How to use the GPS module of STM32F103C8 to obtain location coordinates
Source: InternetPublisher:奥特man123 Keywords: Microcontroller GPS module LCD display STM32 Updated: 2024/12/27
GPS stands for Global Positioning System and is used to detect the latitude and longitude of any location on Earth with precise UTC time (Coordinated Universal Time). The device receives coordinates from satellites every second, including time and date. GPS provides high accuracy and also provides other data in addition to location coordinates.
We all know that GPS is a very useful device that is very commonly used in mobile phones and other portable devices to track location. It has very wide applications in various fields, from calling a taxi at home to tracking the altitude of an airplane.
In this tutorial, we will interface GPS module with STM32F103C8 microcontroller to find the location coordinates and display it on 16x2 LCD display.
Required Components
STM32F103C8 microcontroller
GPS Module
16x2 LCD display
Breadboard
Connect the wires
GPS Module
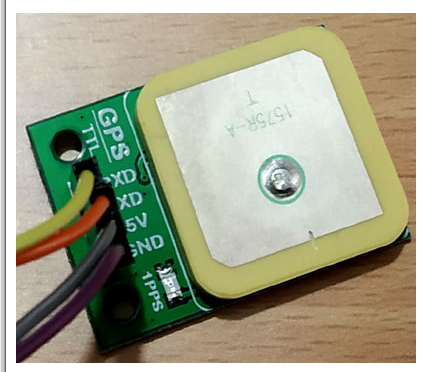
This is a GY-NEO6MV2 XM37-1612 GPS module. This GPS module has four pins +5V, GND, TXD and RXD. It uses serial pins for communication and can be easily connected with the serial port of STM32F103C8.
The GPS module sends data in NMEA format (see the screenshot below). The NMEA format consists of several sentences, of which we only need one. This sentence starts with $GPGGA and contains coordinates, time, and other useful information. This GPGGA is called Global Positioning System Fix Data.
The following is a sample $GPGGA string and its description:
$GPGGA,104534.000,7791.0381,N,06727.4434,E,1,08,0.9,510.4,M,43.9,M,,*47
$GPGGA, HHMMSS.SSS, latitude, N, longitude, E, FQ, NOS, HDP, altitude, M, height, M, , checksum data
But in this tutorial, we use a TinyGPSPlus GPS library which extracts all the needed information from the NMEA sentences and we only need to write one simple line of code to get the latitude and longitude as we will see later in this tutorial.
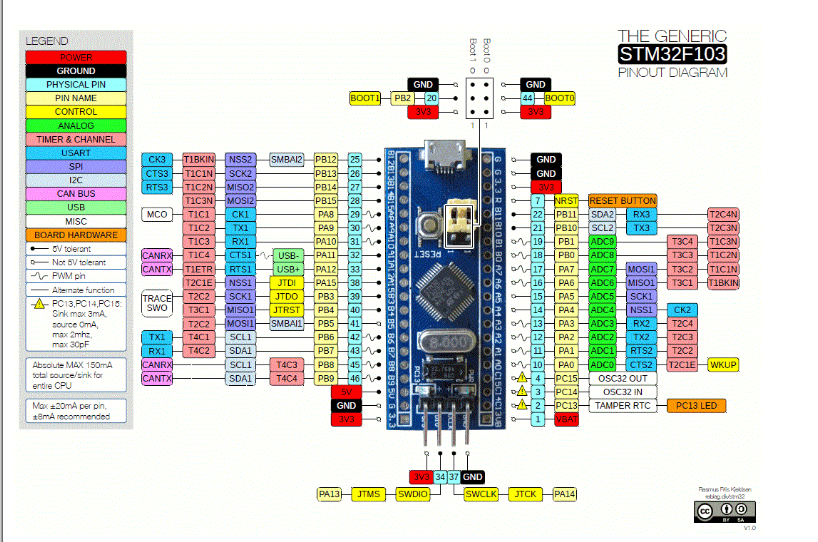
STM32F103C8 pinout
The STM32F103C8 (BLUE PILL) USART serial communication ports are shown in the figure below. These are the blue ones (PA9-TX1, PA10-RX1, PA2-TX2, PA3-RX2, PB10-TX3, PB11-RX3). It has three such communication channels.
