Travel burglar alarm
Source: InternetPublisher:偷熊计划 Keywords: CD4069 alarm circuit Updated: 2024/11/01
The travel anti-theft alarm consists of two parts, one is the receiver, which is placed in the owner's pocket; the other is the transmitter, which is placed in the items that need to be protected. The receiver circuit is shown in Figure 1, which is mainly composed of ultra-high frequency receiving and audio signal detection circuit, amplifier circuit, voltage doubler rectifier circuit, dual-tone modulation audio oscillation and drive and sound circuit. The working process is: when the receiver's receiving antenna L0 (printed antenna) receives the ultra-high frequency (about 250MHz) signal sent by the transmitter, the super-regenerative detection circuit composed of transistor T1, inductor L1, capacitor C2, C3 and other components detects a 1kHz square wave audio signal, and then couples it to the three-stage high-gain amplifier composed of six inverters A1 (CD4069) I, II, III through capacitor C6 for amplification. In the figure, R5, R7, and C7 are negative feedback elements set to stabilize the operation of the amplifier, and the amplified signal is output by C9. After double voltage rectification by D1 and D2, it is added to the input of inverter IV. Because it is high level, it outputs low level after inversion (pin 12 of A1), so diode D3 is turned on. Therefore, the input of inverter V is also low level, and the output (pin 10 of A1) outputs high level. That is, the input of inverter VI is high level. Obviously, its output (pin 8 of A1) also outputs low level. Therefore, diode D4 is also turned on. That is, the input of inverter VII (pin 1 of six inverters A2) is clamped to low level. At this time, the two oscillators composed of inverters VII, VIII and inverters IX, X do not work, so the piezoelectric ceramic Y in the receiver will not sound an alarm. If the protected item (together with the transmitter) is moved away by someone (the distance from the receiver exceeds 3 to 4 meters), the signal received by the receiver will be weakened or even not received. At this time, the super-regenerative detector will have no signal output, causing the negative pole of D2, that is, the input end of inverter IV (pin 13 of A1) to be low level, and the output is high level, causing D3 to be cut off_the input end of inverter V is high level due to the power supply of R9 → the output end is low level → the input end of inverter VI (i.e. pin 9 of A2) is low level → the output end is high level → D4 is cut off → the two oscillators composed of inverters VII, VIII and inverters IX, X start to oscillate. Among them, inverters IX and X form an audio oscillator with a frequency of about 1kHz. Its oscillation is modulated by the ultra-low frequency oscillator (oscillation frequency is about 1Hz) composed of inverters VII and VIII, so it generates an oscillating audio signal of "beep, beep". This oscillation signal is inverted by two parallel inverters XI and X, and then sent to transistor T2 for power amplification, and then drives the piezoelectric ceramic piece Y to emit a loud "beep, beep" alarm sound. Tell the owner to find their belongings quickly.

In Figure 1, R9 and C11 form a 3S delay anti-interference network, which can effectively prevent false alarms caused by power-on or short-term signal suspension of the transmitter for some reason. The red light-emitting diode LED lights up when the receiver is in the power-on standby state. When the receiver is in the alarm state, the level of the inverter VII output terminal (i.e., the ② foot of A2) changes alternately between high and low, so the LED flashes.
The transmitter circuit of the anti-theft alarm is shown in Figure 2. It is also composed of two circuits: an audio oscillator composed of inverters and a high-frequency oscillator composed of transistors. In Figure 2, inverters I and II, resistor R1, and capacitor C1 form an audio oscillator with a frequency of about 1kHz. Its oscillation signal is inverted by inverter III and modulated by R2 to generate a high-frequency oscillation wave (frequency of about 250MHz) generated by a high-frequency oscillator composed of transistors T and other components. The modulated high-frequency signal is transmitted to the surrounding space by the loop antenna printed on the transmitter printed circuit board. Its size is 50mm×40mm. The size of the receiver printed board is recommended to be 70mmx60mm.
