TI's LM3466 is a smart linear LED driver for multi-channel LED systems. It can automatically balance the current of each LED channel, easily preset and fine-tune the current between LED strings, with a current accuracy of ±1% at room temperature and ±1.5% over temperature. If a string of LEDs opens, it can maintain a constant output power. The input voltage ranges from 6V to 70V. It is mainly used in street lighting and solid-state lighting systems. This article introduces the main features of the LM3466, block diagram, lighting system application circuit diagram, LM3466 evaluation board reference design circuit diagram, bill of materials, connection diagram and PCB component layout diagram.
LM3466 Smart Linear LED Driver for Multi-Channel LED Systems The LM3466 integrates a linear LED driver for lighting systems which consist of multiple LED strings powered by a constant current power supply. It equalizes the current provided by the supply in a pre-set ratio for each active LED string, where an active string is a fully turned on LED string, regardless of the number of strings connected to the supply or the forward voltage of each LED string. If any LED string opens during operation, the LM3466 automatically equalizes the supply current through all of the remaining active LED strings. As a result, the overall brightness of the lighting system is maintained even if some LED strings open during operation.
The LM3466 lighting system is simple to design owing to a proprietary control scheme. To minimize the component count, the LM3466 integrates a 70V, 1.5A N-channel power MOSFET with a current limit of 2.06A. To add one more LED string to the system, only a single resistor, a capacitor, and a LM3466 are required. Other supervisory features of the LM3466 include under-voltage lock-out, fault reporting, thermal latch off, and thermal shutdown protection.
The LM3466 consists of only linear circuitry so that the EMI of the application circuit is not deteriorated. The LM3466 lighting system is EMI friendly if the constant current power supply used is complied to EMI standards. The LM3466 is available in the PSOP- 8 exposed DAPs package.
LM3466 main features:
■ Easy to design and use for lighting systems consisting of multiple LED strings (support modular design)
■ Automatically equalizes the current of every active LED string, even the forward voltage of each string is different
■ Easy to pre-set and fine-tune current ratio among LED strings (eg color temperature adjustment or CRI enhancement)
■ ±1% current accuracy at room temperature and ±1.5% over temperature
■ Maintains constant output power if some strings open (inactive) by automatically equalizing the current of remaining active LED strings
■ Works with a constant current power supply (ac/dc or dc/ dc), and no communication to/from the constant current power supply is required
■ Operates with minimum voltage overhead to maximize power efficiency
■ Wide input voltage range from 6V to 70V
■ Fault status output
■ Thermal shutdown
■ Integrated 70V 1.5A MOSFET with 2.06A current limit
■ Maximum 70V per LED string, 20 LEDs
■ Linear circuitry does not deteriorate EMI
■ PSOP-8 exposed DAP package
LM3466 application:
■ Street lamps
■ Solid state lighting systems
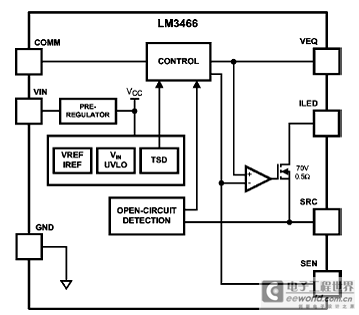
Figure 1. LM3466 block diagram

Figure 2. LM3466 lighting system application circuit
diagramLM3466 demonstration board reference designThis
application note details the design of an LM3466 evaluation board that drives 5 LED strings, each of which consists of 14 LEDs. The input current IS (of the constant current power supply) is 1.75A such that the LED current is 0.35A per string.
The evaluation board schematic, PCB layout, Bill of Materials, and circuit design procedures are shown. Typical performance and operating waveforms are also provided for reference.Figure

3. LM3466 evaluation board circuit diagram
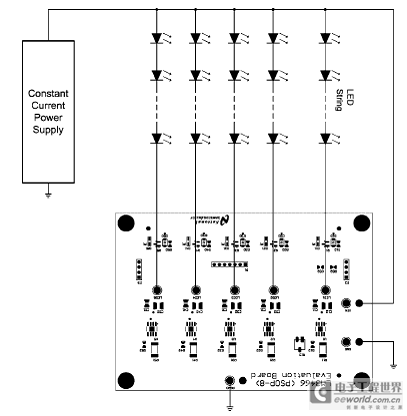
Figure 4. LM3466 evaluation board connection
diagramLM3466 evaluation board bill of materials:


Figure 5. LM3466 evaluation board PCB component layout For
details, please see:
http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/snosb96a/snosb96a.pdf
and
http://www.ti.com/lit/an/snoa566/snoa566.pdf
Keywords:LED Driver
Reference address:TILM3466 multi-channel intelligent LED driver design
LM3466 Smart Linear LED Driver for Multi-Channel LED Systems The LM3466 integrates a linear LED driver for lighting systems which consist of multiple LED strings powered by a constant current power supply. It equalizes the current provided by the supply in a pre-set ratio for each active LED string, where an active string is a fully turned on LED string, regardless of the number of strings connected to the supply or the forward voltage of each LED string. If any LED string opens during operation, the LM3466 automatically equalizes the supply current through all of the remaining active LED strings. As a result, the overall brightness of the lighting system is maintained even if some LED strings open during operation.
The LM3466 lighting system is simple to design owing to a proprietary control scheme. To minimize the component count, the LM3466 integrates a 70V, 1.5A N-channel power MOSFET with a current limit of 2.06A. To add one more LED string to the system, only a single resistor, a capacitor, and a LM3466 are required. Other supervisory features of the LM3466 include under-voltage lock-out, fault reporting, thermal latch off, and thermal shutdown protection.
The LM3466 consists of only linear circuitry so that the EMI of the application circuit is not deteriorated. The LM3466 lighting system is EMI friendly if the constant current power supply used is complied to EMI standards. The LM3466 is available in the PSOP- 8 exposed DAPs package.
LM3466 main features:
■ Easy to design and use for lighting systems consisting of multiple LED strings (support modular design)
■ Automatically equalizes the current of every active LED string, even the forward voltage of each string is different
■ Easy to pre-set and fine-tune current ratio among LED strings (eg color temperature adjustment or CRI enhancement)
■ ±1% current accuracy at room temperature and ±1.5% over temperature
■ Maintains constant output power if some strings open (inactive) by automatically equalizing the current of remaining active LED strings
■ Works with a constant current power supply (ac/dc or dc/ dc), and no communication to/from the constant current power supply is required
■ Operates with minimum voltage overhead to maximize power efficiency
■ Wide input voltage range from 6V to 70V
■ Fault status output
■ Thermal shutdown
■ Integrated 70V 1.5A MOSFET with 2.06A current limit
■ Maximum 70V per LED string, 20 LEDs
■ Linear circuitry does not deteriorate EMI
■ PSOP-8 exposed DAP package
LM3466 application:
■ Street lamps
■ Solid state lighting systems

Figure 1. LM3466 block diagram

Figure 2. LM3466 lighting system application circuit
diagramLM3466 demonstration board reference designThis
application note details the design of an LM3466 evaluation board that drives 5 LED strings, each of which consists of 14 LEDs. The input current IS (of the constant current power supply) is 1.75A such that the LED current is 0.35A per string.
The evaluation board schematic, PCB layout, Bill of Materials, and circuit design procedures are shown. Typical performance and operating waveforms are also provided for reference.Figure

3. LM3466 evaluation board circuit diagram

Figure 4. LM3466 evaluation board connection
diagramLM3466 evaluation board bill of materials:


Figure 5. LM3466 evaluation board PCB component layout For
details, please see:
http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/snosb96a/snosb96a.pdf
and
http://www.ti.com/lit/an/snoa566/snoa566.pdf
Previous article:·Analysis of the selection of LED lighting driver IC
Next article:LED driver power supply must require aluminum electrolytic capacitors?
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 16:51
LED driver solutions for medium voltage general lighting applications

Many medium voltage LED applications are powered by off-line AC-DC power supplies, batteries, or electronic transformers with low voltage AC outputs. But some of these power supplies, such as lead-acid batteries, are only simply regulated. Therefore, there is a need for an LED driver solution that can operate over a
[Power Management]