Circuit Diagram and Connections
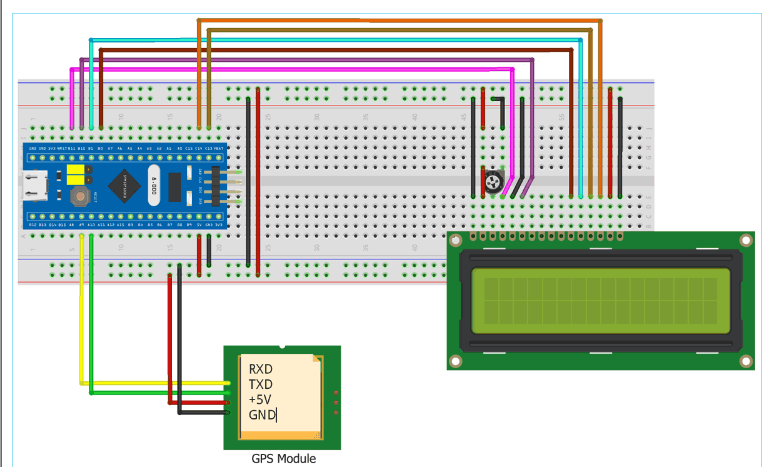
Circuit connection between GPS module and STM32F103C8

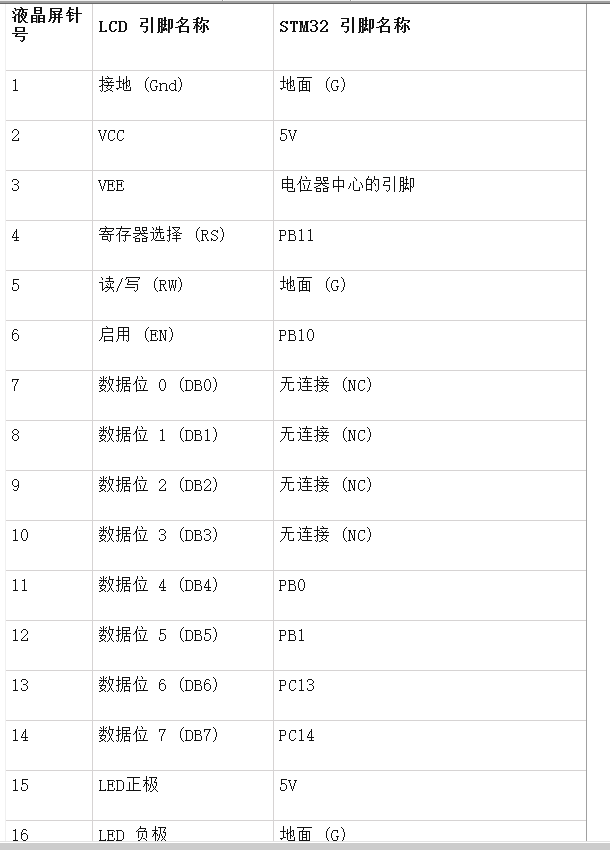
Connection between 16x2 LCD and STM32F103C8
The whole setup looks like this:
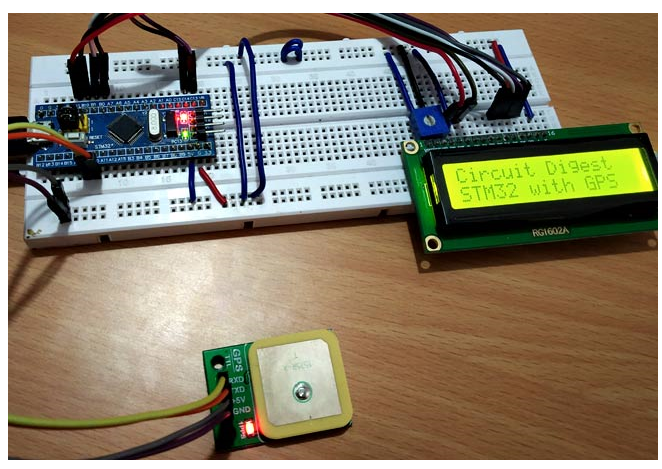
Programming STM32F103C8 for GPS module interface
The complete program to find the location using GPS module using STM32 is given at the end of this project. STM32F103C8 can be programmed using Arduino IDE by simply connecting it to the PC via USB port. Make sure to remove the pins TX and RX while uploading the code and connect them after uploading.
To interface GPS with STM32, first we have to download a library from GitHub link TinyGPSPlus. After downloading the library, it can be included in Arduino IDE through Sketch -> Include Library -> Add .zip Library. The same library can be used to interface GPS with Arduino.
So first include the necessary library files and define the pins for the 16x2 LCD:
#include
Then create a gps object called TinyGPSPlus class.
TinyGPSPlus Global Positioning System;
Next, in void setup, use Serial1.begin(9600) to start serial communication with the GPS module. Serial1 is used as the Serial 1 port (Pins-PA9, PA10) of the STM32F103C8.
Serial1.start(9600);
Then the welcome message is displayed for a while.
lcd.start(16,2);
lcd.print("Circuit Abstract");
lcd.setCursNext in void loop(), we receive the latitude and longitude from GPS and check if the received data is valid and display the information in the serial monitor and LCD.
