The meaning and importance of circuit protection, common types of circuit protection
Source: InternetPublisher:jikai233 Keywords: Circuit protection electronic circuits Updated: 2025/01/14
1. What is circuit protection?
1.1 Circuit Protection Concept
Circuit protection is mainly to protect the components in the electronic circuit from damage due to overvoltage, overcurrent, surge, electromagnetic interference, etc. With the development of science and technology, power and electronic products are becoming increasingly diversified and complex. In the past, the circuit protection components used were mostly simple glass tube fuses, and the common protection devices were varistors, TVS, and gas discharge tubes. Circuit protection has developed into a diversified field of emerging electronic components.

1.2 The significance and importance of circuit protection
(1) As the integration of circuit boards becomes higher and higher, the price of boards also rises accordingly. Therefore, we must strengthen protection.
(2) The operating voltage of semiconductor devices and ICs is much lower, and the purpose of circuit protection is to reduce energy loss, reduce heat generation, and extend service life.
(3) In-vehicle equipment, because the use environment is worse than that of general electronic products. The driving conditions of the car change frequently, and the car has a very large instantaneous peak voltage when starting, etc. Therefore, the power adapters of these electronic equipment products should generally use overvoltage protection components.
(4) Communication equipment and communication sites have certain requirements for lightning surge protection. Overvoltage protection and overcurrent protection components are very important in these devices. They are the key to ensuring normal personal safety and communication.
(5) Most electronic product failures are caused by overvoltage or circuit phenomena in the electronic device circuit. As our requirements for the quality of electronic equipment become higher and higher, electronic circuit protection is becoming more and more necessary.
1.3 How many amperes can a wire safely conduct?
The American Boat and Yacht Council (ABYC) publishes the following table showing how much amperage each size of wire can carry:
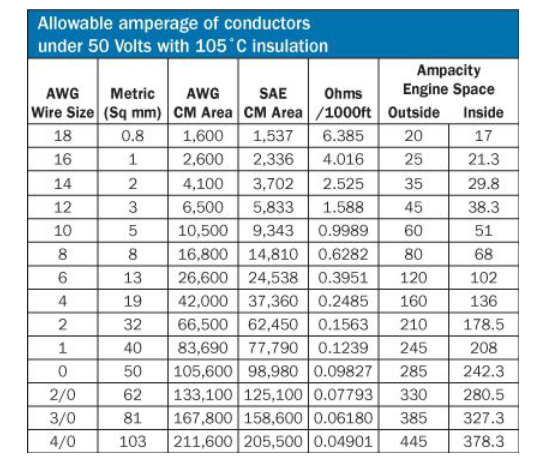
"Allowable amperage" is not the only factor to consider when sizing wire. Voltage drop must also be considered. Voltage drop is the amount of voltage "consumed" when the voltage is "pushing" amperage through the resistance of the wire. Sometimes the allowable amperage will be the determining factor in determining wire size, while in other cases, the voltage drop will determine the wire size. The wire must be the larger of the allowable amperage or voltage drop requirement.
Common types
2.1 Overcurrent
In power systems, overcurrent or overcurrent is when the current through a conductor is greater than expected, resulting in excessive heat generation and the risk of fire or equipment damage. Possible causes of overcurrent include short circuits, excessive loads, incorrect design, or ground faults. Fuses, circuit breakers, temperature sensors, and current limiters are common protection mechanisms to control overcurrent risks.
When the current is too large, the overcurrent protection is automatically cut off to prevent the electronic components of the circuit from being damaged due to exceeding the rated current.
2.2 Overvoltage
When a circuit or part of it experiences voltage above its designed upper limit, this is called overvoltage. The condition can be dangerous. Depending on its duration, an overvoltage event can be temporary (voltage spike) or permanent, resulting in a power surge.
Electronic and electrical equipment are designed to operate at a certain maximum supply voltage, and voltages above the rated voltage of the equipment may cause considerable damage.
Overvoltage protection is mainly to prevent electronic components from being damaged by overvoltage or electrostatic discharge. It is widely used in electronic system products such as telephones, fax machines and high-speed transmission interfaces (USB, IEEE1394, HDMI, SATA), especially electronic communication equipment. This is particularly important to avoid damage to electronic equipment due to overvoltage or EOS (electrical overstress) or electrostatic discharge (ESD).
For example, a light bulb has a wire that, at a given rated voltage, will carry enough current that the wire gets very hot (giving off light and heat), but not enough that it melts. The amount of current in a circuit depends on the voltage supplied: if the voltage is too high, then the wire might melt and the light bulb will "burn out in real time." Likewise, if overvoltage is delivered to a circuit, other electrical equipment might stop working or even catch fire.
2.3 OT (Over Temperature)
Temperature protection components have come a long way since commercial use. Currently, over-temperature protection components are widely used in situations where a specific temperature is required. These protection components can be divided into chemical activation type and low-temperature alloy drive type according to their working principle.
The main feature is that the chemical drive product type can be made into low temperature products (currently 48°C), but it is more complicated and expensive. The other is the low temperature alloy drive type. The role of the low temperature alloy type is mainly carried out through a low temperature fuse with a larger diameter. We must ensure that the heat generated by the rated current does not melt the fuse. Low temperature fuses usually adjust the melting point by adjusting the components such as tin (Sn), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), bismuth (Bi), and indium (In).
2.4 Overall efficiency
In recent years, with the upgrading of applications, simple temperature protection can no longer meet the ever-changing safety protection needs of electrical appliances, motors and 3C products, so components that can provide monitoring functions and timely protection are redeveloped to deal with temperature, current and voltage anomalies. The rise of lithium-ion batteries and lithium polymer batteries is the largest application.
2.5 OCOV (overcurrent and overvoltage)
With the complexity of modern electronic products, the requirements for protection components are becoming higher and higher, such as comprehensive protection and limited reserved space. With these requirements, the protection component community has set off a wave of packaging. As mentioned above -
Over temperature protection is also considered as a combination package. But most OCOV protection packaging products are still under development. No mature commercial products are available.
- Controlling LEDs with Node-RED in Raspberry Pi
- Tutorial for building a remote-controlled Arduino Air-Boat
- DIY an electromagnetic levitation device
- What are the challenges in designing a permanent magnet linear generator?
- Replace the GE LOGIQ a200 ultrasound measurement key with a self-made touch switch
- Working principle of one Xipu STR soft starter controlling two motors
- Amplitude and phase detection leakage protection device designed and manufactured using PIC16C711A
- Homemade short circuit alarm device
- Homemade anti-theft watchdog
- Bicycle anti-theft alarm
- Rural fish farming control circuit
- Mobile phone camera flash control circuit
- Stapler control circuit
- Car window control circuit
- AM radio automatic search and trigger circuit
- Automatic tuning control circuit
- Digital current loop control circuit
- Automatic door detection control circuit
- Intelligent iron control circuit
- Temperature detection control circuit of electric kettle







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号