The GPIO of STM32 can be configured by software into several different modes. Each I/O port bit can be freely programmed, but the I/O port register must be accessed as a 32-bit word:
A. Chip side:
1. Input:
| MODE | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Input floating | The pin is configured to be floating and connected to a Schmitt trigger. The common scenario is external buttons. |
| Input pull-up | The input is connected to a pull-up resistor to clamp the uncertain signal to a high level |
| Input Dropdown | The input is connected to a pull-down resistor to clamp the uncertain signal to a low level |
| Analog Input | The signal directly enters the ADC module, which means that the status of the IO port can no longer be read from the input register. |
2. Output:
| MODE | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Open-drain output | The so-called open drain refers to the drain of the MOSFET. When the IO outputs 1, it is suspended and requires an external circuit pull-up resistor to achieve a high-level output (low-level grounding). It is generally used in situations where the levels do not match, and different level outputs are achieved through external pull-up and pull-down resistors. |
| Push-pull output | Output 0 is connected to GND, output 1 is connected to VCC (ie 0=》GND, 1=》3.3V) |
| Open-drain multiplexing | PinMux to other functions |
| Push-Pull Multiplexing | PinMux to other functions |
B. Hardware side:
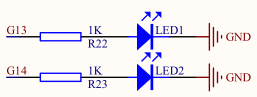
The corresponding board has two GPIOs connected to the LED:
Uses GPIO Port G Pin13 and Pin14
C. Code side:
The steps required to configure the above two GPIOs to work are as follows:
1. Enable the corresponding GPIO_G clock
2. Configure GPIO_G13/GPIO_G14 as general push-pull output, and configure the port line flip speed to 50M
3. After configuration is complete, set the port output to 1/0 to control the GPIO output.
1. Clock settings:
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOG, ENABLE); // Here RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOG is (0x01 << 8)
void RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(uint32_t RCC_APB2Periph, FunctionalState NewState)
{
/* Check the parameters */
assert_param(IS_RCC_APB2_PERIPH(RCC_APB2Periph));
assert_param(IS_FUNCTIONAL_STATE(NewState));
if (NewState != DISABLE)
{
RCC->APB2ENR |= RCC_APB2Periph;
}
else
{
RCC->APB2ENR &= ~RCC_APB2Periph;
}
}
2. Configure GPIO_G13/GPIO_G14 as general push-pull output, 50M speed
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_13|GPIO_Pin_14;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOG, &GPIO_InitStructure);
3. Configure output:
STM32 provides multiple ways to configure GPIO output 1/0, including directly writing 1/0 registers (GPIOx_ODR) to the port, registers specifically set to 1 value (GPIOx_BSRR), and registers specifically set to 0 value (GPIOx_BRR). You can use them at will:
#define LED1_ON GPIO_SetBits(GPIOG, GPIO_Pin_13);
#define LED1_OFF GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOG, GPIO_Pin_13);
#define LED2_ON GPIO_SetBits(GPIOG, GPIO_Pin_14);
#define LED2_OFF GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOG, GPIO_Pin_14);
void GPIO_SetBits(GPIO_TypeDef* GPIOx, uint16_t GPIO_Pin)
{
/* Check the parameters */
assert_param(IS_GPIO_ALL_PERIPH(GPIOx));
assert_param(IS_GPIO_PIN(GPIO_Pin));
GPIOx->BSRR = GPIO_Pin;
}
void GPIO_ResetBits(GPIO_TypeDef* GPIOx, uint16_t GPIO_Pin)
{
/* Check the parameters */
assert_param(IS_GPIO_ALL_PERIPH(GPIOx));
assert_param(IS_GPIO_PIN(GPIO_Pin));
GPIOx->BRR = GPIO_Pin;
}
The basic usage is as described above. Later, in the specific peripheral part, the multiplexing function of GPIO will be introduced.
Previous article:STM32F103ZET6 — USART
Next article:STM32 Boot mode setting method
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 12:25


 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Understanding of TIMERA timing interrupt of MSP430F149
- What is the difference between pyb.delay and time.sleep?
- Stepper motor current test
- [RVB2601 creative application development] + light intensity detection
- 【DIY Creative LED】Effect Demonstration
- [GD32450I-EVAL] USART and DMA variable length reception
- ESP32-S3 Technical Reference Manual Latest Manual
- 【DSP】TMS320F28035 ADC routine (software trigger + query)
- Ask for help either
- STEVAL-MKI109V3 Unico-GUI cannot connect, prompting The adapter board has not been recognized


 Digilent Vivado library
Digilent Vivado library Raspberry Pi Development in Action (2nd Edition) ([UK] Simon Monk)
Raspberry Pi Development in Action (2nd Edition) ([UK] Simon Monk)
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号