1. Reciprocating motion of the trolley
Use S7-200 to realize the automatic control of the trolley's reciprocating movement. The control process is to press the start button, and the trolley moves from the left to the right (right to the left). When it moves to the right (left) and touches the right (left) travel switch, the trolley automatically returns, and when it touches the travel switch on the other side, it returns again. This reciprocating movement continues until the stop button is pressed and the trolley stops moving.
▲ Electrical Wiring diagram
I/O Allocation Table
Ladder diagram program
PLC Wiring Diagram
Program debugging and result analysis
▲Control platform operation panel
When SB2, that is, i0.0, is pressed (mouse click i0.0f), Q0.0 is turned on, and the car moves to the right (indicator light Q0.0 is on). When the car runs and hits the right limit switch SQ2, that is, i0.4 (click i0.4f with the mouse to simulate SQ2 being pressed down), the car moves to the left (indicator light Q0.0 is off, and indicator light Q0.1 is on). When it runs to the left and hits the left limit switch SQ1, that is, i0.3 (mouse click i0.3f), the car moves to the right again (indicator light Q0.1 is off, and indicator light Q0.0 is on). The car moves back and forth like this until SB1, that is, i0.2, is pressed (mouse click i0.2f), and the car stops.
Attachment:
2. Flash Photoelectric Road
When the start button is pressed, the light is required to be on for one second and off for one second within two seconds, and repeat this process, with the light flashing.
I/O Allocation Table
Ladder diagram program
PLC Wiring Diagram
Program debugging and result analysis
Download the written program to Siemens s7-200PLC for debugging. Observe whether the running results are the same as the experimental requirements. Debug through the online control panel. When I0.0f on the online control panel is pressed (i.e. I0.0 is turned on), Q0.0 has output, and the load light connected to Q0.0 is on. At the same time, start timer T37 to start timing. After one second of timing, T37 is activated and its normally closed contact is disconnected, so Q0.0 has no output and the connected load light is off. When the light is off, start timer T38. After T38 counts for one second, the normally closed contact in series with timer T37 is disconnected, so T37 is reset and the normally closed contact of T37 is restored to normally closed. At this time, Q0.0 has output again, and the connected load light is on again. In this way, the load light connected to output Q0.0 keeps flashing at a frequency of one second on and one second off until I0.1f on the online control panel is pressed (i.e. I0.1 is turned on), and the flash circuit no longer continues to work. If you want to change the frequency of the light flashing, just change the time of the timer to achieve the change requirement.
3. Star-delta step-down starting
The Siemens S7-200 PLC is used to realize the star-delta connection step-down starting.
Circuit diagram and control diagram of star-delta step-down starting
The process framework diagram is as follows
I/O Allocation Table
Ladder diagram program
PLC Wiring Diagram
Program debugging and result analysis
Download the written program to the PLC of Siemens S7-200 for debugging. After downloading, we open the online control panel for debugging to see if the running results meet the requirements. First, set i0.2f on the control panel to a button and press it, that is, i0.2 is turned on, indicating that the circuit breaker QF is closed. Press the start button i0.0f (SB2), that is, i0.0 is turned on. At this time, the motor starts in star shape, Q0.0 and Q0.1 have outputs. The experimental wiring diagram shows that the two lights L1 and L2 are both on and drive the time counter at the same time. When the timer counts to 10S, it switches to delta start. At this time, Q0.1 has no output, Q0.2 has output, then Q0.0 and Q0.2 have output, and the motor runs in triangle star. L1 and L3 lights on the wiring panel are on. After pressing i0.1f on the online panel (i0.1 is turned on), the motor stops running. All output points have no output.
4. Color Light Control
Use the eight output terminals Q0.0 to Q0.7 of the PLC to control eight colored lights, so that one lights up every second and cycles. When I0.0 is turned on, all lights go out. When I0.1 is turned on, the cycle starts again from Q0.0.
I/O Allocation Table
Ladder diagram program
PLC Wiring Diagram
Program debugging and result analysis
Download the written program to the PLC for debugging. After downloading, we open the online control panel for debugging to see if the running results meet the requirements.
As soon as the PLC is powered on, sm0.0 remains connected. So t37 performs delay timing, and after the delay is up, t38 timing is started. After t38 timing is up, the normally closed contact of t38 is disconnected, so t37 timing is disconnected. The normally open contact of t37 returns to normally open, so t38 timing is also disconnected. At this time, the normally closed contact of t38 returns to normally closed, so t37 starts timing again, and counter C0 starts counting once. This counting is repeated. When the count is 1, Q0.0 is connected. When the counter counts to 2, Q0.1 is connected... and so on. When the counter counts to 8, Q0.7 is connected. When the counter counts to 9, counter C0 is cleared. When I0.0f (i.e. I0.0) on the online control panel is pressed to turn it on, the counter, and Q0.0~Q0.7 are all cleared, that is, no light is on. When I0.1f on the online control panel is pressed (i.e. I0.1 is turned on), the counter starts counting again, and the lights start lighting up one by one from Q0.0.
5. Comparison Instructions
Record the goods in and out of the warehouse. The warehouse can hold up to 6,000 cartons of goods. If there are more than 1,000 cartons, light L1 will be on, and if there are more than 5,000 cartons, light L2 will be on.
I/O Allocation Table
Ladder diagram program
PLC Wiring Diagram
Program debugging and result analysis
Download the program to the S7-200 PLC for debugging. Before downloading, we first reduce the numbers in the program so that we can see the experimental results better and faster in the experiment. We set the light of L1 to 5. We set the light of L2 to 10. In this way, we can see the experimental results faster.
