Home wireless burglar alarm circuit
Source: InternetPublisher:newlandmark Keywords: Anti-theft circuit Updated: 2024/11/04
The alarm introduced in this article adopts the wireless feedback alarm principle and consists of two parts: the first part is composed of the anti-theft intrusion detector and the miniature wireless alarm transmitter; the second part is the wireless alarm receiving controller. When in use, the first part is installed in the storage room, garage and other places that need to be protected; the second part is placed in the residents' residence.
Circuit Principle
1. Intrusion detector and micro alarm transmitter part
Figure 1 is the circuit diagram of the intrusion detector and the micro wireless alarm transmitter. The small magnet and the contact normally closed reed switch E form an intrusion detector. The small magnet is installed on the door leaf of the storage room, and the reed switch E is installed on the opposite door frame close to the small magnet. Usually the door is closed. Since the small magnet is close to E, the two normally closed contacts inside E are disconnected by the external magnetic force, and the micro transmitter does not work due to no power supply. Once theft occurs, the small magnet will move away from E with the door leaf, and E will lose the effect of the external magnetic field. The two contacts inside it will close by their own elastic force, and the micro transmitter will immediately send out a coded alarm signal after receiving power. IC1 (VD5026) is a digital coding integrated circuit, which has a total of 8 address codes, namely A1~A8; 4 data codes, namely D1~D4. (Editor's note: For the relevant introduction of VD5026/5027, please refer to the article "Encoding Circuit and System Security" in the 35th issue of "Electronic News" this year). The address-coded data is output by the pin of IC1. The oscillation frequency of IC1 is determined by the external resistor R1. The smaller the resistance of R1, the higher the oscillation frequency. The resistance of R1 can be selected between 120kΩ and 470kΩ, but it should be noted that the resistance of R1 must be strictly consistent with the resistance of the oscillation resistor R15 (see Figure 2) of the alarm receiving part of the ***VD5027, otherwise reliable decoding cannot be achieved. Transistor V1 and components such as C1, C2, L1, and L2 form a modulation and RF transmission circuit, and its transmission frequency is around 300MHz. In order to increase the stability of the transmission circuit, the antenna L2 can be directly printed on the circuit board.

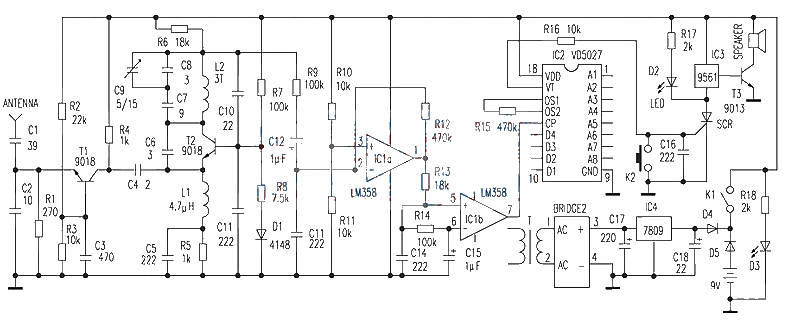
2. Wireless receiving alarm controller
Figure 2 is the circuit diagram of the wireless receiving alarm controller, which consists of super regenerative receiving, amplifying, shaping, decoding circuits and alarm signal generating circuits.
The 300MHz RF signal input by the antenna is sent to the emitter of T1 through C1, and after high-frequency amplification by T1, it is sent to the emitter of the super-regenerative RF demodulator T2 through C4. The demodulated coded data pulse signal is sent to A1 and A2 of the operational amplifier integrated circuit IC1 through C12 for amplification and shaping, and finally sent to the pin 1 of the decoding circuit IC2 for data decoding. The decoding integrated circuit VD5027 is the paired circuit of the encoding integrated circuit VD5026. During use, the address codes A1~A8 of the two circuits VD5026 and VD5027 should be absolutely consistent, and their status codes should also remain the same. When VD5026 stops sending signals (transmitter is turned off), the VT pin of VD5027 is reset to zero. The circuit uses a thyristor SCR to maintain the alarm. When the pin of VD5027 is at a high level, SCR is triggered to conduct, and the music piece 9561 outputs an alarm signal due to power, which drives the speaker to sound and the alarm indicator D2 lights up. After that, even if the pin of VD5027 is reset to zero, the thyristor SCR is already turned on, so the alarm speaker will continue to sound until the alarm release switch K2 is pressed.
In order to prevent the alarm from being missed due to power failure, the wireless alarm receiving controller adopts AC and DC power supply, and can switch automatically. When there is AC power supply, the 9V power supply output by the rectifier is added to the cathode of diode D5, diode D5 is cut off, and the circuit relies on AC power supply to work. Once the AC power is cut off, the negative end of D5 is turned on due to the loss of 9V voltage, and the 9V battery supplies power to the circuit through D5, realizing the automatic switching of AC and DC power supply.
