Regarding the automotive electronic control system, it is actually not exclusive to new energy electric vehicles. Fuel vehicles also have it, but the electronic control system of new energy electric vehicles is more complex and more powerful.
The electronic control system of new energy vehicles, in a narrow sense, refers to the whole vehicle controller. In a broad sense, it includes the whole vehicle controller, battery management system, drive motor controller, etc.
New energy vehicle electronic control system composition diagram
These controllers on the car communicate through the CAN network. CAN, the full name of which is "Controller Area Network", is one of the most widely used field buses in the world. Initially, CAN was designed as a microcontroller communication in the automotive environment, exchanging information between the various electronic control units ECU on the vehicle to form an automotive electronic control network. For example: CAN control devices are embedded in the engine management system, transmission controller, instrument equipment, and electronic backbone system.

In this article, we will briefly introduce the composition and functions of the vehicle's electronic control system.
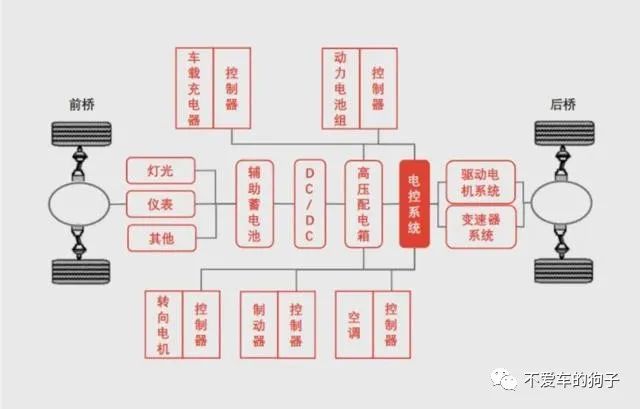
Vehicle Control VCU
During the driving process of the vehicle, a window is needed to interact with the driver for instructions. This window is the vehicle control unit (VCU). The VCU is responsible for receiving various driving operation instructions and configuration function operation requirements from the driver, such as power-on, acceleration, brake pedal and other signals, and combining the operation instructions or cooperative control information issued by other vehicle systems, as well as various vehicle condition signals fed back by sensors of various components, to analyze the working conditions of the entire vehicle and various components, and form instructions that can ensure the safe driving of the vehicle, so as to achieve the purpose of each control system executing actions.
High and low voltage components coordinated by VCU
The electrified powertrain of new energy vehicles has added many high and low voltage electrical components. VCU is the "brain" of the new energy vehicle drive system control. Mature system software plays an important role in improving operating efficiency, reducing energy consumption and emissions, and improving the robustness of post-fault processing. It is one of the core capabilities for the real implementation of electrified powertrain system solutions.
As the core controller of the vehicle drive coordination control system, VCU is responsible for the most basic and important functions such as vehicle status coordination and driver driving demand realization. Therefore, the perfection of VCU software directly affects the stability and driving safety of vehicle operation. With the promotion of the concept of "domain integration", more and more new functions are gradually integrated into the VCU controller, such as: AC/DC vehicle-side charging master control function related to charging, and electric four-wheel drive control function related to chassis.
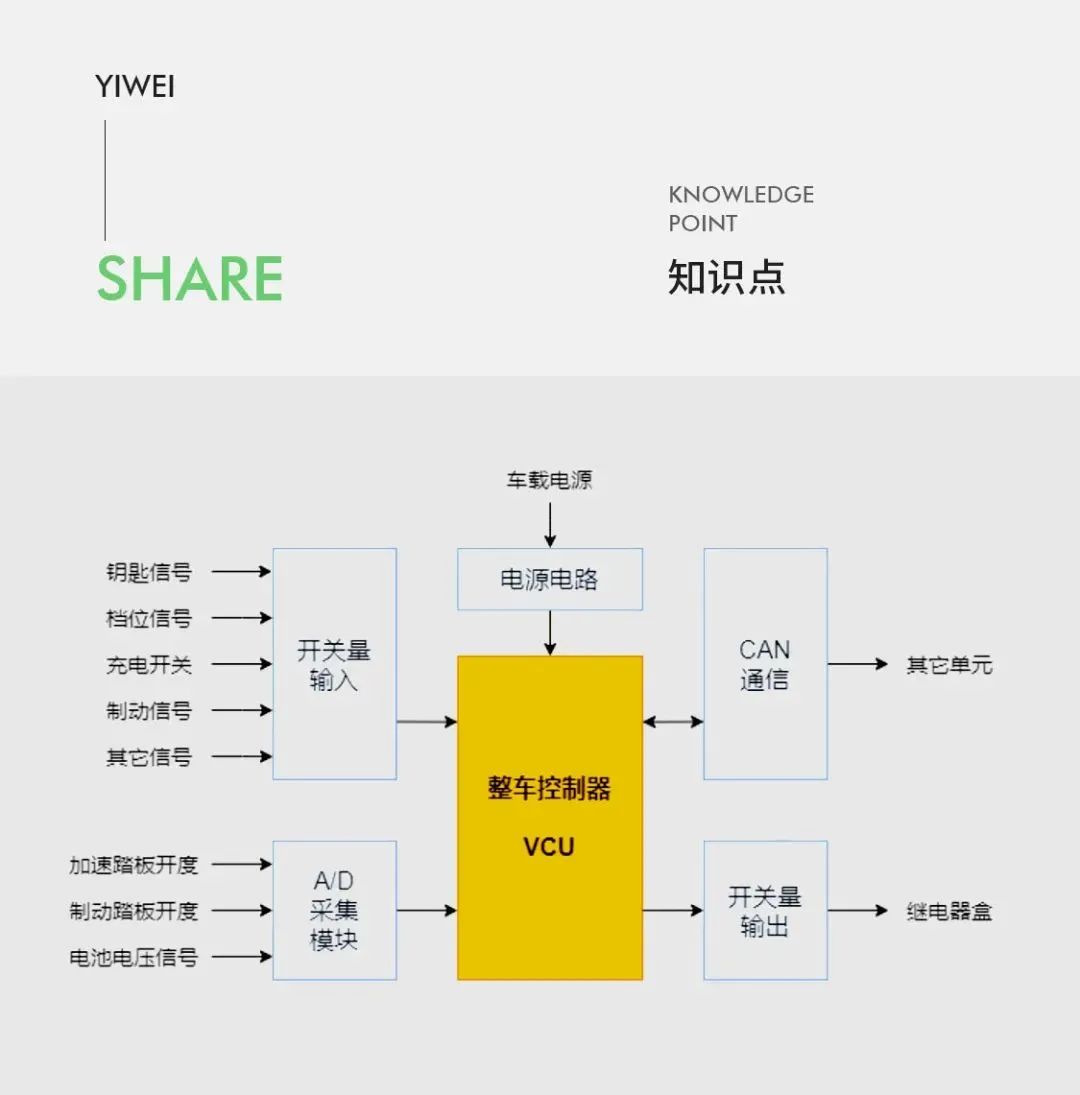
From the perspective of system function division, the functions of VCU can be divided into: vehicle system, transmission system, power system, thermal management system, as well as OBD diagnosis, communication, safety monitoring and other system functions. The main functions of VCU are as follows.

