STM32 is a low-power chip, so its peripherals all have a corresponding clock, and these clocks are turned off when the chip is just powered on, so if you want the peripherals to work, you must turn on the corresponding clock.
This article introduces how to control the switch of the LEN lamp by pressing buttons based on GPIO.
(1) Button control
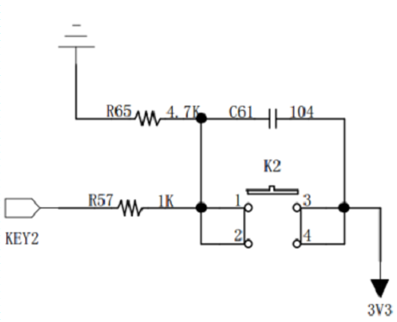
The figure above shows the circuit of the key. When the key is not pressed, the output signal of KEY2 is low level (the circuit where the key is located is blocked and connected to the ground); when the key is pressed, the output state of KEY2 is high level (the circuit where the key is located is connected and connected to the 3.3V power supply). Therefore, by detecting the level of the pin, it is possible to determine whether the key is pressed.
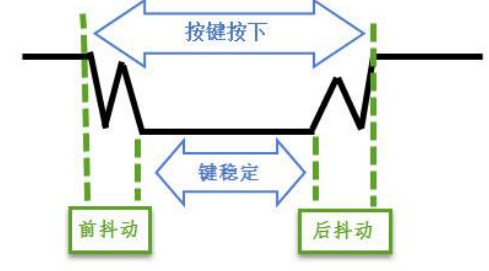
When the mechanical contact of the key is disconnected or closed, due to the elastic effect of the contact, the key switch will not be immediately connected or disconnected, and it will produce a ripple signal as shown in the figure below. Software debouncing processing and filtering are required, which is not convenient for input detection. In addition, the hardware can also realize the debouncing function. As shown in the figure above, the hardware debouncing function is to achieve delay through the charge and discharge of C61 to eliminate ripples, thereby simplifying the software processing, so that the software only needs to detect the level of the pin.
As mentioned above, the first step is to turn on the GPIO clock so that the peripheral can work. This article uses the STM32 library function to write the code:
//Start the clock of the button port (port A)
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA,ENABLE);
//Define a structure to configure the settings of the PA0 pin
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
//Set the pin of the structure to 0
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_0;
//Set the structure mode to floating input
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING;
//Set the structure to port A, that is, set the PA0 pin to floating input
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
The above code first fills in the GPIO structure, and then writes parameters to the corresponding GPIO register through the function GPIO_Init() to complete the initialization of GPIO.
Then we need to detect the status of the button. The code is as follows:
// Check if the button is pressed
if(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_0) == KEY_ON) {
// Check if the button has been released
while (GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_0) == KEY_ON);
//Subsequent code processing after pressing the key
............................................
}
(II) GPIO output
Similar to GPIO input, the code for GPIO output is as follows:
//Define a GPIO_InitTypeDef type structure
GPIO_InitTyopeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
// Enable GPIO related peripheral clocks
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB, ENABLE);
//Select the GPIO pin to be controlled
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_5;
//Set the output mode of the GPIO pin to push-pull output
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP;
//Set the pin rate to 50MHZ
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHZ;
//Call library function to initialize GPIO
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure);
After using the above code settings, you can control the LED light in the main function.
Set GPIOB->BSRR to 1 to output a high level to light up the LED, and set GPIOB->BRR to 1 to output a low level to turn off the LED.
Previous article:STM32F407 study notes - GPIO_button control LED on and off
Next article:Button lights up LED
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 13:28





- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- How to write printf macro switch
- Start with a Routine
- Share a reference book on servo motor drive
- Is FPGA a big deal in the field of artificial intelligence?
- 【GD32F310G-START】Voltage meter
- C language algorithm to calculate the age of beautiful women
- LOTO virtual oscilloscope about trigger sensitivity function
- [ST60 short-distance test] Part 2: Communication rate test
- PT4115 cannot be completely shut down
- STM32 Linux development board recommendation | PHYTEC development board: Help you reduce development risks and improve product stability

 usb_host_device_code
usb_host_device_code Transplantation of real-time operating system RT-ThreadSmart on STM32MP1
Transplantation of real-time operating system RT-ThreadSmart on STM32MP1
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号