When I0.0f on the online control panel is pressed, I0.0 is connected, indicating that there are goods entering. When we click I0.0f on the online control panel five times, the count value in the timer is 5 (that is, there are already 1000 boxes of goods in the warehouse), then the light L1 will be on, that is, Q0.0 has output. When I0.0f is clicked ten times, the count value of the counter is 10 (that is, there are 5000 items in the warehouse), and the light L2 is also on, that is, Q0.1 has output. When I0.0f on the online control panel is clicked, the count value in the counter continues to increase. When I0.1f is pressed on the online control panel, the counter starts to decrease. Click once, and the count value in the counter decreases once. When the value in the counter is less than 10, it means that there are less than 5000 boxes of goods in the warehouse, and the light L2 is off (that is, Q0.1 has no output). When I0.1f is clicked, the count value in the counter continues to decrease, and when it decreases to less than 5 times. Indicates that there are less than 1000 items in the warehouse, and the light L1 is off. Q0.0 has no output. When I0.2f on the online control panel is pressed, the counter is reset. L1 and L2 are not lit (that is, Q0. and Q0.1 have no output).
6. 8 color lights shift control
Use IO wires to control the cyclic shift of the eight colored lights connected to Q0.0 to Q0.7. Use t37 timing to shift one position every 0.5S. Set the initial value of Q0.0 to Q0.7 during the first scan, so that Q0.0 and Q0.2 have output first. Use I0.1 to control the direction of the colored lights' displacement.
I/O Allocation Table
Ladder diagram programming
PLC Wiring Diagram
Program debugging and result analysis
Download the program to the Siemens S7-200 PLC for debugging. Once the PLC is powered on, Q0.0 and Q0.2 will have outputs, and Q0.0 and Q0.2 will light up. When the I 0.0f (indicates that I0.0 has input) setting switch on the online panel is pressed, timer T37 starts timing, and the colored lights shift to the right based on Q0.0 and Q0.2 every 0.5 seconds. When I0.1f (indicates that I0.1 has input) on the online control panel is pressed to set it, the colored lights move to the left in the same way.
7. Jump Instructions
Use the jump instruction to control the two lights L1 and L2, connect them to Q0.0 and Q0.1 respectively, switch position I0.0, and the control switch positions of the two lights are I0.1 and I0.2. When manually, use the control switches of the two lights to control them respectively. When automatically, the two lights light up alternately every one second.
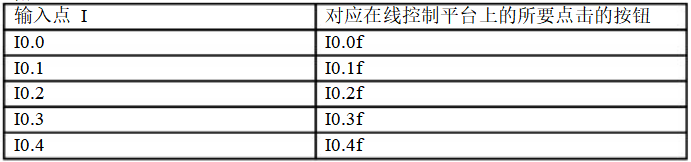
I/O Allocation Table
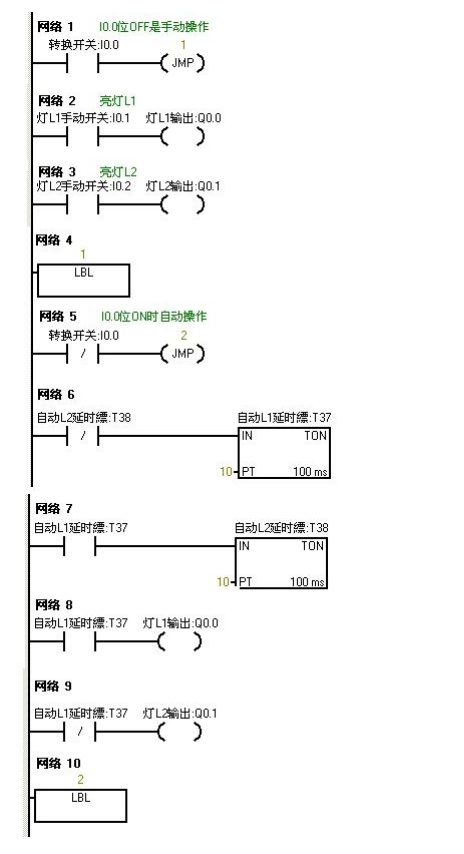
Ladder Diagram Programming
Program debugging and result analysis
Download the written program to the PLC of s7-200 for debugging. When I0.0 is OF, the PLC runs the manual program. Pressing the set buttons I0.1f and I0.2f on the online control panel means (I 0.1 and I0.2 are closed) the lights L1 and L2 are on, and Q0.0 and Q0.1 have outputs. When we press I0.0f on the online control panel, I0.0 is ON at this time, and the program jumps to the automatic program operation. The two lights cycle every second. L1 lights up for one second and then L2 lights up. When I0.0f on the online control panel is pressed, I0.0 is OFF at this time, and the program jumps to the manual program operation.
Previous article:What is inductive? What is non-inductive? The difference between inductive and non-inductive brushless DC motors
Next article:A brief analysis of the key points of YTM32's DMA controller
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 09:43






- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Sharing a carefully adjusted hysteresis comparator
- The simulation result of LC parallel resonance frequency is inconsistent with the calculation. Is it because the component model is not selected correctly?
- Using Bluetooth module for fast IoT circuit design
- Using the Ginkgo USB-I2C adapter and the BMP180/BMP085 sensor to implement an atmospheric pressure detector
- High-speed plate actual application case
- What is the difference between TMS320C6416 and TMS320C6416T?
- Disassembling the x990
- Greenhouse automatic spraying system ---- H743 water lamp
- Design of wireless serial port hub using ARM microprocessor and ZigBee module
- [TI recommended course] #Live replay: TI mmWave millimeter wave radar application in automobiles#




























 Siemens PLC Programming Technology and Application Cases (Edited by Liu Zhenquan, Wang Hanzhi, Yang Kun, etc.)
Siemens PLC Programming Technology and Application Cases (Edited by Liu Zhenquan, Wang Hanzhi, Yang Kun, etc.)
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号