1. Scope
This specification specifies the symbols, codes, terms and their definitions, design criteria, layout requirements, structural design requirements, material selection requirements, performance design requirements, design calculation methods, and safety requirements involved in the design process of high-voltage wiring harnesses for electric vehicles.

II. Normative Reference Documents
The following documents are essential for the application of this document. For any referenced document with a date, only the version with the date is applicable to this document. For any referenced document without a date, the latest version (including all amendments) is applicable to this document. GB/T 2423.17 Basic environmental testing procedures for electric and electronic products - Salt spray test GB 4208 Degrees of protection of enclosures (IP code) GB/T 12528-2008 Cables for rail transit vehicles with rated voltage of 3 kV or less for AC GB 14315 Crimp-type copper and aluminum terminals and connecting tubes for power cable conductors GB/T 14691 Technical drawing - Fonts GB/T 18384.2 Electric vehicles - Safety requirements - Part 2: Functional safety and fault protection GB/T 18384.3 Electric vehicles - Safety requirements - Part 3: Protection against electric shock GB/T 18487.1 Electric vehicle conductive charging system - General requirements GB/T 18487.2 Electric vehicle conductive charging system - Requirements for connection of electric vehicles to AC and DC power sources GB/T 18488.1 Technical requirements for motors and their controllers for electric vehicles GB/T 19596 Terminology for electric vehicles QC/T 413 Basic technical requirements for automotive electrical equipment Q/TEV 100 Numbering rules for complete vehicle product drawings and technical documents Q/TEV 31306 Numbering rules for electric vehicle wiring harnesses Q/TEV 31307 Numbering rules for electric vehicle powertrain wires SAE J1654 High-voltage cables SAE J1673 Design of high-voltage cable assemblies for electric vehicles SAE J1742 High-voltage connections for on-board wiring harnesses for road measurement - Test methods and general performance requirements

III. Terms and Definitions
(1). Working voltage: The maximum value of the AC voltage (RMS) or DC voltage (not considering the instantaneous voltage) that may be generated by the electrical system under any normal working conditions. (2). High voltage: According to the specific voltage level, the voltage level of electric vehicles is Class B. DC: DC60V
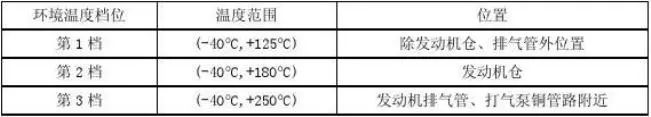
The long-term allowable operating temperature of the cables of the wiring harness of road vehicles shall not exceed 125℃. If the ambient temperature of the cable layout exceeds the allowable operating temperature of the cable, it is advisable to increase the cross-sectional area of the cable in accordance with the provisions of Section 8.1 of this specification so that the wiring harness meets the ambient temperature requirements. ② Voltage requirements According to the voltage level of electric vehicles, which is Class B, the rated voltage of the high voltage of the whole vehicle is: DC1000V, AC660V; The rated voltage of the high-voltage wiring harness must be slightly higher than the rated voltage of the whole vehicle, and the rated voltage of the high-voltage wiring harness is specified to be: AC750V. ③ Withstand voltage According to GB/T 18488.1, the dielectric strength between circuits that are not electrically connected to each other should be able to withstand the test voltage of (2U+1000), that is, when the wiring harness is disconnected from the components, the wiring harness withstands the voltage of the vehicle body: AC2500V/50HZ/1min, the leakage current does not exceed 10mA, and no flash breakdown occurs. ④ Insulation resistance According to SAE J1742, the insulation resistance test voltage is DC1000V. When the wiring harness is disconnected from the connected components, the insulation resistance of the wiring harness to the vehicle body should be greater than 100mΩ under any circumstances. ⑤ Salt spray requirements The salt spray test is carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 2423.17, and the high-voltage wiring harness should be in a normal installation state in the test chamber. The test time is 16h. After the test, the high-voltage wiring harness should be able to work normally after being powered on after (1-2) hours of static recovery, and the appearance is not assessed. ⑥ Flame retardant requirements The flame retardant grade of the materials used in the wiring harness is required to be UL94V-0. ⑦ The pull-off force of the wiring harness requires that the pull-off force after the cable is crimped to the connector should not be less than the minimum pull-off force. According to SAE J1742, the minimum pull-off force is shown in Table 2.
