Pointer-type mechanical multimeter, from the perspective of its structure, the meter head is a highly sensitive magnetoelectric microampere DC current meter head. The commonly used magnetoelectric microampere meter head is made based on the principle of the effect of magnetic field on the current-carrying wire, and its structure is shown in the figure below.
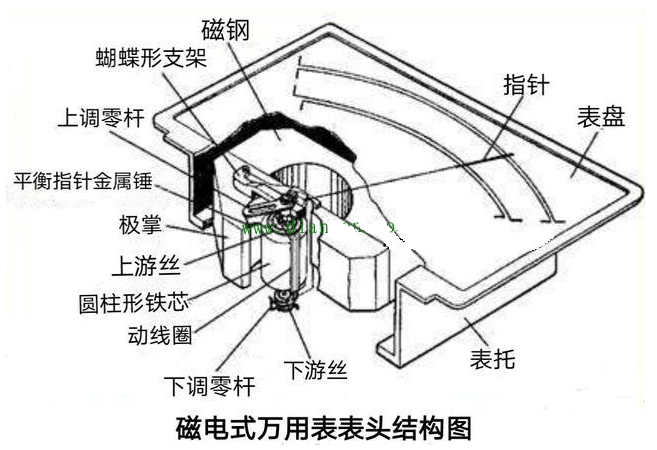
A set of cylindrical iron cores is embedded in the circular magnetic steel. The outside of the cylinder is a movable aluminum frame. The aluminum frame is wound with a coil made of fine enameled wire. There are sharp needles at both ends of the coil, a hairspring and a zero-adjustable rod. Its flexibility determines the sensitivity of the meter head, just like the pendulum needle of a watch. There is a positive pole head and a negative pole head at both ends of the coil. The red line represents the positive pole + and the black line represents the negative pole 1. It is an aluminum frame that can rotate around an axis. Two flat spiral springs and a pointer are installed on the rotating shaft of the aluminum frame. The two ends of the coil are connected to the two spiral springs respectively, and the measured current enters the coil through the spring. There is a pole shoe with a cylindrical inner wall on each pole of the horseshoe magnet. There is a fixed cylindrical iron core in the aluminum frame. The function of the pole shoe and the iron core is to make the magnetic flux lines between them along the radial direction and evenly distributed along the circumference.

When the coil moves in the magnetic field, no matter where it turns, its plane is parallel to the magnetic flux lines. When the current passes through the coil, the two sides of the coil parallel to the axis are affected by the magnetic field force, and the two forces act to make the coil rotate. When the variable meter coil rotates, the spiral spring is twisted, generating a force that hinders the rotation of the coil, and its torque force increases with the increase of the coil rotation angle. When this hindering effect increases to offset the rotation effect of the magnetic field force, the coil stops rotating. According to the principle that like charges repel and opposite charges attract, once the microampere-level coil magnetic field is reversed, the magnetic field it generates will become an opposite magnetic field and act on each other and deflect in the opposite direction. Furthermore, the current force passing through the coil is proportional to the current, so the larger the current in the coil, the greater the rotation effect of the magnetic field force, and the greater the angle of deflection of the coil and the pointer. Therefore, according to the size of the pointer deflection angle, the strength of the measured current can be known. When the direction of the current in the coil changes, the direction of the magnetic field force will also change, and the deflection direction of the pointer will also change. Therefore, according to the deflection direction of the pointer, the direction of the measured current can be known.
There is no reverse bias in AC voltage measurement, but for DC voltage measurement: set a switch of the multimeter to the DC voltage range V of the appropriate range, and connect the "+" probe (red probe) to the high potential, and the "-" probe (black probe) to the low potential, that is, let the current flow into the "+" probe and out of the "-" probe. If the probes are connected in reverse, the pointer of the meter will deflect in the opposite direction, which can easily bend the pointer.

When measuring DC current, set a switch of the multimeter to the appropriate range of 50uA to 500mA. The range selection and reading method of current are the same as those of voltage. When measuring, the circuit must be disconnected first, and then the multimeter is connected in series to the circuit being measured in the direction of the current from "+" to "-", that is, the current flows in from the red test lead and flows out from the black test lead. If the multimeter is mistakenly connected in parallel with the load, the internal resistance of the meter head is very small, which will cause a short circuit and burn the instrument. The reading method is as follows: actual value = indicated value × range/full deviation.
Previous article:Using Keithley's DMM7510 multimeter to reduce power consumption of smart devices
Next article:How to use a multimeter to distinguish between PNP sensors and NPN sensors
- Keysight Technologies Helps Samsung Electronics Successfully Validate FiRa® 2.0 Safe Distance Measurement Test Case
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- Seizing the Opportunities in the Chinese Application Market: NI's Challenges and Answers
- Tektronix Launches Breakthrough Power Measurement Tools to Accelerate Innovation as Global Electrification Accelerates
- Not all oscilloscopes are created equal: Why ADCs and low noise floor matter
- Enable TekHSI high-speed interface function to accelerate the remote transmission of waveform data
- How to measure the quality of soft start thyristor
- How to use a multimeter to judge whether a soft starter is good or bad
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of non-contact temperature sensors?
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- Rambus Launches Industry's First HBM 4 Controller IP: What Are the Technical Details Behind It?
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- Award-winning live broadcast: Hidden costs of isolation system design
- UA level constant current source output chip
- Issues with changing MAC when batch flashing blueNRG-1 with BlueNRG-X Flasher Utility
- EEWORLD University Hall ---- Lao Wu's MCU Practice_NO.1 Project Practice
- [NXP Rapid IoT Review] + Rapid IoT Studio online IDE
- I'm studying BQ76940 recently and want to develop a BMS. I've been looking for information and encountered some questions during the process.
- [Sipeed LicheeRV 86 Panel Review] 4. Building a cross-compilation environment
- [Speech and vision module based on ESP32S3] Software development progress - ESP32S3 JPEG encoding performance test
- 【GD32E231 DIY Contest】4. Achieve 60-second timing
- 【DIY Creative LED V2】V2 version

 零起步巧学巧用万用表 (楊清德 & 胡萍 主編)
零起步巧学巧用万用表 (楊清德 & 胡萍 主編)
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号