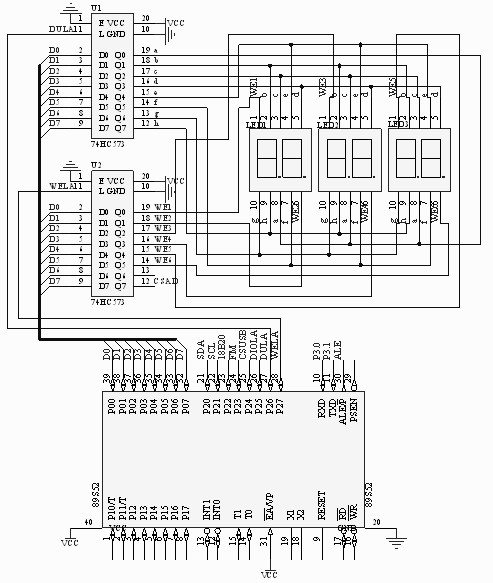
Using a single-chip microcomputer to control the display of 6 common cathode 8-segment digital tubes, two latches can be used to select the position (which digital tube is the position) and the segment (which segment of the digital tube is the number to be displayed). The enable end of the 74HC573 latch is valid at a low level. When LE is high, the output end (output) follows the input end (D); when LE is low, the output end maintains the value when LE is high. The circuit diagram of the single-chip microcomputer controlling the digital tube through the latch is shown in Figure 1:
0x3f , 0x06 , 0x5b , 0x4f , 0x66 , 0x6d ,
0 1 2 3 4 5
0x7d , 0x07 , 0x7f , 0x6f , 0x77 , 0x7c ,
6 7 8 9 A B
0x39 , 0x5e , 0x79 , 0x71 , 0x00
C D E F No display
Reference address:Single chip microcomputer controls digital tube display

illustrate:
1) When the digital tube is a common cathode, when the bit selects Q0~Q5, the response bit is 0 for selected, and 1 for unselected. For example, if the first digital tube P0 is selected = 0xfe;
2) Common cathode digital tube meter (segment selection meter)
0x3f , 0x06 , 0x5b , 0x4f , 0x66 , 0x6d ,
0 1 2 3 4 5
0x7d , 0x07 , 0x7f , 0x6f , 0x77 , 0x7c ,
6 7 8 9 A B
0x39 , 0x5e , 0x79 , 0x71 , 0x00
C D E F No display
3) Common cathode position selection table
0xfe,0xfd,0xfb,0xf7,0xef,0xdf
1 2 3 4 5 6 (Choose which one)
3) Generally, the bit selection is performed first, then the lock is stored, and then the segment selection is performed, and the program example is
sbit dula=P2^7;
sbit wela=P^8;
while(1)
{
wela=1;//bit selection
P0=0xfe; //Select the second digital tube
wela=0; //bit latch
dula=1;//segment selection
P0=0x39; //display 6
dula=0; //segment latch
delay (); //Usually write a delay function yourself or use an interrupt timer to delay
}
Previous article:What is SBUF
Next article:LED flashing program (bit operation)
Recommended Content
Latest Microcontroller Articles
He Limin Column
Microcontroller and Embedded Systems Bible
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
MoreSelected Circuit Diagrams
MorePopular Articles
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
MoreDaily News
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
Guess you like
- FPGA learning experience - matrix keyboard
- Welcome the moderator "天意无罪" to take office~~
- Task stack overflow detection mechanism in FreeRTOS
- GaN RF Circuits and Applications
- How to quickly learn to use a chip?
- Lei Jun lost the 1 billion bet with Dong Mingzhu. It seems that the typhoon still can't blow up the pigs.
- The pad is 0.3mm/center distance is 0.5mm and the wire cannot come out
- C2000 Code Generation Tools - Compiler
- The CC3200 LaunchPad crashed before I even got it warm?
- TMS320F28377S Study Notes 3 Building a fully portable CCS9.3 project

 Multifunctional music player based on AT89S52 single chip microcomputer
Multifunctional music player based on AT89S52 single chip microcomputer Mst 9E89 Schematic
Mst 9E89 Schematic
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号