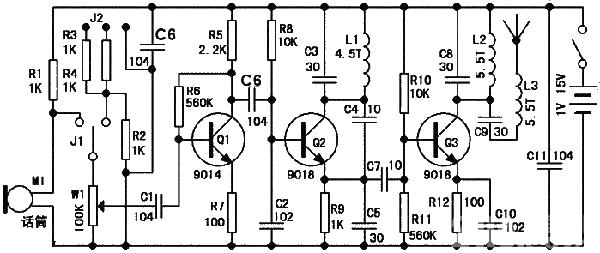
Wireless microphone circuit diagram composed of 9018 triode
Source: InternetPublisher:方世玉223 Keywords: Transistor wireless microphone circuit diagram headphones Updated: 2020/12/09
The transmitting frequency is designed in the FM radio band, so it can be used with any FM radio to receive the high-frequency signal and restore the sound signal from the high-frequency signal to complete various purposes.
Wireless microphone uses:
1. Wireless microphone: Users can rotate and move 360 degrees at will when singing, speaking or performing without any wires getting in the way.
2. Wireless broadcast: The teacher carries out live broadcast during the lecture, and countless students can use the radio to listen to the lecture, greatly increasing the number of people attending the lecture.
3. Wireless hawking device: When selling goods on the street, using a wireless microphone to hawk products has a certain novelty and will receive better advertising effects than ordinary microphones.
4. Wireless*: It has relatively good concealment and security. You can use radio headphones to listen to it from a distance without worrying about the embarrassment of meeting on site.
5. Wireless alarm: Achieve unattended operation at a certain distance. For example, the door lock sound on the second floor and the first floor can act as a burglar alarm.
6. Wireless electronic doorbell: Since it can transmit sound wirelessly, it can also transmit doorbell sound wirelessly. When paired, it can also be converted into a wireless intercom.
7. Wireless electronic musical instruments: Use a radio to receive the sounds of musical instruments such as harmonica, erhu, and guitar, or use a power amplifier to amplify and broadcast them, so you can enjoy music better.
8. Electronic hearing aids: By adjusting the volume of the radio or microphone, amplifying the sound and then sending it to the earphones, the hearing of the elderly can be effectively improved.
9. Voice-controlled lantern: Change the speaker at the output end of the high-power amplifier to a 6V or 12V car light bulb with the same wattage, and adjust the volume and position.
10. Reading memory enhancer: Similar to a hearing aid, point the microphone at yourself and listen to the sound of your own reading to eliminate external interference and help focus.
11. Small radio station: It is suitable for schools, factories and other units to organize various programs by themselves. It can play music, news, notices, etc. and listen to it on the radio.
12. TV sound transponder: Using headphones to listen to TV while watching TV can not affect other people's sleep, but it is controlled by the length of the headphone cable. This device is not subject to this restriction.
- Why does CAN FD communication need to enable TDC for sending and receiving delay compensation? How to configure TDC and SSP in TCAN4550?
- Analysis of the reasons why bow-tie antennas are preferred over microstrip antennas for 5G antennas
- TA7792 Medium Wave Radio Circuit Diagram
- Production of a FM wireless microphone
- Making an FM receiver with a high-frequency head
- Design and Analysis of Half-duplex Intercom Circuit Using LM386
- Frequency modulation circuit for crystal oscillator stabilization in radio transmitter alarm
- RF2942 I/Q 915 MHz Transmitter
- RF2919 ASK/OOK 915/868/433 MHz Receiver
- MAX2440/MAX2441/MAX2442 900 MHz Receivers
- Six common constant current source circuit diagrams and analysis
- Acousto-optic digital level detector circuit diagram
- Basic regulating tube voltage stabilizing circuit b
- Transistor time relay circuit three
- Three types of transistor amplification circuits and their characteristics - common emitter circuit
- Transistor common emitter amplifier circuit b
- Water full alarm circuit 2
- One of the water full alarm circuits
- Automatic water supply control circuit 3 for simultaneous monitoring of water tower and reservoir
- Automatic water supply control circuit 2 for simultaneous monitoring of water tower and reservoir







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号