Check if the available location data is valid
loc_valid = gps.location.isValid();
Receiving latitude data
lat_val = gps.location.lat();
Receiving longitude data
lng_val = gps.location.lng();
If invalid data is received, the serial monitor displays "*****" and the LCD displays "Waiting".
if (!loc_valid)
{
lcd.print("WIf valid data is received, the latitude and longitude will be displayed on the serial monitor as well as on the LCD display.
lcd.clear();
Serial.println("GPS reading: ");
Serial.print("Latitude: ");
Serial.println(lat_val, 6);
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Latitude:");
lcd.print(lat_val,6);
Serial.print("Longitude: ");
Serial.println(lng_val, 6);
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Length: ");
lcd.print(lng_val,6);
delay(4000);The following function provides a delay in reading data. It keeps looking for data on the serial port.
static void GPSDelay(unsigned long ms)
{
unsigned long start = millis();
do
{
while (Serial1.available())
gps.encode(Serial1.read());
} while (millis() - start < ms);
}Finding Latitude and Longitude using GPS and STM32
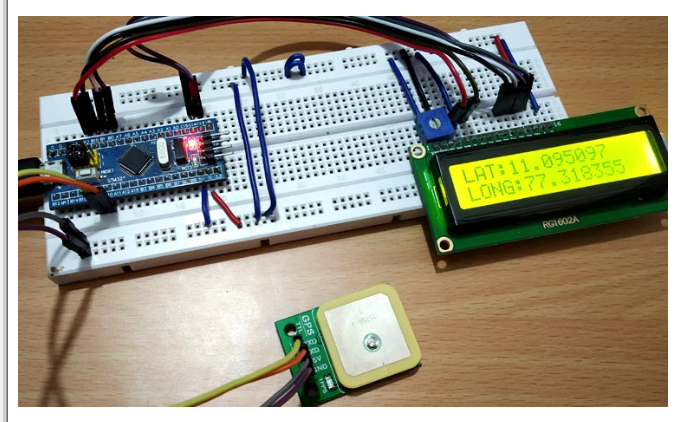
After building the setup and uploading the code, make sure to place the GPS module in an open area to receive the signal quickly. Sometimes it takes a few minutes to receive the signal, so wait for a while. When the GPS module starts receiving the signal, the LED will start blinking and the location coordinates will be displayed on the LCD display.
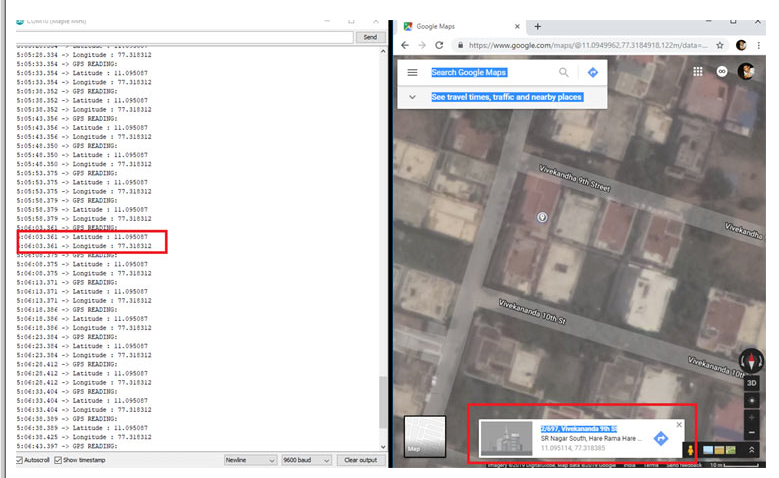
You can verify the latitude and longitude of the location using Google Maps. Just turn on GPS Go to Google Maps and click on the blue dot. It will show the address with the latitude and longitude as shown in the image below
#include
- How to Make a PIC Programmer
- Schematic diagram of MCU SPI interface circuit
- Phase-locked loop controller using AT89S51 microcontroller
- Computer USB port to mobile phone interface conversion circuit
- How to Implement a Bipolar LED Driver Circuit Using 8051 Microcontroller
- Using 89C2051 to make a four-way digital display water level controller circuit
- Use PC’s RS232 port to control LED lights
- Circuit diagram: 8051
- Circuit diagram: AT88RF
- Communication conversion circuit diagram of RS232 and RS485
- Cypress CYW20719 SoC supports Bluetooth mesh networking, did you know?
- Renesas Synergy™ low-power S1JA microcontroller, did you know?
- STM32 system chip worth knowing about
- Circuit design and structure of universal card reader based on NFC
- Circuit connection diagram between TC35I and microcontroller
- USB communication circuit
- Intelligent hydrological monitoring system module
- Circuit connection diagram between TC35I and microcontroller
- KTY87 temperature sensor microcontroller interface circuit
- RS232 transmission circuit between PC serial port and MC68HC70-5K1 microcontroller







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号