Comparison of FDD and TDD transmission
Frequency Division Duplex (FDD)
FDD requires two independent communication channels (i.e., transmit frequencies) separated by a guard band to minimize co-channel interference (Figure 1). Good filtering, duplexers, and possibly radio shielding are necessary to ensure that the transmitter does not desensitize adjacent receivers. FDD radios continuously transmit in both directions over the radio link to provide full-duplex capability.

Figure 1. FDD requires two symmetrical spectrums for uplink and downlink.
Time Division Duplex (TDD)
TDD uses a single frequency band for both transmission and reception by allocating alternating time slots for transmission and reception operations (Figure 2). The information to be transmitted—whether voice, video, or computer data—is in serial binary format. Each time slot can be either 1 byte long or a multi-byte frame.
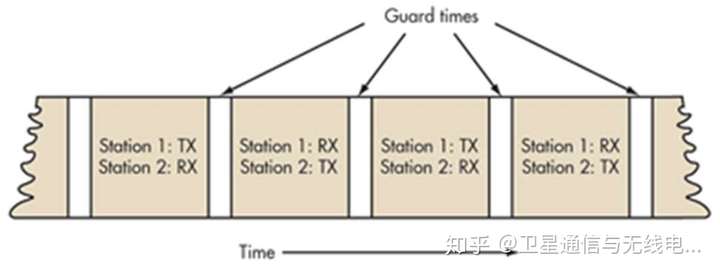
Figure 2. TDD alternates sending and receiving station data over time. The time slots may vary over time.
In some TDD systems, the alternating time slots are of equal duration or have equal download and upload time slots, however, TDD systems do not have to be 50/50 symmetrical. Systems can be designed to operate asymmetrically (e.g. 75/25 or 90/10 is common) or dynamically based on traffic conditions.
TDD spectrum scanning with Spectrum Compact
Time-division duplex radio systems transmit rapid physical carrier changes in the time domain. In order to be able to display such signals on the screen of the Spectrum Compact, the Spectrum Compact must be configured accordingly.
1. Disable "Signal ID" mode under TOOLS → SETTINGS
2. To ensure maximum reading speed, use 100MHz SPAN. 0OMHz span can be set under the "SPAN" menu by pressing the "MIN SPAN" button. Using a SPAN value larger than 100MHz will result in a longer scan refresh cycle, increasing the time required for accurate measurements.
3. Due to the frequency hopping nature of TDD signals (e.g. OFDM modulated carriers), it is necessary to accumulate the Spectrum Compact scans over a period of time. This can be done using the "MAXHOLD" or "CUMULATIVE" traces under the "TRACE MODE" menu on the main screen. SAF recommends selecting at least 100 scans, regardless of the SPAN selection.
MAXHOLD trajectory
The blue trace shows the highest level detected since the start of the sweep. During each sweep, only the frequency point with the highest power level is updated. Clicking the MAXHOLD button repeatedly resets the MAXHOLD trace. The blue counter below the grid shows the number of sweeps since the most recent MAXHOLD mode started. Above the grid, the power levels of the CENTER and MARKER (if activated) frequencies are indicated in blue.

Figure 3. Display of WIFi signal readings in “MAXHOLD” tracking mode
CUMULATIVE trace
The power level of each frequency for all previous sweeps since the start of the sweep is displayed in green. During each sweep, only the frequency points for which no levels were previously saved are updated.

Figure 4. Display of WIFI signal readings in “Accumulation” tracking mode
A list of TDD applications where Spectrum Compact can be used include:
Interference and available channel detection;
Relative power observation between different TDD signals;
Channel bandwidth determination;
Traffic intensity survey of TDD signals (e.g. using frequency hopping systems);
Use point-to-point narrow beam xternal antenna to find TDD signal source.
Example
In the next two figures, a spectrum scan of a 5GHz point-to-point (PtP) radio unit using TDD transmission is shown and detailed. Note that in most cases it is not possible to observe an accurate PtP TDD signal by connecting a spectrum analyzer directly to the radio unit, as most TDD radios only detect TDD signals after the link between a master and slave (PtP) or access point and client (Point-to-Multipoint or PtMP) is established.

Figure 5. PtP 5GHz TDD radio signal scan using “MAXHOLD” tracking mode
Delta channel bandwidth for a TDD signal. Since Spectrum Compact is set to 100MHz SPAN, each grid cell is 10MHz wide. In this example, the signal occupies 2 cells, which means the channel under investigation is 20MHz wide.
Figure 6 shows the same situation as Figure 5, but using the "Accumulation" tracking mode. The "Accumulation" tracking mode allows a more precise view of how the scanned spectrum is occupied and how the signal energy is distributed within the spectrum.

Figure 6. PtP 5GHz TDD radio signal scan using “CUMULATIVE” tracking mode

Previous article:How to choose the appropriate FFT window function in real-time spectrum analyzer
Next article:Application of fat analyzer in fish meal market
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Keysight Technologies Helps Samsung Electronics Successfully Validate FiRa® 2.0 Safe Distance Measurement Test Case
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- Seizing the Opportunities in the Chinese Application Market: NI's Challenges and Answers
- Tektronix Launches Breakthrough Power Measurement Tools to Accelerate Innovation as Global Electrification Accelerates
- Not all oscilloscopes are created equal: Why ADCs and low noise floor matter
- Enable TekHSI high-speed interface function to accelerate the remote transmission of waveform data
- How to measure the quality of soft start thyristor
- How to use a multimeter to judge whether a soft starter is good or bad
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of non-contact temperature sensors?
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- [N32L43x Review] 6. Software and Hardware I2C Driver for 0.96-inch OLED
- GD32E231 DIY Competition (2) - Unboxing and Testing
- 【Case Study】Application of Wireless Wake-up Technology in Irrigation System
- 【Share】Parallel power supply
- Some bytes of code in the application memory area of MSP430FR5949IDAR FRAM are tampered
- Overview of RFID Anti-collision Technology
- MSP430 low power mode - while loop fails
- [MM32 eMiniBoard Review] Give feedback on this board
- IWR6843 Smart mmWave Sensor Antenna-Package Evaluation Module
- Three designs of constant current circuit

 Wimax network planning related information
Wimax network planning related information















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号