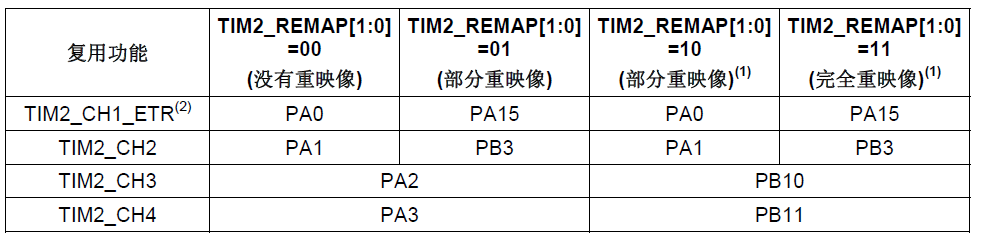
There are four port usage combinations of TIM2 of stm32:
1. When not remapped, the default four IO ports of TIM2 are PA0, PA1, PA2, and PA3
2. To use the port combination of PA15, PB3, PA2, and PA3, call the following statement for partial remapping:
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO, ENABLE); //Remapping requires turning on the AFIO clock
GPIO_PinRemapConfig(GPIO_PartialRemap1_TIM2, ENABLE);
3. To use the port combination of PA0, PA1, PB10, and PB11, call the following statement for partial remapping:
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO, ENABLE); //Remapping requires turning on the AFIO clock
GPIO_PinRemapConfig(GPIO_PartialRemap2_TIM2, ENABLE);
4. To use the port combination of PA15, PB3, PB10, and PB11, call the following statement for complete remapping:
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO, ENABLE); //Remapping requires turning on the AFIO clock
GPIO_PinRemapConfig(GPIO_FullRemap_TIM2, ENABLE);
At the same time, the JTAG function must be disabled so that PA15, PB3, PB10, and PB11 can output normally.
Fully mapped port configuration function:
static void TIM2_GPIO_Config(void) //CH1-PA15 CH2-PB3 CH3-PB10 CH4-PB11 remapping
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB1Periph_TIM2, ENABLE);
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA | RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB | RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO, ENABLE);
GPIO_PinRemapConfig(GPIO_FullRemap_TIM2, ENABLE);
GPIO_PinRemapConfig(GPIO_Remap_SWJ_JTAGDisable, ENABLE); //Disable JTAG function and use PB3 and PB4 as normal IO ports
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_15;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP; // Multiplexed push-pull output
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_3 | GPIO_Pin_10 | GPIO_Pin_11;
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure);
}
Previous article:STM32 Self-study Notes - External Interrupts
Next article:STM32 external interrupt configuration steps
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 23:49




- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Simplify the design of automotive body motor controllers and quickly achieve lightweighting
- Does anyone know how to calculate the input power by first boosting the voltage and then reducing it?
- Remote control aircraft, electric vehicles, motorcycle anti-theft devices, flashlights, etc. single chip computer development
- Why do I/O ports of microcontrollers need drivers?
- There is a constant current source circuit. The simulation is fine, but the actual circuit is incorrect. Can you help me take a look? Thank you!
- The boost circuit is unstable, what is the reason?
- Wireless PLC remote download 4-20ma wireless transmission 0-5v wireless transmission analog quantity wireless transmission solution
- FPGA most downloaded related materials
- What does it mean to connect an isolated 485 transceiver and a non-isolated transceiver in parallel?
- How to understand the equivalent of capacitors passing AC

 usb_host_device_code
usb_host_device_code Transplantation of real-time operating system RT-ThreadSmart on STM32MP1
Transplantation of real-time operating system RT-ThreadSmart on STM32MP1
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号