports of the AD2S90 chip, and then the AD2S90 chip converts the angle θ representing the slider position into a digital signal by phase detection. This signal is output by the serial digital port or the incremental encoder port. In addition, AD2S90 can also provide speed and direction signals of the slider displacement.

Figure 12.2.6 Connection between AD2S90 and induction synchronizer
2. Amplitude detection method
The so-called amplitude detection method is a signal processing method that identifies the displacement according to the amplitude of the induced potential. Sinusoidal excitation voltages with the same frequency and phase but different amplitudes are applied to the positive and cosine windings of the slider, that is,
 (12.2.6)
and the amplitude of the excitation voltage is made to meet
(12.2.7)
(12.2.6)
and the amplitude of the excitation voltage is made to meet
(12.2.7)
using a function transformer
where
—— the amplitude of the excitation voltage;
—— the phase angle of the excitation voltage.
Therefore, the total induced potential output by the fixed-length winding is
(12.2.8)
where
—— the amplitude of the induced potential;
θ
—— the displacement phase angle,
.
Formula (12.2.8) is the theoretical basis of the amplitude detection method. It can be seen from the above formula that the amplitude of the induced potential changes with the phase angle
θ
(i.e. the displacement
x
). At this time, the induction synchronizer is equivalent to an amplitude modulator. The induced potential e is input into the digital amplitude detection circuit, and the displacement can be measured by the amplitude change.
3. Direction discrimination and subdivision of induction synchronizer
Induction synchronizer can also distinguish displacement direction and improve resolution through direction discrimination and subdivision circuit of output signal. The direction discrimination and subdivision circuit is similar to the implementation method of grating digital sensor, so it will not be described here.
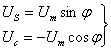
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Previous article:Application of induction synchronizer
Next article:Working principle of induction synchronizer
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- High signal-to-noise ratio MEMS microphone drives artificial intelligence interaction
- Advantages of using a differential-to-single-ended RF amplifier in a transmit signal chain design
- ON Semiconductor CEO Appears at Munich Electronica Show and Launches Treo Platform
- ON Semiconductor Launches Industry-Leading Analog and Mixed-Signal Platform
- Analog Devices ADAQ7767-1 μModule DAQ Solution for Rapid Development of Precision Data Acquisition Systems Now Available at Mouser
- Domestic high-precision, high-speed ADC chips are on the rise
- Microcontrollers that combine Hi-Fi, intelligence and USB multi-channel features – ushering in a new era of digital audio
- Using capacitive PGA, Naxin Micro launches high-precision multi-channel 24/16-bit Δ-Σ ADC
- Fully Differential Amplifier Provides High Voltage, Low Noise Signals for Precision Data Acquisition Signal Chain
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- Rambus Launches Industry's First HBM 4 Controller IP: What Are the Technical Details Behind It?
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- Silicon carbide industry chain science video: substrate and epitaxy
- Share an open source software download URL
- "Practice Together in 2021" + Looking Forward
- Senior foreigner explains the misunderstandings of high-speed PCB design and testing (video-Chinese)
- After zigbee sends data to nb-iot, nb-iot sends data to the cloud, but the data displayed on the cloud is completely wrong. How to solve it?
- Notice: The new markdown editor is now online!!
- Design of password lock using AT89S52 single chip microcomputer
- 【Development and application based on NUCLEO-F746ZG motor】4. Share information
- encryption
- Motor control basics - timer basics and PWM output principles

 M38510/13501BGX
M38510/13501BGX











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号