How to Correctly Select LED Driver Power Supply
Although the stability of LED lights has reached a relatively good level recently, some products have problems with light decay and color drift, mainly due to unreasonable heat dissipation design. Relatively speaking, the problem of LED light drive power supply is much more serious, which is the main reason for dead l
[Power Management]
Backlight driver application design for large-size LED screens

Traditional boost LED driver The traditional LED driver uses a boost circuit, and the simplified circuit form is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 The input voltage VIN of the boost type LED backlight driver is lower than the tube voltage VF of the LED Light Bar. It is boosted through V1, L1, and D1, and the LED const
[Power Management]

Summary of character driver writing (based on mini2440, LED driver)
Programming: what features are needed (mechanisms), how to use them (strategies)
As driver writers, we need to choose an acceptable compromise between the required programming time and the flexibility of the driver. Readers may be surprised to say that the driver is "flexible". We use this word to emphasize
[Microcontroller]
Multi-level LED driver design for efficient dimming

Although the basic LED driver designed for general lighting applications is relatively simple, the design becomes very complex when additional features such as phase cut dimming and power factor correction are required. Non-dimming LED drivers without power factor correction generally include an offline switching po
[Power Management]

Design ideas for LED drivers in different applications

In the past incandescent lamp and energy-saving lamp markets, the mainstream lamp models with limited specifications formed by large companies are difficult for LEDs to continue to comply with. LEDs have their own application flexibility, and will bring more power supply specifications in future designs. 1 Int
[Power Management]

LED drive technology exchange and experience sharing
1.
LED lighting
Driving
Method
1. Netizens asked: In AC-DC conversion, some are non-isolated. Does this circuit have any problems in terms of safety regulations? The structural mode of high-
power
products nowadays is metal shell and aluminum-based circuit board. The shell and circuit boar
[Power Management]
Based on cost-effective RGB LED driving solution

One of the fastest growing areas of LED applications is effect lighting, also known as architectural lighting. Effect lighting can use RGB LEDs, which use three chips, each responsible for generating a color of light (red, green, and blue). Another way to generate different colors of light is to use red, green, and
[Power Management]

- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
-
 Virtualization Technology Practice Guide - High-efficiency and low-cost solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (Wang Chunhai)
Virtualization Technology Practice Guide - High-efficiency and low-cost solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (Wang Chunhai) -
 MCU C language programming and Proteus simulation technology (Xu Aijun)
MCU C language programming and Proteus simulation technology (Xu Aijun) -
 100 Examples of Microcontroller C Language Applications (with CD-ROM, 3rd Edition) (Wang Huiliang, Wang Dongfeng, Dong Guanqiang)
100 Examples of Microcontroller C Language Applications (with CD-ROM, 3rd Edition) (Wang Huiliang, Wang Dongfeng, Dong Guanqiang) -
 Research on three-phase all-solid-state high-efficiency LED tunnel lighting system based on chip drive_Li Jian
Research on three-phase all-solid-state high-efficiency LED tunnel lighting system based on chip drive_Li Jian
Recommended Content
Latest Power Management Articles
- MathWorks and NXP Collaborate to Launch Model-Based Design Toolbox for Battery Management Systems
- STMicroelectronics' advanced galvanically isolated gate driver STGAP3S provides flexible protection for IGBTs and SiC MOSFETs
- New diaphragm-free solid-state lithium battery technology is launched: the distance between the positive and negative electrodes is less than 0.000001 meters
- [“Source” Observe the Autumn Series] Application and testing of the next generation of semiconductor gallium oxide device photodetectors
- 采用自主设计封装,绝缘电阻显著提高!ROHM开发出更高电压xEV系统的SiC肖特基势垒二极管
- Will GaN replace SiC? PI's disruptive 1700V InnoMux2 is here to demonstrate
- From Isolation to the Third and a Half Generation: Understanding Naxinwei's Gate Driver IC in One Article
- The appeal of 48 V technology: importance, benefits and key factors in system-level applications
- Important breakthrough in recycling of used lithium-ion batteries
MoreSelected Circuit Diagrams
MorePopular Articles
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
MoreDaily News
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
Guess you like

 Virtualization Technology Practice Guide - High-efficiency and low-cost solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (Wang Chunhai)
Virtualization Technology Practice Guide - High-efficiency and low-cost solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (Wang Chunhai)
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号