The energy-saving concept of LED display screens has quietly become a highlight that attracts consumers' attention and is also the reason for its explosive growth in recent years. Of course, after the crazy growth in recent years, the industry is now in a deadlock and in a dilemma of reshuffle. In this dilemma, many companies will inevitably be seriously injured and even go bankrupt. Of course, many companies will also come out of the haze and achieve more long-term development. This is the law of industry development. No company can escape this disaster. How to be reborn in the disaster is a problem that every company is currently concerned about.
In this era of high calls for energy conservation, further energy conservation of LED displays has become the support point pursued by the industry. Many companies have made various improvements in this regard, and have achieved energy conservation to a certain extent. However, there is still a long way to go to achieve greater energy conservation, which requires the joint efforts of the entire industry.
Recently, a few energy-saving LED displays have appeared on the market. The improvement of the power supply has greatly improved the energy-saving effect of LED displays, which has attracted the attention of many consumers and given them high expectations. Many LED display manufacturers are eager to try and are ready to introduce this technology first to gain development opportunities. Based on the current technology, how is the energy-saving effect of energy-saving LED displays achieved?
Let's analyze the power consumption of a small LED module! As shown in Figure 2, it is a small LED module with CYT62726 launched by Changyuntong Optoelectronics as the driver chip. Its power supply voltage is 5V. The power consumption of peripheral devices is not calculated first, because they account for a very small proportion of the entire screen. The power consumed by the entire screen is all on the lights. First calculate the power of the light point as Pled=n*Uvf*Iled (n is the number of channels, Uvf is the voltage drop of the LED light point, and Iled is the set current value). The pin voltage drop of CYT62726 driver IC is generally about 0.6V, and the voltage drops of red, green and blue light points are 1.8V, 3.0V, and 3.0V respectively. So each channel only needs 4V (3.0+0.6V) to work normally. For example, we can conservatively set the red channel to 2.8V and the blue and green channels to 3.8V. In fact, our power supply voltage is 5V, which is equivalent to increasing the power consumption of 1V*Iled inside the IC. So as above, we can imagine that as long as the power supply is reduced to 2.8V for red, 3.8V for green and 3.8V for blue, we can save the 1V*Iled power consumption added to the IC channel. With other components unchanged, the LED display can save at least 15% of energy. In addition, the reduction of the heat dissipation requirements of the LED screen can also achieve a certain degree of energy saving. This is already a considerable number for a large screen, and I believe customers will be happy to accept it!
We can further analyze its energy-saving principle!
First of all, from the perspective of power supply, as shown in Figure 3, which is a traditional switching power supply schematic, if 5V is to be reduced to 4V, the proportion of the output voltage occupied by the rectifier Schottky forward voltage drop will inevitably increase. The lower the output voltage of the switching power supply, the lower the power output efficiency will be, because the proportion of the rectifier Schottky forward voltage will be higher (its proportion X = V voltage drop / V output, the output is reduced from 5V to 4V, and its voltage drop is 0.5V, then its proportion will increase from 0.1 to 0.125, an increase of 25%), which is not obvious for the overall energy saving effect of the LED screen, so it is obvious that the use of this power supply design principle cannot achieve the improvement of the power supply working efficiency. At the same time, 5V is the nominal value voltage, which is quite mature in market application. Enabling a new switching power supply voltage will only increase costs while reducing efficiency, and the quality is difficult to guarantee, which is difficult to achieve.
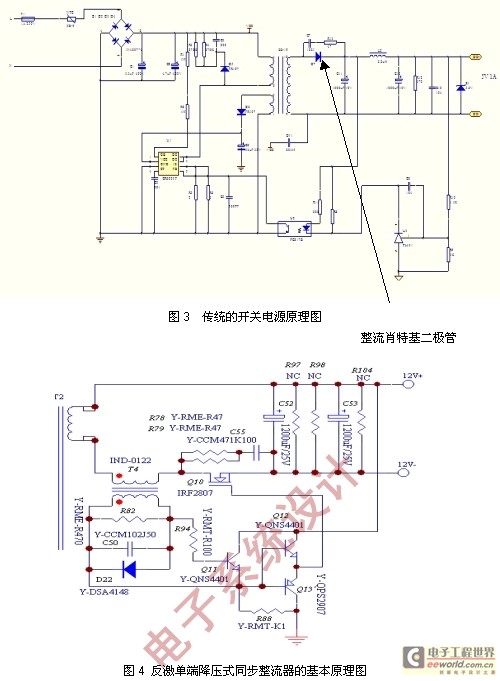
The design of power supply is a relatively mature field. Another design idea can be used to realize the power supply of the display screen, such as synchronous rectification technology. The basic principle is shown in Figure 4. Q10 is a power MOSFET. In the positive half cycle of the secondary voltage, Q10 is turned on and Q10 plays a rectifying role; in the negative half cycle of the secondary voltage, Q10 is turned off. The power loss of the synchronous rectification circuit mainly includes the conduction loss of Q10 and the gate drive loss. When the switching frequency is lower than 60KHz, the conduction loss is dominant; when the switching frequency is higher than 60KHz, the gate drive loss is dominant. When driving a relatively high-power synchronous rectifier, when the gate peak drive current IG (PK) is required to be ≥ 1A, a CMOS high-speed power MOSFET driver can also be used. After synchronous rectification replaces Schottky rectification, the proportion of consumption in the output power can be effectively reduced. The use of synchronous rectification technology is necessary.