VCU system function classification and overview
Drive motor controller
The main function of the motor controller (Micro Controller Unit) is to receive the torque command from the vehicle controller, and then control the drive motor to work according to the set direction, speed, angle, and response time.
In electric vehicles, the function of the motor controller is to convert the electrical energy stored in the power battery into the electrical energy required to drive the motor according to instructions such as gear position, throttle, and brake, to control the starting, forward and backward speed, climbing intensity and other driving conditions of the electric vehicle, or to help the electric vehicle brake and store part of the braking energy in the power battery.
Every motor has a controller, and the features and complexity of the controller vary depending on the performance the motor needs to provide. The simplest controller is a switch that connects the motor to a power source, such as a small appliance or power tool. More complex motor controllers can precisely control the speed and torque of the motor, or may be part of a closed-loop control system that controls the position of a machine.
In addition, during the energy recovery process, the motor controller is also responsible for rectifying the AC power generated by the auxiliary torque of the drive motor and charging it back to the power battery. The working conditions it faces are relatively complex, requiring frequent start and stop, acceleration and deceleration, high torque at low speed/climbing, low torque at high speed, and a large speed range.
Battery Management System
Compared with the first two controllers, the battery management system is relatively "young". Its main functions include: real-time monitoring of battery physical parameters, online diagnosis and alarm, charge and discharge and pre-charge control, balancing management and thermal management, etc.
The core functions of the battery management system BMS:
1. Battery cell monitoring technology
a. Single battery voltage collection;
b. Single battery temperature collection;
c. Battery pack current detection;
Accurate temperature measurement is very important for the working state of the battery pack, including the temperature measurement of a single battery and the temperature monitoring of the cooling liquid of the battery pack. This requires the reasonable setting of the location and number of temperature sensors to form a good match with the BMS control module. The focus of monitoring the cooling liquid temperature of the battery pack is the fluid temperature at the inlet and outlet, and the selection of its monitoring accuracy is similar to that of the single battery.
