Advanced Driver Assistant System (ADAS) is an active safety technology that uses various sensors installed on the car to collect environmental data inside and outside the car at the first time, and perform technical processing such as identification, detection and tracking of static and dynamic objects, so that the driver can be aware of possible dangers as quickly as possible to attract attention and improve safety.
Automobile sensors are equipped for different purposes and can be divided into two categories: traditional micro-electromechanical sensors (MEMS) that improve the level of informationization of individual vehicles and smart sensors that support autonomous driving. MEMS is the "neuron" of the car, providing feedback during the control of various systems in the car to achieve automatic control. Smart sensors, on the other hand, collect information directly from the outside world and are the "eyes" of autonomous vehicles.
Sensors are the foundation of automotive intelligence
Sensors are the information source of automotive electronic control systems and are the basic key components of vehicle electronic control systems. Sensors are usually composed of sensitive elements, conversion elements and conversion circuits. The sensitive element refers to the part of the sensor that can directly sense or respond to the measured value, the conversion element converts the above non-electrical quantity into an electrical parameter, and the function of the conversion circuit is to process and convert the electrical signal output by the conversion element into a part that is easy to process, display, record and control. Based on the different purposes of current automotive sensor equipment, they can be divided into two categories: traditional micro-electromechanical sensors that improve the level of informationization of single vehicles and intelligent sensors that provide support for unmanned driving.
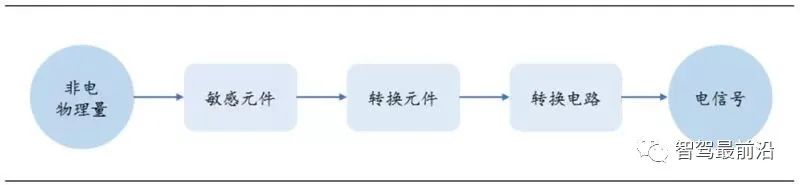
The composition of automotive sensors
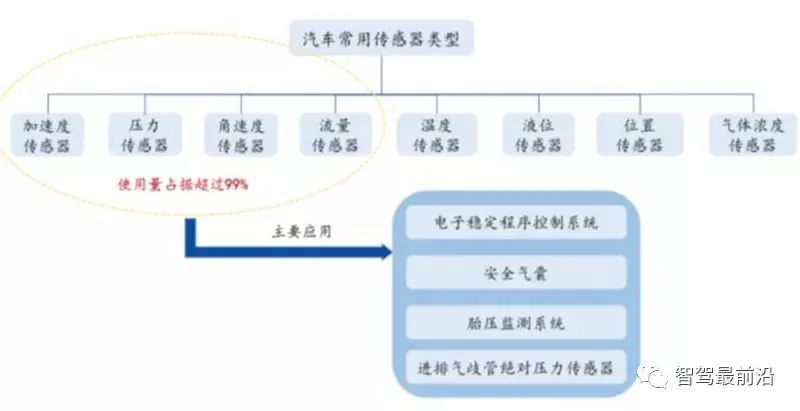
Traditional sensors: Each system control process relies on sensors to provide information feedback and realize automatic control. They are the "neurons" of the car. Traditional automotive sensors can be divided into eight categories according to their functions, including pressure sensors, position sensors, temperature sensors, acceleration sensors, angular velocity sensors, flow sensors, gas concentration sensors, and liquid level sensors. Automotive sensors are mainly used in powertrain systems, body control systems, and chassis systems. Automotive sensors are responsible for the collection and transmission of information in these systems. The information they collect is processed by the electronic control unit to form instructions to the actuator to complete electronic control.

