Advantages and disadvantages of organic semiconductors, the conductive mechanism of organic semiconductors
Source: InternetPublisher:smallembedded Keywords: Semiconductors Organic Semiconductors Updated: 2025/01/14
Organic semiconductor concepts and properties
Organic semiconductors are organic materials with semiconductor properties. They are organic compounds with thermal and electrical conductivities ranging from 10-10 to 100S. Cm-1, between conductive metals and insulators. It is mainly a class of small organic molecules and polymers containing TT conjugated structures. Organic semiconductors can be divided into three types: organics, polymers, and donor-acceptor complexes. This article introduces organic semiconductors in detail, including their advantages and disadvantages, and the conductive mechanism.
Advantages and disadvantages of organic semiconductors
Advantages
1. Soft, large area (soft screen)
2. Simple preparation (no high vacuum, high temperature)
3. Photoelectricity (conductive, transparent, luminescent)
4. Molecular devices
5. Diversity and variability of molecular structure (material design)
Disadvantages
A. Equipment life and stability need to be studied and improved
B. The application field needs to be further expanded
Conductive Mechanism of Organic Semiconductors
P-type hybrid: [CH]n + 3x/2 I2 to [CH]nx+ + xI3-
N-type hybrids: [CH]n + xNa, [CH]nx- + xI3-
Experiments have shown that in organic polymers, doping causes the conductivity to rise rapidly, while the magnetic susceptibility is almost zero in a comparable range. This indicates that the carriers that cause the conductivity to rise are not electrons and holes in general conductors or semiconductors.
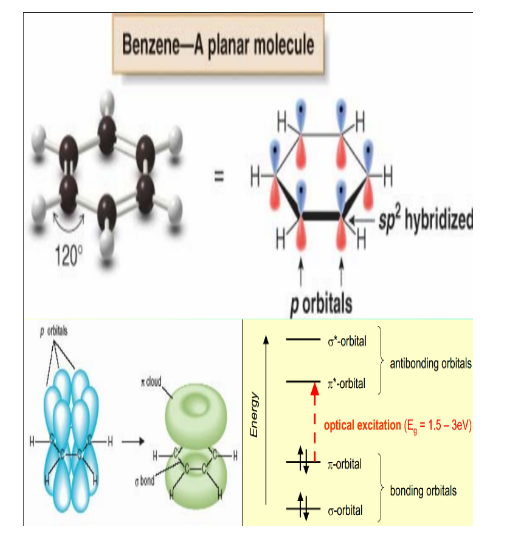
If ordered, macromolecules - > amorphous structure - > low carrier mobility 5. Research status and development trends
The different order levels of amorphous structures lead to different energy levels of molecules, which will form different energy levels similar to the band structure of crystalline materials. Generally, the LUMO energy level of organic semiconductor materials with a certain energy gap is usually opposite to the bottom of the conduction band of traditional semiconductors, while the HOMO energy level is opposite to the top of the valence band of traditional semiconductors.
Because the energy gap of organic semiconductor materials can be stabilized, that is, the energy difference between LUMO and HOMO is usually large, the electron affinity is low. Most organic semiconductor materials are p-type, that is, most materials can only transmit positive charges. This positive charge represents the oxidation state of organic molecules that have lost electrons (usually electrons at the HOMO level).
4.1 Porous (P-type) organic semiconductors
(The HOMO energy level is lower and the electron ionization potential is larger, which is conducive to receiving the injection cavity).
Structural features
1. The molecule has a large PI conjugate and a p-PI conjugated orbital with charge transfer tasks.
2. The molecule contains N atoms that can provide P electrons, usually aromatic amines, and the aromatic ring contains electron groups.
3. Small molecule crystals with a molecular weight of less than 1000 have a certain glass transition temperature and clear melting point.
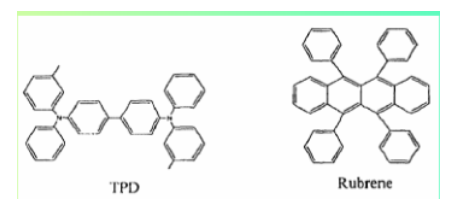
type
Including hydrazone, triphenylamine, butadiene styrene triphenylamine, etc.
4.2 Electronic (N-type) organic semiconductors
(The higher the LUMO energy level, the smaller the electron affinity potential, which is conducive to receiving the injected electrons.
Structural features
Aromatic rings have electron-absorbing groups, such as oxygen atoms, nitro groups, amides, metal ions, etc.
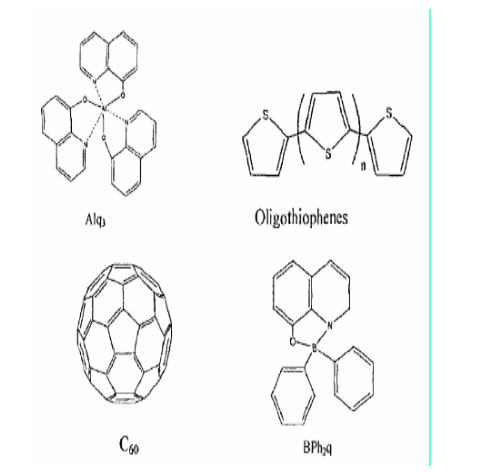
type
Aromatic compounds
- What is the relationship between capacitance and impedance in an AC circuit? How do you calculate the impedance of a capacitor?
- In-depth analysis of energy losses in oscillation frequencies
- How does sand become chips?
- Why Do Amplifier Fuses Blow? How Do You Prevent Amplifier Fuses from Blowing?
- What is power factor and three ways to improve it
- Simple Wired Spy Bug Circuit Built Based on IC741
- Beautiful crown wreath made with LED
- LED lights that “drain” battery power
- An example of proportional integral circuit diagram
- Frequency divider that converts 50Hz or 60Hz frequency into 1/60 frequency (CD4040)
- The ins and outs of silicon carbide semiconductor materials
- How semiconductor holes conduct electricity
- Technical Analysis of Semiconductor Wide Bandgap
- Domestic semiconductor industry is blooming in many places
- Semiconductor timer circuit
- 3W semiconductor amplifier circuit
- Semiconductor refrigeration switching power supply - application examples
- Semiconductor component withstand voltage test circuit
- Semiconductor refrigerator temperature control circuit
- Semiconductor pressure sensor interface circuit







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号