For LED driving, the constant current method is better than the constant voltage method. In the circuit proposed in this article, the constant voltage regulator commonly used for LEDs is replaced with a constant current source. In addition, a starting current limiter is used to suppress large inrush currents, and the voltage chopper can be used for an AC input voltage range as wide as 96VRMS~260VRMS.
The concept of this article is derived from two design examples published in 2011 (Reference 1 and Reference 2), which have been improved to improve power efficiency at a low cost. The circuits in Figure 1 and Figure 2 have the same inductorless chopper and controversial power efficiency issues. To improve power efficiency, the following two principles should be followed: the heat loss of the chopper resistor should be minimized; the chopper should switch at the appropriate threshold voltage VTH. In addition, VTH should be as close as possible to the operating voltage of the LED string. This method minimizes the power dissipation of the constant current regulator (CCR) while maintaining a constant LED current.
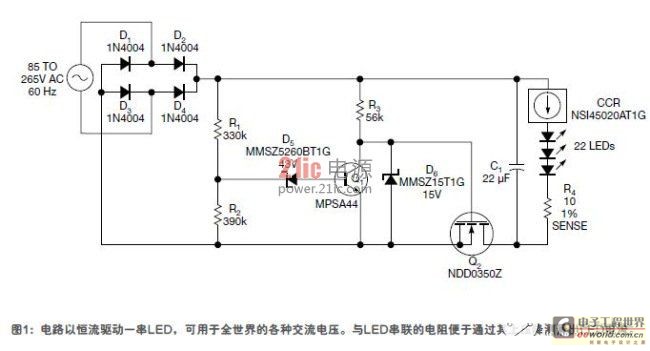
The circuit in Figure 3 is an example of following the above principles, with a power efficiency of about 85%. Regulator IC1 and R5 form a 20mA CCR. The LED string contains enough LEDs to require 120V at 20mA. The voltage across R6 provides an indirect way to measure the LED current.

VTH is the output voltage of the full-wave rectifier bridge. After the voltage divider from R1 to R3, it exceeds the 68V bias voltage of D5, turning Q1 on and Q2 off. When Q2 turns on, C1 quickly charges to VTH and then slowly discharges through the LED string until the next half cycle of the AC line. At the end of C1 discharge, VTH must not fall below the 120V voltage required to maintain LED operation, nor exceed 1.414 times the minimum AC level VRMS. When the LED requires 120V voltage, add the 3V input-output voltage difference required by IC1, plus the 1.25V voltage of R5, so the minimum C1 voltage will be 124.25V. For simplicity, this figure is rounded to 125V.
As shown in Figure 4, in a 10 ms 50 Hz half cycle, C1 discharges much longer than it charges. During this period, the peak-to-peak value across C1 is approximately 20 mA × 10 ms / 22 μF = 9.09 V. Therefore, UC1-MAX = 125 V + 9.09 V = 134.09 V. For simplicity, this value is rounded to 135 V. This value is VTH, and any voltage greater than this value will turn Q1 on and be cut off by Q2.

When Q1 is on, R4 in Figure 3 dissipates less than 20mW at 260VRMS input, while the R1-R2-R3-D5 divider dissipates less than 100mW. This is negligible compared to the 2.4W dissipation of the LED. These resistors are large values, so the power dissipation is low. R3 is used to precisely adjust VTH to match the actual voltage drop across the LED string.
There is a startup current limiter in the circuit to limit the inrush current through C1 and Q2, which occurs in the cycle just before VTH is reached, just when the AC line is applied. The current limiting resistor reduces the efficiency of each cycle, and R9 only limits the power-up surge to 1.35A until C2 is charged enough to turn on Q3.
When the AC input increases, the power consumption of the chopper increases slightly, while the power efficiency decreases slightly, as shown in Table 1.