Traditional sensor classification Smart sensors: Smart sensors are the "eyes" of driverless vehicles. Cars are rapidly evolving into secure, networked autonomous driving robots that perceive the environment, make planning decisions, and ultimately arrive at their destinations safely. Currently, the mainstream sensor products used for environmental perception mainly include four categories: lidar, millimeter-wave radar, ultrasonic radar, and cameras.
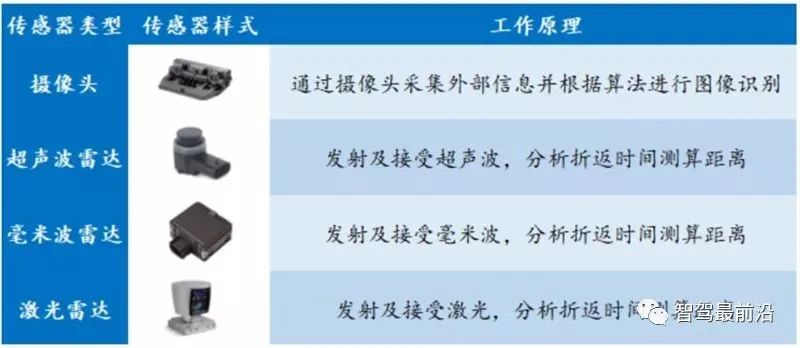
Smart sensor classification
MEMS Sensors: Automotive Micro-Senses
MEMS sensors are developed on the basis of semiconductor manufacturing technology and are new sensors manufactured using microelectronics and micromachining technology. MEMS sensors are widely used in systems such as electronic body stability program (ESP), anti-lock braking system (ABS), electronically controlled suspension (ECS), and tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS). Among them, pressure sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and flow sensors are the most commonly used MEMS sensors in automobiles, accounting for 99% of automotive MEMS systems.
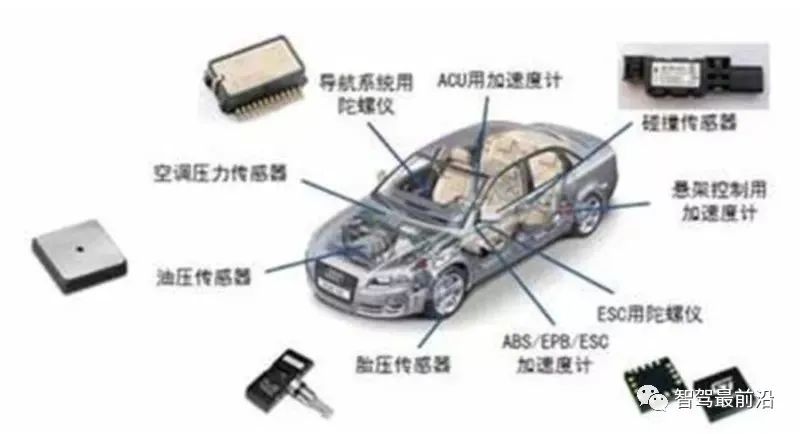
MEMS has a wide range of applications
The value of MEMS sensors is relatively concentrated. MEMS has obvious advantages and is one of the main choices for building sensors in the perception layer of the Internet of Things in the future. Its advantages are mainly reflected in: 1) miniaturization, 2) silicon-based processing technology, 3) mass production, and 4) integration. 1) Miniaturization: MEMS devices are small in size, with single dimensions measured in millimeters or even microns, light in weight, and low in energy consumption. The higher surface-to-volume ratio (surface area to volume) of MEMS can improve the sensitivity of surface sensors. 2) Mass production: Taking a single 5mm5mm MEMS sensor as an example, about 1,000 MEMS chips can be cut out simultaneously on an 8-inch silicon wafer using silicon micromachining technology. Mass production can greatly reduce the production cost of a single MEMS. 3) Integration: Generally speaking, a single MEMS often integrates an ASIC chip while packaging a mechanical sensor to control the MEMS chip and convert analog quantities into digital outputs.
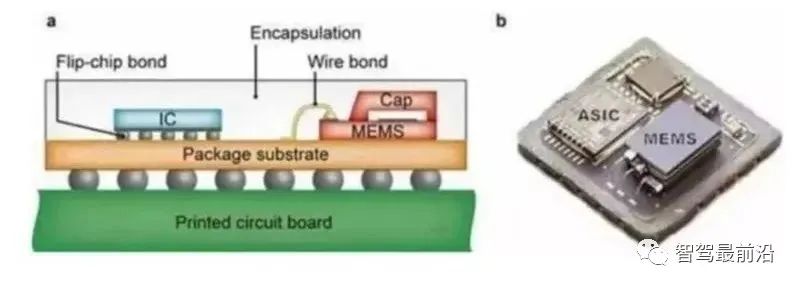
MEMS and ASIC chip integrated packaging