5. Design input and output requirements
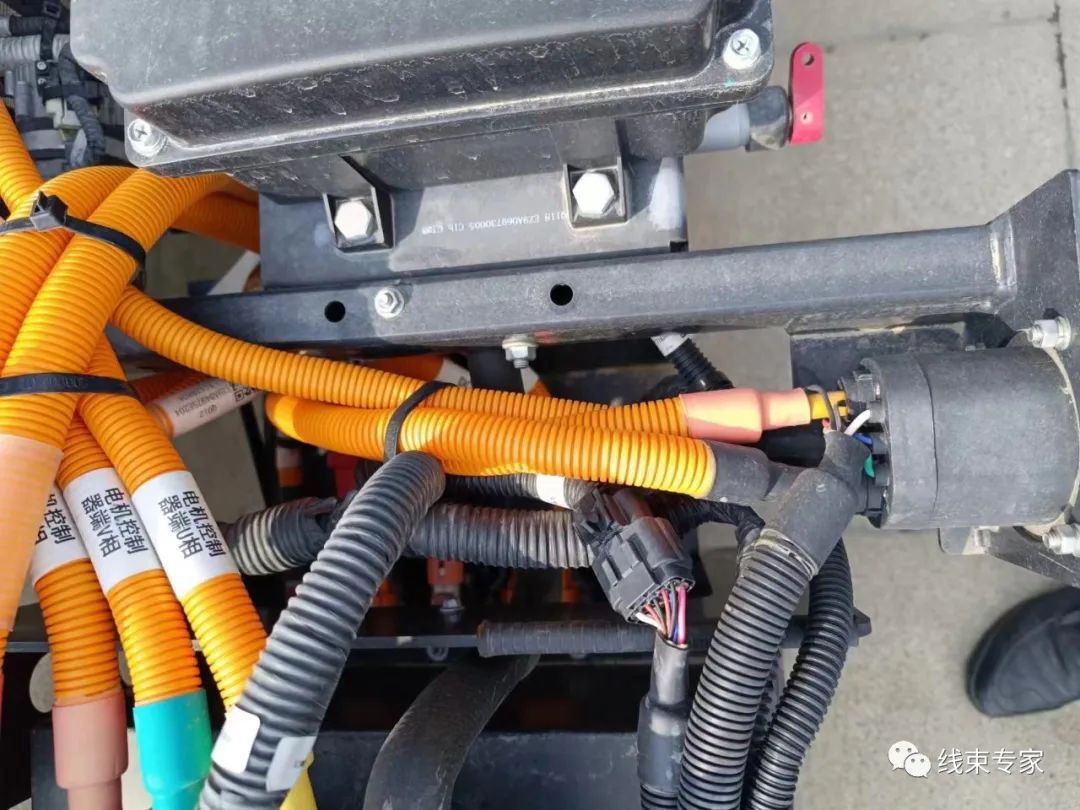
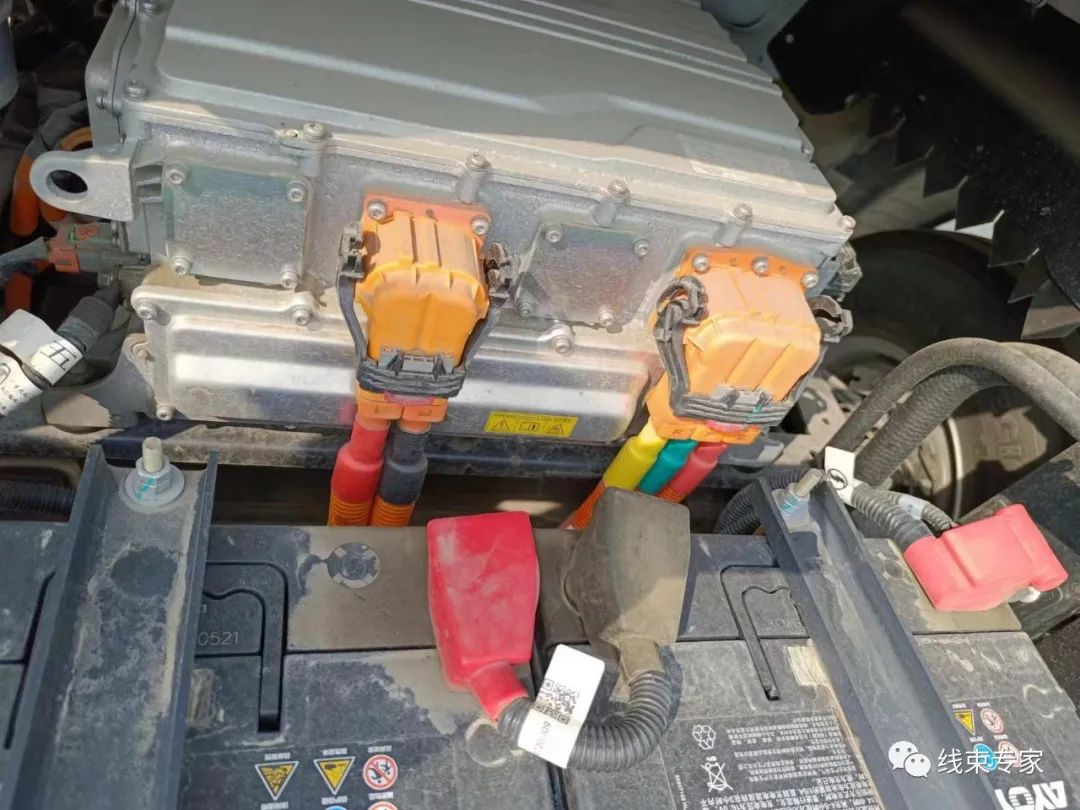
1. Design input requirements (1) Input requirements for electrical design and power system configuration. (2) Layout diagram of the whole vehicle. (3) Wire harness wiring diagram. (4) Installation position of each electrical component in the high-voltage system, and the docking form of the wire harness and electrical components. (5) Load characteristics of each electrical component in the high-voltage system. Characteristics include steady-state current intensity, voltage requirements, transient conditions and current intensity and current waveform (steady, pulse, frequency, etc.). 2. Design output requirements (1) Contents of the wire harness diagram The content of the wire harness diagram includes the main line, branch line, site, connector appearance, plug-in name and model, the name of the component corresponding to the plug-in, plug-in hole number, cable number corresponding to the hole number, wire diameter, and definition; secondly, it should also include the wire harness wiring table, plug-in view direction, technical requirements, etc. The cable should be marked with the wire model. (2) Color of the wire harness protective cover The wire harness protective cover includes corrugated tube and heat shrink tube. The color of the corrugated tube is orange (GB30). Color of heat shrink tubing: Different colors of heat shrink tubing are used to distinguish polarity. The positive pole is red, the negative pole is blue, the U phase is yellow, the V phase is green, and the W phase is red. (3) Length of the wiring harness ① The length of the cable is measured according to the overall layout of the vehicle and the wiring harness wiring diagram. On the basis of the measured length, a margin of no more than 200mm should be added. ② The length of the corrugated tube is based on the length of the cable. The length of the cable extending into the component must be subtracted from the length of the cable. The specific value of the subtracted length depends on the specific component. ③ The length of the heat shrink tubing must be ironed at both ends of the corrugated tube to ensure that the connection between the corrugated tube and the cable does not shake. The length of the heat shrink tubing must be equal to the length of the cable extending into the component. ④ Length of shielding layer of shielded cable When shielded cable is required, such as the three-phase high-voltage wire harness connecting the controller and the motor, the shielding layer must be stripped and separately connected with a cross-linked polyolefin heat shrink tubing of specification (φ8/4.0). The length of the shielding layer after heat shrinkage should be greater than or equal to 200mm and less than or equal to 250mm. (4) Wire