Component Selection
The small magnet and reed switch E in Figure 1 can be purchased as a finished product of normally closed door and window alarm sensors on the market. The gap between the door leaf and the door frame of the guarded place should be small, and the door should be firm after closing, otherwise it may cause false alarms if blown by the wind. L2 can be surrounded by silver-plated wire or ∮1.5mm enameled wire, or it can be directly printed on the circuit board. The encoder does not need an encoding switch, just connect a certain point to the positive or negative pole of the power supply. The power supply uses a 15V laminated battery. The entire transmitting circuit can be made on a circuit board smaller than a matchbox.
In the alarm signal receiving and alarm control part in Figure 2, the β value of T1 and T2 is required to be no more than 100. The inductor L1 is a 4.7μH color code inductor, L2 is made by winding 3 turns of ∮0.5mm enameled wire on a ∮4mm drill bit, the antenna can be replaced by a 30cm long soft wire, K2 is the alarm release switch, and a contact normally open button should be used. The battery is a 9V laminated battery. Except for the power switch, alarm release switch, power indicator light, and alarm indicator light installed on the panel, all other components of the entire circuit are installed on a circuit board.
Production and debugging
Select the components according to Figure 1 and Figure 2, solder them on the circuit board, set the address code and status code of VD5026 and VD5027 to be consistent, and power on for debugging after checking that they are correct.
The difficulty of debugging is that the receiving and transmitting frequencies must be strictly consistent. For this reason, the debugging of the alarm transmitting part and the alarm receiving part needs to be coordinated. For the first installation and debugging, in order to ensure the success of the debugging, it is best to carry out the debugging with the cooperation of an oscilloscope. First, short-circuit the two ends of the reed switch in the transmitter part with a short-circuit wire, let the transmitter work all the time, turn on the power of the receiving part, first weld R16, connect the oscilloscope probe to the ⑦ pin of IC1 (LM358) in Figure 2, bring the transmitter close to the receiver (about 20cm apart), and use a non-inductive screwdriver to adjust the fine-tuning capacitor C3 of the transmitter and the fine-tuning capacitor C9 of the receiver until the coded pulse is displayed on the oscilloscope. Then pull the distance between the transmitter and the receiver apart, so that the transmitter and the receiver are about 10m apart, and change the oscilloscope probe to the ② pin of IC1 (LM358) in Figure 2. Carefully adjust the trimming capacitor C9 and inductor L2 of the receiving part until the waveform amplitude of the demodulated output coded pulse signal displayed by the oscilloscope is the largest. Then adjust the trimming capacitor C1 of the transmitter, and observe the changes in the waveform of the oscilloscope while adjusting, so that the waveform amplitude reaches the maximum value. Repeat several times to achieve the best state. If everything is normal, you can connect the resistor R16. At this time, the speaker should sound an alarm, and the alarm indicator light will light up. Disconnect the power supply of the transmitter, and the alarm can still be maintained. After pressing the alarm release switch, the alarm should be released. Finally, you can increase the distance to conduct experiments. Under normal debugging conditions, the alarm distance of this alarm can reach more than 50m.
The circuit of this alarm is simple, and the whole machine costs only tens of yuan. By changing the sensor of its transmitting end and setting the address code and status code of VD5026/5027, the use of this alarm can be greatly expanded (such as multi-channel alarm, data transmission, etc.).
Experimental comments: The design of the whole circuit is relatively complete and the structure is simple. According to the author's circuit, R1 and R15 are 240kΩ, SCR is CR100-6. After the circuit is completed, the circuit is adjusted with an oscilloscope, and the effect can achieve what the author said in the article. The disadvantage is that the anti-interference and transmission distance of this machine need to be improved. When there are interference and obstacles, the effect is significantly reduced.
The working principle and design method of this circuit can be used as a reference for radio enthusiasts.
- How to Make a Simple Chicken Incubator
- Tutorial for building a remote-controlled Arduino Air-Boat
- Homemade Bluetooth controlled car using HC-05 Bluetooth module to communicate with mobile phone
- What is a RADAX motor?
- Perform surgery on the speaker protection circuit
- Design and analysis of touch delay switch circuit composed of CD4011 and CD4001
- Design and manufacture of three-phase motor protection circuit
- Guanghua brand anti-theft doorbell electronic lock circuit
- Night dog barking anti-theft reminder circuit
- Water supply reminder after water outage
- Photocell trigger control circuit
- PLC transmission line automatic reclosing control circuit
- Multi-pole leakage protector circuit b
- Multi-pole leakage protector circuit a
- Photoelectric output control circuit
- Bedside touch light detection control circuit
- Temperature detection control circuit of electric hot water bottle
- Forward and reverse control circuit of micro DC motor b
- Micro DC motor steady speed control circuit b
- Temperature detection control circuit for vegetable greenhouses







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号