The core of Bluetooth headsets is the radio frequency and baseband processing. To adapt to the integration of functions and miniaturization of design, companies such as CSR and Broadcom have integrated the radio frequency and baseband processing functions together, such as the CSR BlueCore4 highly integrated Bluetooth chip, which has a minimum package size of 6×6mm. The power management design of the entire headset requires fewer peripheral components and high integration, while meeting the requirements of the Bluetooth chip for load response and noise suppression.
Bluetooth headsets are mostly powered by lithium batteries with a voltage range of 2.7V to 4.2V. The battery capacity is 90mAH to 170mAH. To meet the needs of longer calls and music playback, the battery capacity tends to increase gradually. In addition, Bluetooth chips based on ARM or DSP cores require two sets of power supplies (such as 1.8V and 2.7V) to power the core and I/O respectively. At the same time, the microphone also needs a "clean" bias voltage.
Based on the above system power requirements, Microchip has launched highly integrated, small-size power management solutions, including TC1303 and MCP73855. Among them, TC1303 is a highly integrated power conversion chip, and MCP73855 is a highly integrated linear lithium battery charging chip. TC1303 integrates a 500mA synchronous buck converter and a 300mA low-dropout LDO in a 3×3mm 10-pin DFN package, and has a voltage-good indication pin (Power-Good). Its standard fixed voltage output combination, such as 1.8V/2.7V, just meets the power requirements of BlueCore2. Figure 1 shows the application circuit of TC1303 on Bluetooth headsets.
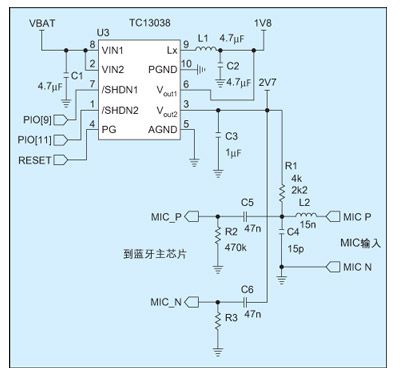
Figure 1: Application circuit of TC1303 in Bluetooth headset.
The 500mA synchronous DC/DC converter in the figure integrates P-channel and N-channel MOSFETs, uses a switching frequency of 2MHz, and achieves a conversion efficiency of more than 92%. The high switching frequency and PWM/PFM automatic switching technology allow engineers to choose surface-mount inductors and ceramic capacitors as low as 2.2μH to meet the ripple requirements of filtering and Bluetooth chips. The LDO integrated in the TC1303 can provide an output current of 300mA with only a voltage difference of 137mV. In order to further reduce the impact of DC/DC switching noise on circuit design, the power ground pin of the LDO and the DC/DC power ground pin are separated during chip design to ensure that the LDO output can provide a "clean" voltage to the I/O part and the microphone.
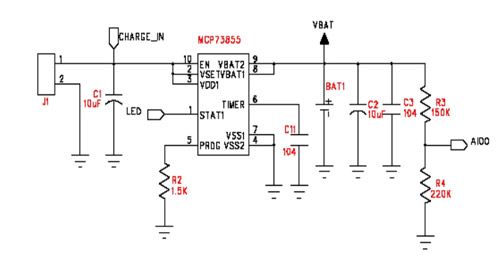
Figure 2: Application circuit of MCP73855 in Bluetooth headset design.
The voltage normal indication pin provided by TC1303 can be connected to the I/O of the Bluetooth chip to monitor the status of the power supply voltage. The voltage normal indication pin can detect the DC/DC output voltage (TC1303A) or the LDO output voltage (TC1303B), and can even detect these two outputs separately to achieve sequential power-on and meet the power supply requirements of different Bluetooth chips.
MCP73855 can provide lithium battery charging management function. The integrated MOSFET, current detection resistor and reverse blocking diode can provide a maximum charging current of 400mA, and the required charging current can be set through an external resistor or directly through the I/O output. MCP73855 can automatically complete the pre-charge, constant current and constant voltage charging control of lithium batteries, and output the charging status to the LED or Bluetooth chip. With the appropriate peripheral circuit, the charging status indication pin can drive a two-color LED to display the charging process and the end of charging respectively. Figure 2 shows the application circuit of MCP73855 in the design of Bluetooth headset.
The small package size (3×3mm) of TC1303 and MCP73855 and simple peripheral circuits constitute a low-cost, high-performance, highly integrated Bluetooth headset power management solution, which can also be applied to the latest stereo Bluetooth headset design for playing MP3. Engineers can use it and Bluetooth chips to design more comfortable, fashionable, easy-to-use, and lightweight Bluetooth stereo headsets, allowing users to enjoy music while moving and never miss a call.
Previous article:A summary of the design and optimization solutions for DC-DC power modules, providing complete software and hardware design guidance
Next article:Battery monitoring improves UPS reliability
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- MathWorks and NXP Collaborate to Launch Model-Based Design Toolbox for Battery Management Systems
- STMicroelectronics' advanced galvanically isolated gate driver STGAP3S provides flexible protection for IGBTs and SiC MOSFETs
- New diaphragm-free solid-state lithium battery technology is launched: the distance between the positive and negative electrodes is less than 0.000001 meters
- [“Source” Observe the Autumn Series] Application and testing of the next generation of semiconductor gallium oxide device photodetectors
- 采用自主设计封装,绝缘电阻显著提高!ROHM开发出更高电压xEV系统的SiC肖特基势垒二极管
- Will GaN replace SiC? PI's disruptive 1700V InnoMux2 is here to demonstrate
- From Isolation to the Third and a Half Generation: Understanding Naxinwei's Gate Driver IC in One Article
- The appeal of 48 V technology: importance, benefits and key factors in system-level applications
- Important breakthrough in recycling of used lithium-ion batteries
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
- Brief Analysis of Automotive Ethernet Test Content and Test Methods
- How haptic technology can enhance driving safety
- Let’s talk about the “Three Musketeers” of radar in autonomous driving
- Why software-defined vehicles transform cars from tools into living spaces
- How Lucid is overtaking Tesla with smaller motors
- Wi-Fi 8 specification is on the way: 2.4/5/6GHz triple-band operation
- Wi-Fi 8 specification is on the way: 2.4/5/6GHz triple-band operation
- The State of Open Source Hardware in 2021
- Implementation of HPI Boot Mode in TMS320C62x
- What is the physical meaning of Gauss's formula in advanced mathematics?
- 【Portable Environmental Status Detector】Compile and download function test
- Learn about TI 15.4-Stack's support for 470M frequency band
- 【Me and Yatli】+My impression of Yatli
- Advanced Algebra Concise Course
- [RT-Thread reading notes] Three timers
- AP6212 driver all firmware & nvram
- Bosch air pressure sensor gives sweeping robots more monitoring functions

 LTC6244CMS8#TRPBF
LTC6244CMS8#TRPBF
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号