What are the challenges in designing a permanent magnet linear generator?
Source: InternetPublisher:吃掉星星 Keywords: EMS generator permanent magnet Updated: 2024/12/13
Permanent Magnet Linear Generator
A permanent magnet linear generator (PMLG) is simply a generator consisting of a stator, a converter, and an air gap. The stator usually consists of copper windings and laminations designed to minimize eddy current losses. The converter consists of permanent magnets, which can be annular, cylindrical, or rectangular and made of rare earth materials. Depending on the required force and air gap magnetic field, the magnets can be arranged radially, axially, or in a Halbach manner. Many research papers report that PMLG has several significant advantages, including high efficiency, i.e. >90%, small air gap, and small size. In addition, PMLG is environmentally friendly as it does not emit CO2 and does not consume fossil fuels.
Lessons Learned from EMS Simulation
To investigate the above design challenges, we used the popular EMWorks virtual prototyping software EMS to find answers and solutions, including the following:
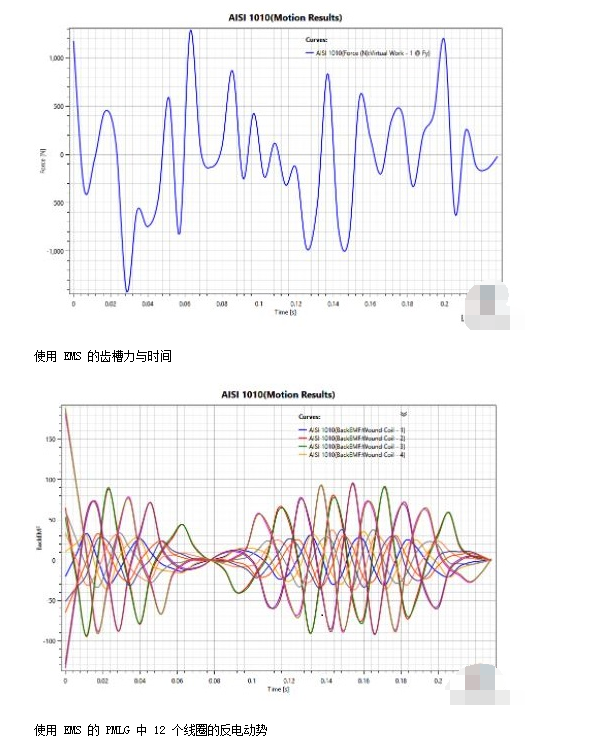
The cogging force depends strongly on the ferromagnetic material of the stator core and the speed of the converter. Somaloy has the lowest cogging force among the various ferromagnetic cores studied. The higher the speed of the converter, the higher the cogging force.
The back EMF is proportional to the speed of the converter.
When comparing permanent magnets, Halbach produces better output power compared to axial and radial arrangements. Also, comparing axial and radial arrangements, the former does not require a back iron, while the latter requires it for better performance.
Thermal analysis must always be performed to ensure that the magnets are not heated to the point of demagnetization.
PMLG is an excellent candidate for generating electricity in the ocean using wave-induced motion.
The smaller the air gap, the higher the back EMF and cogging forces. Therefore, the trade-off between cogging and power must be carefully studied.
Although the generator produces AC voltage and current, the frequency and amplitude of the voltage will change with speed, which makes it essential to use power electronic converters to maximize power utilization. It is worth mentioning that even if the speed is constant, the magnitude of the back EMF will not be constant. Therefore, the efficiency of the power converter should be considered when determining the efficiency of the entire system.
- Working principle of one Xipu STR soft starter controlling two motors
- Motor automatic cycle control circuit
- Using P110C to control 6 DC motors simultaneously
- Methods for Eliminating Noise of Brushed DC Motors
- One-way rotation circuit of motor controlled by contactor
- Temperature control circuit design and analysis
- Design and production of no-load automatic power-off device for household power supply
- Infrared blocking alarm device
- Magnetic door and window anti-theft alarm
- Infrared detection alarm
- Replace the motor with the generator circuit
- Remote control receiving circuit of Panasonic inverter air conditioner indoor unit control circuit
- Water dispenser double sheet control circuit
- External grid power supply and self-generated power supply conversion circuit
- High voltage generator excitation group overvoltage protection circuit
- FKL-32 type thyristor automatic excitation device circuit b
- JZLF-31F thyristor automatic excitation device circuit
- TWL-B type brushless excitation regulator circuit
- Third harmonic excitation circuit
- Application circuit of external tachometer generator







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号