numbering The wire number of each cable should be indicated in the wiring harness diagram, and the numbering of the wire number should strictly comply with the enterprise standard Q/TEV 31307. (5) Wire harness numbering The wire harness number corresponding to the wiring harness diagram should be indicated in the wiring harness diagram, and the numbering of the wire harness number should strictly comply with the enterprise standard Q/TEV 31306. (6) Connectors in the wiring harness diagram The wiring harness diagram should indicate the connector view direction, model, hole layout and number, and wire number corresponding to the hole. (7) Cable model The model of each cable should be indicated in the wiring harness diagram, and the selection of cable model should comply with the provisions of GB/T 12528. Recommended models are shown in Table 3.



Previous article:Comparative analysis of the evolution of electronic and electrical architectures of mainstream car companies
Next article:Development and application of road vehicle trajectory cascade prediction system
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
-
 Multi-port and shared memory architecture for high-performance ADAS SoCs
Multi-port and shared memory architecture for high-performance ADAS SoCs -
 Foundations of Robotics-A Multidisciplinary Approach with Python and ROS
Foundations of Robotics-A Multidisciplinary Approach with Python and ROS -
 CVPR 2023 Paper Summary: Video: Low-Level Analysis, Motion, and Tracking
CVPR 2023 Paper Summary: Video: Low-Level Analysis, Motion, and Tracking -
 Electric Vehicle Wireless Battery Management Revolution Has Begun and the ROI Potential Is Huge
Electric Vehicle Wireless Battery Management Revolution Has Begun and the ROI Potential Is Huge
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- ADC/DCA chip manufacturers
- [RVB2601 Creative Application Development] — Some thoughts on unpacking and CDK installation
- This is how I became an unpaid garbage collector day by day. . .
- [Analysis of the topic of the college electronic competition] —— 2022 Provincial TI Cup F Topic "Signal Modulation Measurement Device"
- Electrochemical sensor signal processing circuit issues
- [2022 Digi-Key Innovation Design Competition] Desktop Robot Dog Material Unboxing
- EEWORLD University Hall----Live Replay: TI Ultrasonic Gas Flow Measurement Innovation Solution
- Cooperate to develop 8-bit MCU chip
- Problem with CCS installation
- [NXP Rapid IoT Review] +5. Write a simple project



 Multi-port and shared memory architecture for high-performance ADAS SoCs
Multi-port and shared memory architecture for high-performance ADAS SoCs CVPR 2023 Paper Summary: Video: Low-Level Analysis, Motion, and Tracking
CVPR 2023 Paper Summary: Video: Low-Level Analysis, Motion, and Tracking
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号