The instruction system of the MCS-51 series microcontroller is a concise and efficient instruction system. It has a total of 111 basic instructions, including 49 single-byte instructions, 45 double-byte instructions, and 17 three-byte instructions. According to the function, these instructions can be divided into five categories: data transfer (29), arithmetic operation (24), logical operation (24), control transfer (17) and bit variable operation (17). For reverse engineering, we are not concerned about the number of specific instructions but the addressing mode of the instructions. The so-called addressing mode is to find the real address of the number involved in the operation. The 111 instructions of the MCS-51 series microcontroller only use 5 addressing modes. The 5 addressing modes and their addressing spaces are shown in Table 1.
1. Register addressing
Register addressing mode can be used to access the 8 working registers RO-R7 in the selected register area. The register used is indicated by the lower three bits of the instruction opcode. Registers A, B, DPTR, AB and Cy (the accumulator of the bit processor) can also be used as addressing objects. In this addressing mode, the content of the addressed register is the operand.
When implementing this type of addressing mode, determining the physical address of the addressed register is critical. Since the selected register area is determined by the relevant bits of the PSW, and the lower three bits of the instruction indicate the specific register, the following VHDL statement can be used to determine the physical address of the relevant register:
rr_ adr<=unsigned((psw and“00011000”)or(rom_data_i and“00000111”));
Among them, rr_adr represents the physical address of the register, and rom_data_i represents the instruction code. After the physical address is determined, the operation on RAM can be carried out easily.
2. Direct addressing
Direct addressing is the only way to access special function registers. It can also be used to access internal RAM (128 bytes). Instructions using direct addressing are two-byte instructions, where the first byte is the opcode and the second byte is the direct address of the internal RAM or special function register. The address is already given, so it is obviously not necessary to calculate the address first like register addressing. You can directly perform related operations on the RAM based on the address given by the ROM.
3. Register indirect addressing
Register indirect addressing can be used to access internal RAM or external data memory. When accessing the lower 256 bytes of internal RAM or external data memory, RO or R1 can be used as the indirect address register. This type of instruction is a single-byte instruction, and its lowest byte indicates whether RO or R1 is used as the indirect address register. Different instructions are used to access internal RAM and external data memory, so there is no confusion.
To access external data memory, the data pointer DPTR can also be used as an indirect address register. DPTR is a 16-bit register, so it can address the entire external data memory space Il (64K).
When executing PUSH (push) and POP (pop) instructions, register indirect addressing is also used, and the stack pointer SP is used as an indirect address register.
The implementation of this type of addressing mode must be divided into two steps. First, determine the addresses of the eight units in the four general working register areas that can be used as indirect addressing registers, and then read the value in the selected register. This value is the physical address of the space to be addressed by the current instruction. Determining the address of the indirect addressing register can be implemented by the following VHDL statement:
ri_adr<=((psw and“00011000”)or(s-command (7downto 0) and“110000000111”)),
Among them, ri_adr represents the physical address of the register used for indirect addressing, and s_command represents the operation code of the current instruction. Then, through another process of reading RAM, the value in the indirect address register can be determined, so as to obtain the address of the memory unit required by the instruction. As for other special function registers used as indirect address registers, since the address of the indirect address register can be determined in advance, in this way, finding the address of the memory unit only requires the latter step of the above two steps to determine the address of the memory unit required by the instruction.
4. Immediate addressing
The instruction using the immediate addressing mode is two-byte, the first byte is the operation code, and the second byte is the immediate operand. Therefore, this addressing mode is easier to implement than direct addressing, and the operand is a constant placed in the program memory.
5. Indirect addressing using base register plus index register
This addressing mode is used to access a unit of program memory, the address of which is the sum of the contents of the base register (DPTR or PC) and the index register A. Although this type of addressing mode is also indirect addressing, for the case of using DPTR as the base register, its implementation method is very similar to the indirect addressing when using the data pointer DPTR as the indirect register, because its indirect register is actually still determined. Unlike the indirect addressing when using the data pointer DPTR as the indirect register, an addition operation is required to confirm the final required address, which is easy to implement when using VHDL language description.
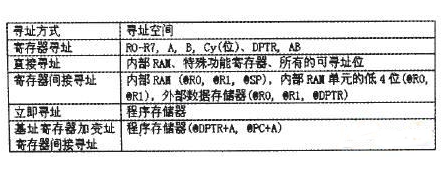
Table 1 Table addressing mode and addressing space
When using PC as the base address register, you need to know the current value of PC, but PC is different from DPTR. DPTR is a special function register and its value can be read using its address. PC has no assigned address and its value cannot be obtained by reading RAM. Therefore, it is necessary to set up and write such a process internally, which is used to read the values of auxiliary registers that are located inside the CPU and have no assigned addresses.
Previous article:MCU achieves key debounce through software
Next article:How to send data from the microcontroller serial port to the host computer
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Learn ARM development(16)
- Learn ARM development(17)
- Learn ARM development(18)
- Embedded system debugging simulation tool
- A small question that has been bothering me recently has finally been solved~~
- Learn ARM development (1)
- Learn ARM development (2)
- Learn ARM development (4)
- Learn ARM development (6)
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
- The Beacon made of CC2640R2F chip has a larger current after running for a period of time. The broadcast is normal, but the current becomes smaller after restart.
- Introduction to the operating environment and interface mode of RFID application system
- Many choices in life are your destiny.
- Experience using the bootloader of TMS320VC33
- Is the CS+ for CACX development environment free to use now?
- Please help me. When the circuit board motor is working, the LED light controlled by the IO port of the main control IC will flash.
- [Qinheng RISC-V core CH582] serial port routine sending and receiving test
- Low-Cost Digital Thermometer Using a Single-Chip Microcontroller
- Motor rotor position detection
- Understanding of analog IC

 ICL7614BMTV/C
ICL7614BMTV/C











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号