/**
* @brief Enables or disables the specified USART interrupts.
* @param USARTx: where x can be 1 or 2 to select the USART peripheral.
* @param USART_IT: specifies the USART interrupt sources to be enabled or disabled.
* This parameter can be one of the following values:
* @arg USART_IT_WU: Wake up interrupt. //Wake-up interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_CM: Character match interrupt.//Character match interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_EOB: End of block interrupt. //Block end interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_RTO: Receive time out interrupt. //Receive timeout interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_CTS: CTS change interrupt. //CTS change interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_LBD: LIN Break detection interrupt. //Termination detection interrupt* @arg USART_IT_TXE
: Tansmit Data Register empty interrupt. //Transmit data register empty interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_TC: Transmission complete interrupt. //Transmission completion interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_RXNE: Receive Data register not empty interrupt. //Receive register not empty interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_IDLE: Idle line detection interrupt. //Idle line detection interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_PE: Parity Error interrupt. //Parity error interrupt
* @arg USART_IT_ERR: Error interrupt(Frame error, noise error, overrun error) //Error interrupt
* @param NewState: new state of the specified USARTx interrupts.
* This parameter can be: ENABLE or DISABLE.
* @retval None
*/
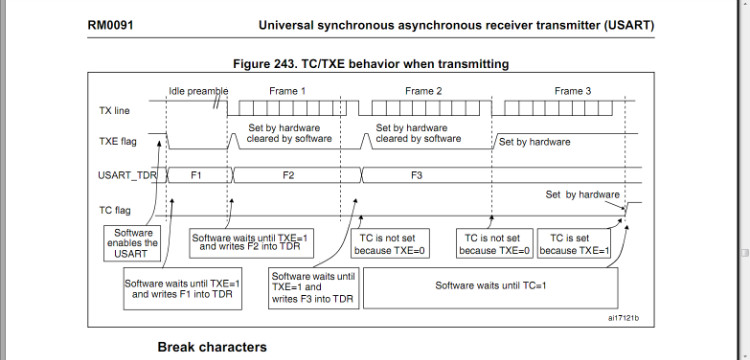
1. Enable the serial port to send TE. At this time, USART_DR is empty. At this time, check whether TXE is set to 1. TXE is set to 1. The TX pin first sends an idle frame, writes the F1 frame to USART_DR, and TXE is cleared. Because the idle frame is being sent at this time, the data written to USART_DR is placed in the TDR register and has not yet been copied to the shift register.
2. After the idle frame is sent, the data in the TDR register is copied to the shift register. At this time, check whether TXE is set to 1. TXE is set to 1, indicating that TDR is empty and the next data can be placed. At this time, the data of the F1 frame will be sent on the TX pin, and the software writes the data of the F2 frame to USART_DR, and TXE is cleared.
3. After the stop bit of the F1 frame is sent, because F2 in the TDR register has not been copied into the shift register, TXE is still 0 at this time, and TC is not set to 1. At this time, check whether TXE is set to 1. TXE is set to 1, indicating that TDR is empty and the next data can be placed. At this time, the data of F2 frame will be sent on TX pin, and the software will write the data of F3 frame into USART_DR, and TXE will be cleared.
4. After the stop bit of F2 frame is sent, because F3 in TDR register has not been copied into shift register, TXE is still 0, and TC is not set to 1. At this time, check whether TXE is set to 1. TXE is set to 1, indicating that TDR is empty, and no data is written to USART_DR later. TXE remains high, and the data of F3 frame will be sent on TX pin.
5. After the stop bit of F3 frame is sent, because TXE is 1 at this time, the TC flag will be set to 1. If TCIE is 1, an interrupt will be generated.
Note a few points when sending via the serial port:
1. If data is being sent, writing data into USART_DR will write the data into the TDR buffer register. After the current transmission is completed, the data in TDR will be copied into the shift register.
2. If data is not being sent, writing data into USART_DR will put the data directly into the shift register without passing through TDR. TXE is cleared, and then the transmission starts, and TXE is set to 1 by hardware.
3. TC will only be set to 1 when the stop bit of a frame of data is sent and TXE is 1.
Previous article:When configuring the STM32 clock, pay attention to setting the FLASH wait cycle
Next article:Understanding of several STM32 startup files
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 14:27




- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Download and get a gift|Keysight Technology Test Equipment Report
- TI MSP430 series microcontroller serial communication baud rate calculation method
- [GD32E231 Work Submission] Environmental Radiation Dose Monitoring Equipment Design
- Op amp second order filter circuit
- A beautiful frame diagram
- Free shape LED ball
- Technology Live: LPC55S69, designed to prevent hackers, helps you build secure edge nodes at low cost (share and win 20E coins)
- The upcoming nrf52840 metro express development board
- Electronic Instrumentation and Electrical Measurement
- Working Principle of Solar Street Lights

 usb_host_device_code
usb_host_device_code Transplantation of real-time operating system RT-ThreadSmart on STM32MP1
Transplantation of real-time operating system RT-ThreadSmart on STM32MP1
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号