Features of explosion-proof motors
(1) It meets the requirements of increased safety explosion-proof motors and adopts a series of reliable measures to prevent sparks, arcs and dangerous high temperatures, so it can operate safely in explosion-hazardous areas in Zone 2.
(2) Brushless excitation is adopted, and a rotating rectifier disk and a static excitation cabinet are set up. The excitation control system is reliable; the forward polarity differential excitation is accurate and shock-free; the excitation system has reliable out-of-step protection and strong re-stepping capability; the line design is reasonable, and the discharge resistor does not heat up during operation; and the excitation current adjustment range is wide.
(3) The synchronous machine, AC exciter and rotating rectifier are coaxial. The rectifier is located between the main motor and the exciter, or outside the bearing seat.
(4) The enclosure protection grade is IP54.
(5) Use F-class insulation and assess the temperature rise according to B-class insulation.
(6) Change the traditional bottom water cooling to top water cooling, that is, the water cooler is placed on the top of the motor.
(7) An increased safety moisture-proof heater is installed and fixed in the cover at the bottom of the motor to provide heating and moisture-proofing when the motor is shut down.
(8) Select high-quality raw materials and leave a large margin in electrical and mechanical calculations to meet the operating reliability and temperature requirements of increased safety motors.
(9) Complete monitoring measures are provided; an increased safety self-balancing current transformer for differential protection is installed in the main junction box; working and spare platinum thermal resistors with a graduation number of Pt100 are buried in the stator winding; a water leakage monitor is installed to monitor the leakage of the water cooler; and the two end seat sliding bearings are respectively provided with on-site temperature display instruments and remote signal terminals.
Structural features of explosion-proof motors
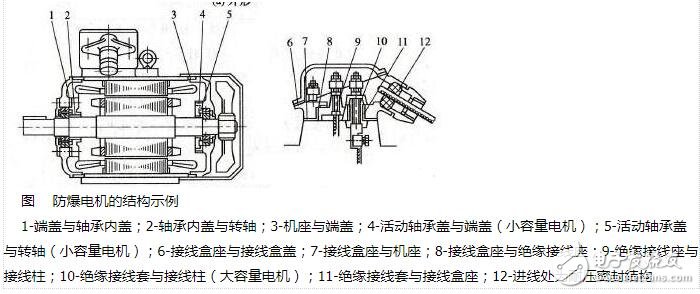
Compared with ordinary motors, the structural characteristics of explosion-proof motors are mainly that the contact surfaces between the base and the end cover, junction box, and the junction box bottom and cover are all set as explosion-proof surfaces. There is no substantial difference between the explosion-proof surface and the mating surface of ordinary motors. It is just that the mating area is increased (such as longer stop) and the mating accuracy is enhanced to meet higher sealing requirements. Measures such as applying sealant and adding rubber sealing pads are adopted in this part; in addition, its junction box and the inside of the casing must also be strictly isolated, which is not paid much attention to by ordinary motors. In order to prevent the casing from being blown open by the pressure generated by the "explosion" inside the motor, the materials used for the base, end cover, junction box, etc. must be high in strength and large in thickness. In addition, these components must be subjected to pressure resistance tests (generally water pressure resistance tests) and can only be assembled and used after passing the test.
Classification of explosion-proof motors
1. According to the motor principle
It can be divided into explosion-proof asynchronous motors, explosion-proof synchronous motors and explosion-proof DC motors.
2. By place of use
It can be divided into explosion-proof motors for underground coal mines and explosion-proof motors for factories.
3. According to explosion-proof principle
It can be divided into flameproof motors, increased safety motors, positive pressure motors, spark-free motors and dust explosion-proof motors.
4. Classification by supporting equipment
It can be divided into explosion-proof motors for coal mine conveyors, explosion-proof motors for coal mine winches, explosion-proof motors for rock loaders, explosion-proof motors for local fans in coal mines, explosion-proof motors for valves, loud explosion-proof motors for fans, explosion-proof motors for ships, explosion-proof motors for lifting and metallurgy, and increased safety brushless excitation synchronous motors for hydrogenation devices. In addition, it can also be divided according to technical indicators such as rated voltage and efficiency, such as high-voltage explosion-proof motors, high-efficiency explosion-proof motors, high-slip explosion-proof motors, and high-starting torque explosion-proof motors.
Previous article:Explosion-proof motor installation method_Explosion-proof motor installation precautions
Next article:Explosion-proof motor flameproof surface principle_Explosion-proof motor flameproof surface standard
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
- Brief Analysis of Automotive Ethernet Test Content and Test Methods
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- LED chemical incompatibility test to see which chemicals LEDs can be used with
- Application of ARM9 hardware coprocessor on WinCE embedded motherboard
- What are the key points for selecting rotor flowmeter?
- LM317 high power charger circuit
- A brief analysis of Embest's application and development of embedded medical devices
- Single-phase RC protection circuit
- stm32 PVD programmable voltage monitor
- Introduction and measurement of edge trigger and level trigger of 51 single chip microcomputer
- Improved design of Linux system software shell protection technology
- What to do if the ABB robot protection device stops
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
- Mobile 5G device antenna tuning revealed
- What is switching AC-DC conversion?
- About PIN-to-PIN compatibility between SI24R1 and NRF24L01P
- Huawei_Large-Scale Logic Design Guide.rar
- Hardware R&D Platform
- MSP430 clock frequency configuration process
- [Mill Edge AI Computing Box FZ5 Review] Pynq Framework - Helloworld!
- pybNano development board added to uf2-stm32f
- Compound tube and complementary push-pull circuit
- [RTT & Renesas high performance CPK-RA6M4 development board review] - Serial and USB communication

 LT6402IUD-6#TR
LT6402IUD-6#TR
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号