The burglar alarm uses three six-inverter CD4069 integrated circuits. In use, pin 7 is connected to the negative end of the power supply, and pin 8 is connected to the positive end of the power supply. Among them, A3 only uses three inverters. The other three are not used. However, their input terminals should be connected to the positive or negative pole of the power supply. The oscillating transistors T and T1 should use ultra-high frequency tubes such as 9018 or 3DG11, and the β value should be ≥120. T2 uses 9012 or 2SA1015PNP silicon tubes, and the β value should be ≥100. All resistors use l/8w metal film or carbon film resistors. All electrolytic capacitors use CD11 electrolytic capacitors with a withstand voltage of 10V. C1 in the receiver and C3 in the transmitter use CCW12E ultra-small ceramic fine-tuning capacitors. C2 in the receiver and transmitter uses high-frequency ceramic capacitors. All diodes use IN4148 switch tubes, and other non-electrolytic capacitors use CT1 ceramic capacitors. L in the transmitter is wound 25 turns of Φ0.51mm enameled wire on a Φ4.5mm drill. Then it is removed. The inner diameter of the printed antenna is 12mm, and the width of the wire is 2mm (note that L0 in the receiver is also a printed antenna, with the same specifications as the printed antenna in the transmitter). L1 in the receiver is wound 10 turns of Φ0.31mm enameled wire on an I-shaped magnetic core (magnetic core diameter is 4mm), L2 uses a 56uH~100uH inductor. L3 uses a 2.2mH inductor. Y is a HTD27A-1 or FT-27 piezoelectric ceramic sheet, and the power supply of the transmitter and receiver are both 3 No. 7 batteries. The power switch uses an ultra-small self-locking push button switch.
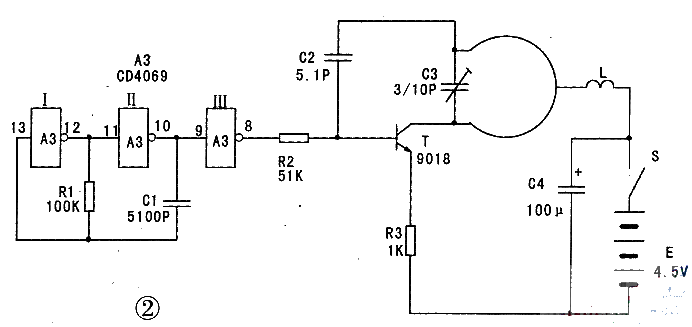
First, turn on the power of the transmitter. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage across the resistor R3, and fine-tune the capacitor C3 so that the multimeter voltage reading is around 0.5v. At this time, if C3 is short-circuited, the voltage meter reading rises. This means that the circuit has started to oscillate and the transmitter is basically working normally. If there is no change, check whether the components are connected incorrectly or the β value of the triode T is too low, and whether the quality is poor. After the transmitter works normally, turn on the power of the receiver. If the piezoelectric ceramic piece Y makes a "beep, beep" sound and the red light-emitting diode flashes (if it does not sound, check whether the components are connected incorrectly or the quality is poor), then gradually move the transmitter closer to the receiver (the distance is less than 1m) and adjust C1 in the receiver to stop the "beep, beep" sound, which means that the frequencies of the two are the same. Then move the transmitter away. When the distance from the receiver is 3 to 4m, if the receiver can make a loud "beep, beep" alarm sound again, the debugging has been successful and the anti-theft device can be put into use.
- Current output characteristics of brushed motor driver chips. How to increase the peak drive current?
- Model rocket launch controller circuit
- How to Build a Gesture-Controlled Elevator Prototype Using Arduino Nano
- Working principle of ZNB-S digital display intelligent motor protector control circuit
- Simple phase failure protection circuit composed of intermediate relay
- Design and production of wireless multi-location control switch circuit
- Audio interface protection circuit
- Infrared blocking alarm device
- Ultra-short wave item left behind reminder alarm
- Night dog barking anti-theft reminder circuit
- Power outage sound and light alarm circuit
- Touch alarm circuit for coronary heart disease patients
- earthquake alarm circuit
- Household harmful gas alarm circuit
- Household gas alarm circuit composed of gas sensor
- Infant bedwetting alarm circuit
- Range hood alarm control circuit diagram
- Gas-sensitive alarm circuit 2
- Soil drying alarm circuit
- Boiling water alarm circuit 2







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号