MEMS can be mass-produced to reduce manufacturing costs. Foreign manufacturers monopolize the MEMS sensor market, and the market concentration is high. According to HIS Automotive statistics, the top three global MEMS suppliers (Bosch, Sensata, and NXP) accounted for 57% of the market share in 2017, among which Bosch took the lead with a market share of 33.62% in 2017, Sensata's market share reached 12.34%, and NXP's market share reached 11.91%. Denso (8.94%), Analog Devices (8.51%), Panasonic (7.45%), Infineon (7.23%) and other manufacturers also have a certain share. Foreign manufacturers have a wide product line, leading technology, many customers, and form a high entry barrier. The difficulty of MEMS sensor research and development and the complexity of its manufacturing process are the main reasons for the formation of industry barriers. Foreign manufacturers such as Invensense and Infineon have 2 to 3 product lines, while Bosch, Denso, STMicroelectronics and other MEMS product lines exceed 4.
In contrast, it is difficult for small suppliers to achieve mass production in a short period of time, so the market share of large suppliers ranked at the top is relatively stable, and the market concentration is relatively high. The assembly volume and value of MEMS sensors are proportional to the price of the models they are installed on. At present, each car contains an average of 24 MEMS sensors, while high-end cars use about 25-40 MEMS sensors. For example, BMW high-end models can use 20-40 sensors in the engine alone, while entry-level models only have about 5. The value of commonly used MEMS sensors installed on a single vehicle ranges from 2,000 to 20,000 yuan; joint venture cars are usually not less than 4,000 yuan, while independent brands are only about 2,000 yuan, and high-end models are about 10,000-20,000 yuan. It is estimated that the MEMS sensor market size will reach 42.013 billion yuan by 2019; with the improvement of intelligence and electrification, the market size will reach 44.621 billion yuan and 47.227 billion yuan in 2020 and 2021 respectively, with a compound growth rate of 6.5% from 2015 to 2021.
Smart Sensors: Core of Autonomous Driving Millimeter-wave Radar: Core Sensor of ADAS System
Millimeter wave radar refers to the use of millimeter waves with a wavelength of 1-10nm and a frequency of 30GHZ-300GHZ to calculate the distance by measuring the time difference of the echo. Millimeter wave radar was first used in the military field, and with the improvement of technology, it has gradually been used in the automotive field. The advantages of millimeter wave radar are mainly the following three aspects: 1) stable detection performance, long range, and good environmental applicability. 2) Compared with ultrasonic radar, it has the characteristics of small size, light weight and high spatial resolution. 3) Compared with optical sensors, millimeter wave radar has a strong ability to penetrate fog, smoke, and dust, and has the characteristics of all-weather and all-day. However, there are also shortcomings such as high cost and difficulty in identifying pedestrians.
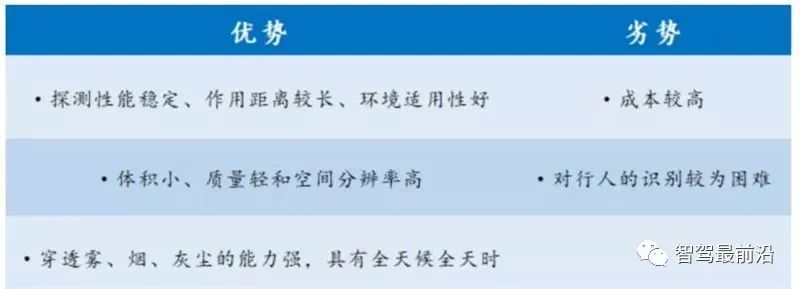
Advantages and disadvantages of millimeter-wave radar 77 GHz has advantages in both performance and size. At present, the frequencies of vehicle-mounted radars are mainly divided into 24GHZ band and 77GHZ band. Compared with 24GHz millimeter-wave radar, 77GHz has higher distance resolution and is one-third smaller in size. In 2018, China New Car Assessment Program (C-NCAP) included the automatic emergency braking system (AEBS) in the scoring system, which will drive the market demand for 77GHz millimeter-wave radar in the future. In the long run, 77GHz millimeter-wave radar is smaller in size and has a longer detection range, which makes it have a larger market space than 24GHz millimeter-wave radar.

Comparison of 24GHz and 77GHz millimeter-wave radars 24GHz and 77GHz millimeter-wave radars are both capable of long- and short-range detection for ADAS. Millimeter-wave radars are widely used in ADAS systems because of their small hardware size and are not affected by bad weather. 24GHz is currently widely used in blind spot monitoring and lane change assistance for automobiles. The radar is installed in the rear bumper of the vehicle to monitor whether there are vehicles in the lanes on both sides of the rear of the vehicle and whether lane changes can be made. The 77GHz radar is superior to the 24GHz radar in detection accuracy and distance. It is mainly used to be installed on the front bumper of the vehicle to detect the distance to the vehicle in front and the speed of the vehicle in front. It mainly realizes active safety functions such as emergency braking and automatic following. To fully realize the various functions of ADAS, it generally requires "1 long + 4 medium and short" 5 millimeter-wave radars. The Audi A8 is equipped with 5 millimeter-wave radars (1LRR+4MRR), and the Mercedes-Benz S-Class is equipped with 6 millimeter-wave radars (1LRR+6SRR). Currently, the unit price of a 77GHz millimeter-wave radar system is around 1,000 yuan, and the unit price of a 24GHz millimeter-wave radar is around 500 yuan.
Previous article:Application Solution of Automotive Electronics CAN Bus Distributed Control System
Next article:Automobile engine ECU principle and common problems in modifying ECU
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
-
 A review of deep learning applications in traffic safety analysis
A review of deep learning applications in traffic safety analysis -
 Dual Radar: A Dual 4D Radar Multimodal Dataset for Autonomous Driving
Dual Radar: A Dual 4D Radar Multimodal Dataset for Autonomous Driving -
 A review of learning-based camera and lidar simulation methods for autonomous driving systems
A review of learning-based camera and lidar simulation methods for autonomous driving systems -
 Multimodal perception parameterized decision making for autonomous driving
Multimodal perception parameterized decision making for autonomous driving
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Today at 10:00 am TI Award Live: Low-power wireless technology for building automation sensor applications
- For SMD components with thin pins, what should be the PCB wiring line width?
- EEWORLD University Hall----Live Replay: TI Sitara? Latest AM64X Platform Introduction
- [Project source code] FPGA-based digital tube font, used to display numbers on the LCD screen
- TMS320F28335 startup process
- Antenna transmission line standing wave conversion conjugate matching
- Getting Started with the ST SensorTile.box Sensor Kit (5) Bluetooth Connection
- Tektronix Live: Senior engineers chat with you about oscilloscopes, and orders are free!
- 【STM32WB55 Review】_01_First Look
- tms320f28335



 A review of deep learning applications in traffic safety analysis
A review of deep learning applications in traffic safety analysis











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号