#include
#define uchar unsigned char
#define uint unsigned int
#define DELAY 1000
void delay(uint z) //1ms
{
uint x,y;
for(x=z;x>0;x--)
for(y=111;y>0;y--);
}
void main()
{
uchar i,dt;
EA=1; //Enable total interrupt
EX1=1; //Enable external interrupt 1
//IT1=0; //Set external interrupt 1 as low level trigger
IT1=1; //Set external interrupt 1 as falling edge trigger
while(1)
{
dt=0x01;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
P2=dt;
delay(DELAY);
dt<<=1;
}
}
}
void exter1() interrupt 2
{
P2=0xff;
}
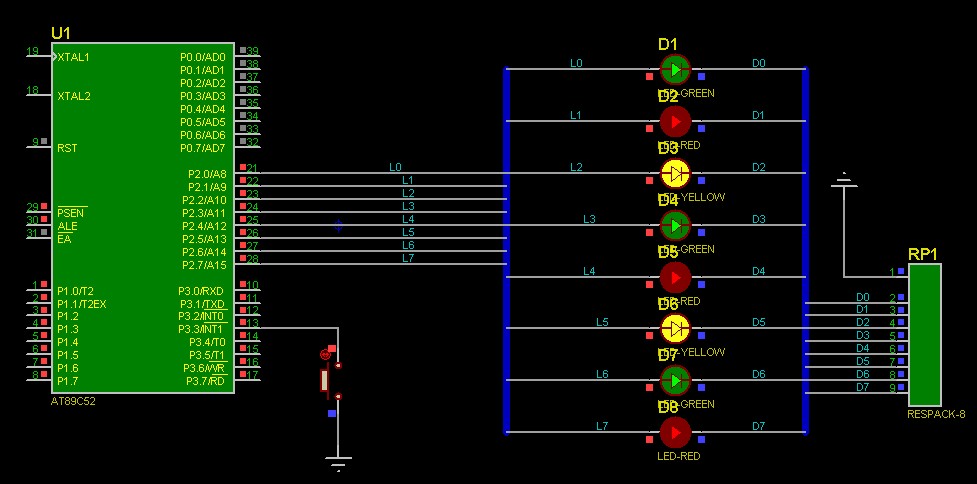
If no interruption occurs, a single lamp will light up in a cycle; if an interruption occurs, all lights will light up.

Previous article:51 single chip microcomputer (AT89C52) controls buzzer
Next article:51 single chip microcomputer (AT89C52) controls dual relays
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-15 15:43

- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
-
 西门子S7-12001500 PLC SCL语言编程从入门到精通 (北岛李工)
西门子S7-12001500 PLC SCL语言编程从入门到精通 (北岛李工) -
 Siemens Motion Control Technology and Engineering Applications (Tongxue, edited by Wu Xiaojun)
Siemens Motion Control Technology and Engineering Applications (Tongxue, edited by Wu Xiaojun) -
 MCU C language programming and Proteus simulation technology (Xu Aijun)
MCU C language programming and Proteus simulation technology (Xu Aijun) -
 100 Examples of Microcontroller C Language Applications (with CD-ROM, 3rd Edition) (Wang Huiliang, Wang Dongfeng, Dong Guanqiang)
100 Examples of Microcontroller C Language Applications (with CD-ROM, 3rd Edition) (Wang Huiliang, Wang Dongfeng, Dong Guanqiang)
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Download from the Internet--ARM Getting Started Notes
- Learn ARM development(22)
- Learn ARM development(21)
- Learn ARM development(20)
- Learn ARM development(19)
- Learn ARM development(14)
- Learn ARM development(15)
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Source Insight Open Issues
- STM Arduion cannot download firmware?
- An article explains the function and principle of Via hole
- NUCLEO's ST-LINK is changed to 1.8V and the computer cannot recognize the hardware
- What programming method should be used for the M9S8AC16CG chip?
- DSP IIR digital filter implementation program source code
- Where can I download the device data sheet of Taiwan REALTEK (Realtek)?
- NXP Rapid IoT Review] +③ NXP Rapid IoT online compilation and operation of various demos
- iis3dwb three-axis acceleration sensor driver code PCB package
- Pre-registration for the live broadcast with prizes | Rochester Electronics Semiconductor Full Cycle Solutions Help You Deal with Supply Chain Disruptions and Component Outages...

 西门子S7-12001500 PLC SCL语言编程从入门到精通 (北岛李工)
西门子S7-12001500 PLC SCL语言编程从入门到精通 (北岛李工)











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号