Based on the design of the electronic control system for new energy vehicles, Yiwei Automobile divides the electronic control system for special vehicles into two parts: high-voltage electronic control system and low-voltage electronic control system.
High voltage electronic control system
In electric vehicles, high-voltage components include power batteries, drive motors, high-voltage distribution boxes (PDU), electric compressors, DC/DC, OBC, PTC, high-voltage wiring harnesses, etc. These components constitute the high-voltage system of the vehicle, among which power batteries, drive motors and high-voltage regulation systems are the three core components of pure electric vehicles.
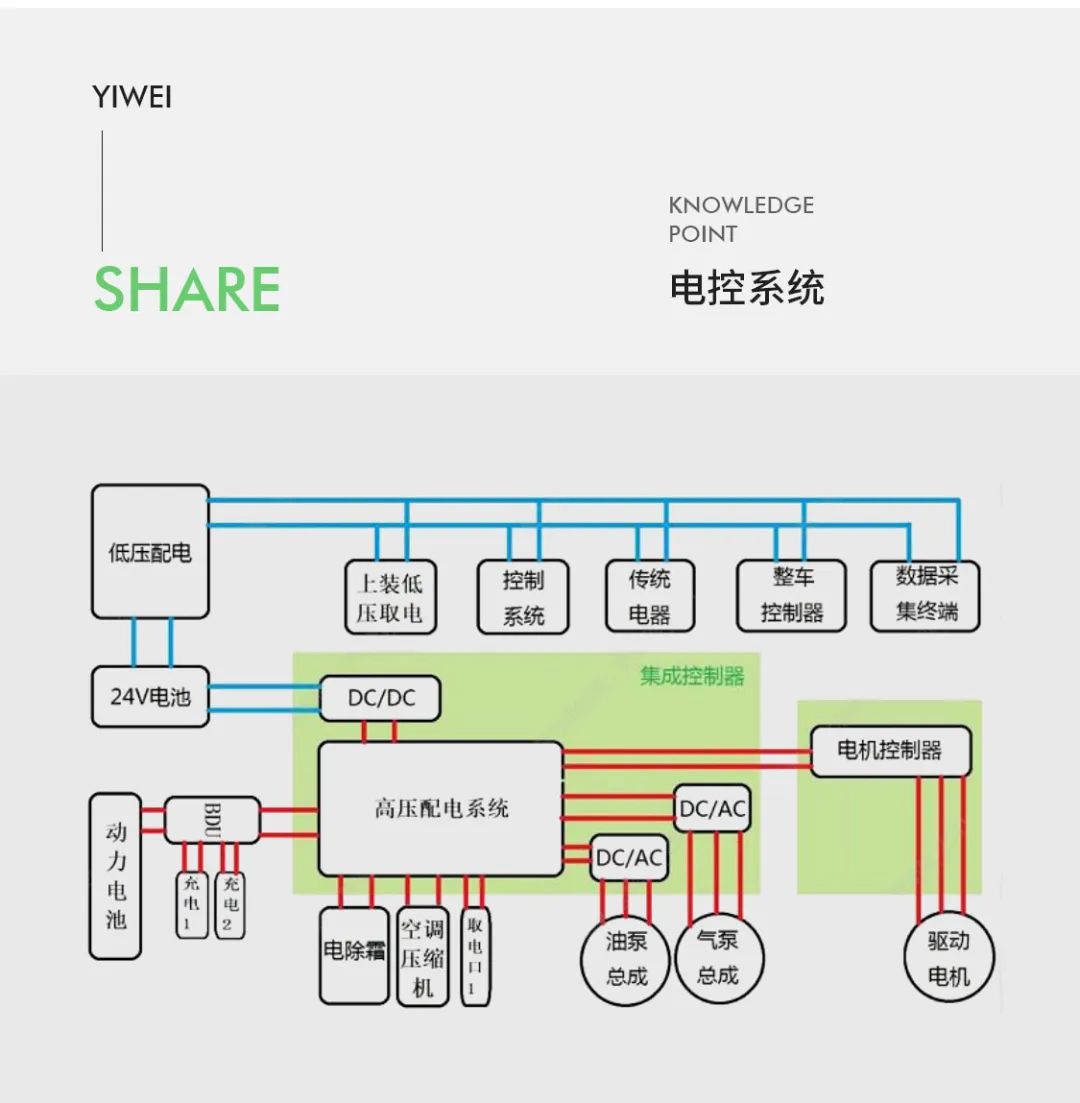
Low voltage electronic control system
The low-voltage electrical system of electric vehicles is mainly composed of DC/DC power converters, auxiliary batteries and several low-voltage electrical equipment. The low-voltage electrical equipment of electric vehicles mainly includes lighting systems, instrument systems and entertainment systems. At present, the low-voltage electrical system usually uses 12V/24V DC power supply as the low-voltage power supply of the whole vehicle, which supplies power to conventional low-voltage electrical appliances such as lights and wipers on the one hand, and supplies power to the vehicle controller, motor control system, battery management system, controller of high-voltage equipment and auxiliary parts such as cooling electric water pump on the other hand.

Previous article:Introduction to the development path and key technologies of redundant electric power steering system EPS
Next article:How to achieve overheat protection for new energy vehicle charging pile plugs?
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Quartus II 11.0 + NIOS soft core fails to program FLASH
- Python Keyboard using circuitpython
- CCS6 Call Array
- RVB2601 simple unpacking
- TI Embedded Live Month: In-depth exploration of new applications of embedded products in industry and automobiles. The second session will be live at 14:00 today.
- Integrate MCU and sensors into multiple nodes to power wireless weather stations
- [Update Mailing Information] 2020-2021 ON Semiconductor and Avnet IoT Creative Design Competition
- About the Standardization of PLC Programming
- MEMS pressure sensors solve new pain points in human-machine interface
- What methods are there to achieve power saving and low power consumption (without screen) for micro wearable devices such as Bluetooth bracelets?

 Optimized drivetrain and new semiconductor technologies enable the design of energy-efficient electr
Optimized drivetrain and new semiconductor technologies enable the design of energy-efficient electr Considerations for ground wire protection in electric vehicles
Considerations for ground wire protection in electric vehicles















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号