This improved circuit can work at 96 V ~ 260 Vac (50 Hz). For larger LED currents, it is recommended to increase the capacity of C1 and reduce the resistance of R5. If the LED operating voltage is different, some parameters should be recalculated in the same way as above. The lower the LED operating voltage, the lower the AC input voltage can be. This design example is also applicable to 60Hz AC.
Author's Note:
1. Use a high-current through-hole resistor or several surface-mount resistors in series that can withstand a voltage of at least 400V. Considering the safety issue during a short circuit, it is recommended to use a fuse.
2. Safety warning for beginners: This circuit contains lethal voltages. Be especially careful during testing and use. If possible, use an isolation transformer to suspend the circuit's AC input to the ground, not to the oscilloscope case. The oscilloscope ground is not isolated, so it cannot be connected to the circuit.
3. Do not press the button when AC voltage is applied. To ensure safety during maintenance, press the button to fully discharge C1 through R10 to D8.
Previous article:AC-driven LED lighting technology is becoming mature
Next article:Slow start constant current electronic load for LED power supply aging test
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
-
 100 Examples of Microcontroller C Language Applications (with CD-ROM, 3rd Edition) (Wang Huiliang, Wang Dongfeng, Dong Guanqiang)
100 Examples of Microcontroller C Language Applications (with CD-ROM, 3rd Edition) (Wang Huiliang, Wang Dongfeng, Dong Guanqiang) -
 Computer Vision Applications in Autonomous Vehicles: Methods, Challenges, and Future Directions
Computer Vision Applications in Autonomous Vehicles: Methods, Challenges, and Future Directions -
 Arduino Advanced Development Definitive Guide (Original Book 2nd Edition)
Arduino Advanced Development Definitive Guide (Original Book 2nd Edition) -
 MCU Principles and C51 Programming Tutorial (2nd Edition)
MCU Principles and C51 Programming Tutorial (2nd Edition)
- MathWorks and NXP Collaborate to Launch Model-Based Design Toolbox for Battery Management Systems
- STMicroelectronics' advanced galvanically isolated gate driver STGAP3S provides flexible protection for IGBTs and SiC MOSFETs
- New diaphragm-free solid-state lithium battery technology is launched: the distance between the positive and negative electrodes is less than 0.000001 meters
- [“Source” Observe the Autumn Series] Application and testing of the next generation of semiconductor gallium oxide device photodetectors
- 采用自主设计封装,绝缘电阻显著提高!ROHM开发出更高电压xEV系统的SiC肖特基势垒二极管
- Will GaN replace SiC? PI's disruptive 1700V InnoMux2 is here to demonstrate
- From Isolation to the Third and a Half Generation: Understanding Naxinwei's Gate Driver IC in One Article
- The appeal of 48 V technology: importance, benefits and key factors in system-level applications
- Important breakthrough in recycling of used lithium-ion batteries
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- [Silicon Labs Development Kit Review] + Key test examples and serial port output examples
- Here is a Tai Chi Bagua diagram of the radio frequency industry
- [Chuanglong TL570x-EVM] Example project running
- How to download KEIL DFP package experience sharing
- Detailed explanation of the flash encryption principle and steps of ESP32, ESP32S2, and ESP-C3 series
- After the stm32 serial port is initialized, the microcontroller does not run automatically, most likely because printf is used
- STMicroelectronics Industry Summit 2020 invites you to attend!
- EEWORLD University----[High Precision Laboratory] Motor Drive: Motor Drive Technology
- CircuitPython Creative Works
- Infineon Tmall store birthday promotion: triple gifts are offered, purchase designated products over 200 yuan and get a development board worth 500 yuan for free!

 100 Examples of Microcontroller C Language Applications (with CD-ROM, 3rd Edition) (Wang Huiliang, Wang Dongfeng, Dong Guanqiang)
100 Examples of Microcontroller C Language Applications (with CD-ROM, 3rd Edition) (Wang Huiliang, Wang Dongfeng, Dong Guanqiang) Arduino Advanced Development Definitive Guide (Original Book 2nd Edition)
Arduino Advanced Development Definitive Guide (Original Book 2nd Edition)
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号