When choosing an AC/DC switching power supply, you can choose a new half-bridge or full-bridge technology, which can increase the efficiency of the switching power supply to more than 90%. Of course, these technical applications can reduce the voltage to the optimal state when powering the LED display, and the efficiency of the power supply can also reach a high efficiency level. Therefore, using new power supply technology to power the LED display can achieve significant energy saving effects. The power supply cost will definitely increase.
Secondly, we can carefully study the LED screen driver IC. As shown in Figure 5, the output end is a MOS switch tube (as shown in Figure 6), which controls the output port to be closed or opened. The output port voltage drop is VDS = about 0.65V, which is determined by the process and materials. To reduce VDS to 0.2V or even 0.1V, the required area must be increased. In the structure of the MOS tube, it can be seen that there is a parasitic capacitance between GS and GD, and the drive of the MOS tube is actually the charging and discharging of the capacitor. This charging and discharging process takes a period of time. If the area increases, the parasitic capacitance on the MOS tube will also increase. In this way, the consequence is that the port response speed of the entire IC decreases, which will be a fatal weakness for an LED screen driver IC. Therefore, if you want to start from the IC, reduce the turning voltage, and make the driver IC have enough response speed, the decisive factor is the process, which is difficult to achieve. Some people think that other design principles can be used, but if it is a constant current IC, the internal circuit may be different, but the switch tube at the channel port must exist, so even if other design principles are used, it is difficult to achieve the purpose of voltage reduction.
In summary, the realization of energy-saving LED display screen mainly starts from the power supply. The existing LED display screen directly adopts half-bridge or full-bridge high-efficiency switching power supply, and the energy-saving effect is remarkable with synchronous rectification. The power supply voltage is reduced as much as possible under the state of constant current for the driver IC, and the red, green and blue tubes are powered separately to achieve better energy-saving effect. Of course, the application cost of this non-standard voltage power supply and new technology will inevitably increase. From the perspective of the screen driver IC, the energy saving is not obvious, and reducing the driving constant current voltage difference will also bring new problems including cost. Some IC companies promote the driving energy-saving design, which is nothing more than a sales strategy.
Previous article:Atmel Launches Complete Digital Audio Platform for Consumer Applications
Next article:Breakthrough multi-touch technology brings innovation to your fingertips
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Innovation is not limited to Meizhi, Welling will appear at the 2024 China Home Appliance Technology Conference
- Enjoy big-screen gaming anytime, anywhere: Making portable 4K UHD 240Hz gaming projector a reality
- AMD surpasses Intel: CPU shipments surge in Q3 this year
- Exynos is losing ground, Samsung plans to use Qualcomm chips in home appliances
- Intel and 50 partners unveiled a full range of 30 notebook and desktop AI PCs equipped with Intel Core Ultra (2nd Generation)
- Innovation leads the new trend of mobile refrigeration GMCC will present new products at 2024 CIAAR
- Lenovo and NVIDIA expand collaboration to jointly launch new liquid-cooled AI servers
- Ceiling fan solution based on XMC1302
- Gartner: Global AI PC shipments are expected to account for 43% of total PC shipments in 2025
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Millimeter wave sensors enable edge intelligence
- A few key points about interrupts
- Disassembling a DALSA S2-12-02K40 line scan camera
- Chapter6 Timer_A
- Do you know the eight important knowledge points of FPGA design?
- Share an ADI one-stop power design tool kit
- Component selection of DCDC power chip
- EEWORLD University - Make your design easier - Get to know TI's latest reference design for motor drive
- Spring is here
- TFT LCD interface problem





 AD8675ARMZ-R2
AD8675ARMZ-R2











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号