What is a RADAX motor?
Source: InternetPublisher:smallembedded Keywords: Motor Back EMF Updated: 2024/12/13
What is a RADAX motor?
The RADAX motor is a hybrid radial-axial (RADAX) flux motor. It combines a radial flux motor with one or more axial flux motors within the same motor housing. It reportedly offers several advantages, including higher torque, higher back EMF, compact size, and suitability for direct drive systems. RADAX technology is recommended for applications requiring high volumetric density and for vehicles that spend a significant amount of time idling or in other low-speed maneuvers. However, there is no "free lunch" in nature. That is, the RADAX motor is subject to high axial forces acting on the axial rotor as well as high initial cogging torque.
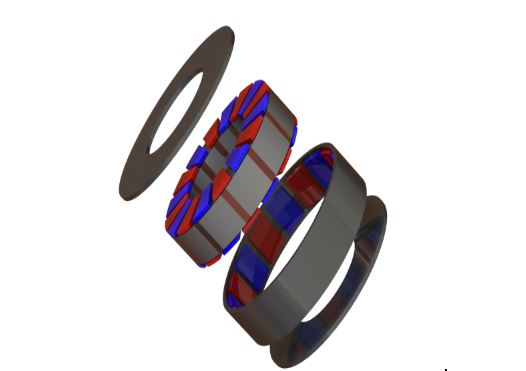
Figure 1. Exploded view of the SolidWorks model of the RADAX motor
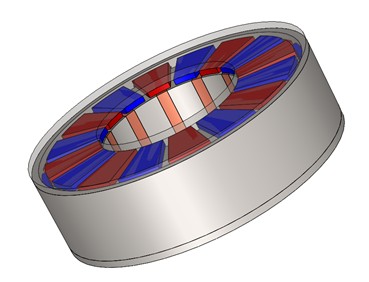
Figure 2. 3D view of the SolidWorks model of the RADAX motor
EMS Simulation of RADAX Motor
To help understand this new and promising technology, we used our virtual prototyping motor software, EMS, to study and simulate the RADAX Flux motor as shown above. A no-load analysis was performed to calculate the back EMF and cogging torque. Here are some EMS no-load results:
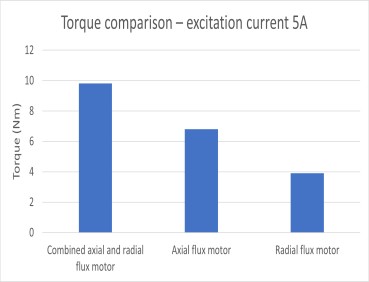
Figure 3 Magnetic flux density fringe diagram in the entire model
Figure 4. Magnetic field fringes in the stator and surrounding permanent magnets

Figure 5. Temperature distribution of the stator core
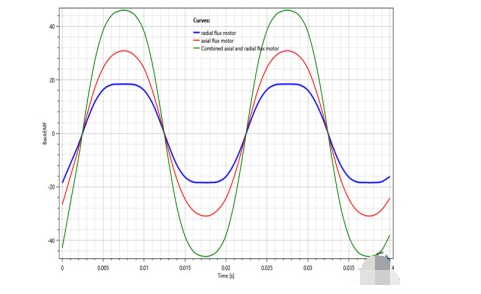
Figure 6. Comparison of back EMF of radial, axial, and RADAX motors

Figure 7. Load torque for three configurations
Clearly, the RADAX motor generates a much higher back EMF compared to the radial and axial configurations. In fact, the RADAX back EMF is nearly the sum of the radial and axial combined. Likewise, the load torque of the RADAX configuration is much higher. Nonetheless, the impressive back EMF and load torque come with a price tag as shown in the figure below.
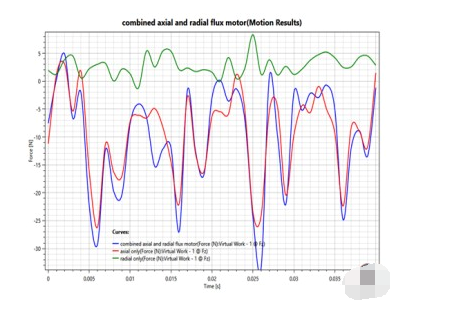
Figure 8 Comparison of axial forces acting on the axially external rotor
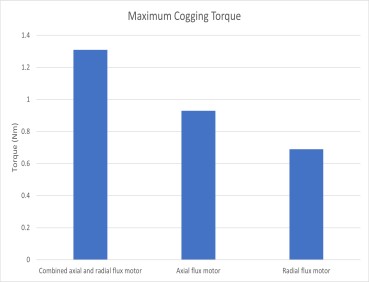
Figure 9. Comparison of maximum cogging torque
Obviously, with the new RADAX design, the axial forces and cogging torque are much higher, which is problematic; high axial forces can cause the rotor to deform or even brake completely; and high cogging torque is notorious for causing ripples and vibrations.
- Analysis of the working principle of car garage door lights
- Servo motor pin diagram/working principle/application
- How can we make the robot move precisely on a predefined path?
- A small improvement on the ordinary refrigerator motor starting circuit
- Working principle of one Xipu STR soft starter controlling two motors
- Hydraulic control circuit design and analysis
- Electric vehicle battery charging protection circuit
- Guanghua brand anti-theft doorbell electronic lock circuit
- Water supply reminder after water outage
- Simple disconnection burglar alarm
- Pyroelectric automatic door control circuit
- fire smoke control circuit
- Water and electricity saving infrared control circuit
- Car window control circuit
- Microwave oven control circuit
- Schematic diagram of motor PLC control circuit
- Bedside touch light detection control circuit
- Temperature detection control circuit of electric kettle
- Typical electronic volume control circuit
- Voltage stabilization control circuit in power circuit







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号