Introduction: The misalignment problem is one of the common problems faced by equipment manufacturers using stepper or servo motors during equipment installation, commissioning and use. Misalignment may be caused by improper mechanical assembly, mismatch between the control system and the driver signal, electromagnetic interference within the equipment, mutual interference between equipment in the workshop, or improper grounding during equipment installation.
Regular deviation
Q: When doing reciprocating motion, the more you move forward, the more (less) you will feel.
Possible reason ①: The pulse equivalent is incorrect
Cause analysis: Both the synchronous wheel structure and the gear rack structure have machining accuracy errors. The motion control card (PLC) does not set the accurate pulse equivalent. For example, the previous batch of synchronous wheel motors rotated one circle and the equipment moved forward 10mm. This batch of synchronous wheel motors with larger size rotated one circle and moved forward 10.1mm. This will cause this batch of machines to travel 1% more distance than the previous equipment each time they run.
Solution: Draw a square as large as possible with the machine before shipping, then use a ruler to measure the actual size, compare the ratio between the actual size and the size set on the control card, then add it to the control card calculation, repeat three times to get a more accurate value.
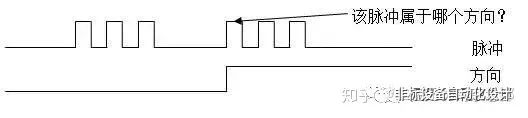
Possible reason ②: The trigger edge of the pulse command conflicts with the level change timing of the direction command.
Cause analysis: The driver requires that the pulse instruction issued by the host computer has a certain timing requirement for the level change of the direction instruction. However, some PLCs or motion control cards do not meet this requirement when programming (or their own rules do not meet the requirements of the driver), resulting in the pulse and direction timing not meeting the requirements and being offset.
Solution: The control card (PLC) software engineer advances the direction signal. Or the driver application technician changes the pulse edge counting method.
Q: The motor vibrates at a fixed point during movement. After passing that point, it can run normally, but it travels a shorter distance.
Possible cause: Mechanical assembly problem
Cause analysis: The mechanical structure has a large resistance at a certain point. Due to the parallelism, verticality or unreasonable design of the mechanical installation, the equipment has a large resistance at a certain point. The torque change law of the stepper motor is that the faster the speed, the smaller the torque. It is easy to get stuck in the high-speed section, but it can pass when the speed is reduced.
Solution: 1. Check the cause of the mechanical structure getting stuck, whether it is due to high friction resistance or non-parallel installation of the slide rails. 2. The stepper motor torque is insufficient. Due to the end customer's requirements for speed increase or load increase, the motor that originally met the requirements did not have enough torque at high speed, resulting in high-speed stalling. The solution is to set a higher output current through the driver or increase the supply voltage within the driver's allowable voltage range, or replace the motor with a higher torque.
Q: The motor does not reach the correct position when reciprocating and the offset is fixed
Possible cause: Belt gap
Cause analysis: There is a reverse gap between the belt and the synchronous wheel, resulting in a certain amount of idle travel when going back.
Solution: If the motion control card has a belt reverse clearance compensation function, you can use it; or tighten the belt.
Q: The cutting tracks do not overlap
Possible reason ①: Too much inertia
Cause analysis: The inkjet process of the flatbed cutting machine is controlled by a grating, scanning motion, and interpolation motion during cutting. The trajectories of the two do not overlap because the inertia of the X-axis trolley of similar equipment is small and is positioned by a grating, so the printing position is accurate, while the inertia of the Y-axis gantry structure is large, the motor responsiveness is poor, and the Y-axis has poor follow-up during interpolation motion, resulting in partial deviation of the trajectory.
Solution: Increase the Y-axis reduction ratio and use the notch function to improve the servo drive rigidity to solve the problem.
Possible reason ②: The overlap between the knife and the nozzle is not adjusted properly
Cause analysis: Because the cutting plotter knife and print head are both installed on the X-axis carriage, but there is a coordinate difference between the two. The upper computer software of the cutting plotter can adjust this coordinate difference to make the knife and print head tracks coincide. If it is not adjusted properly, the cutting track will be separated as a whole.
Solution: Modify the knife and nozzle position compensation parameters.
Q: Draw a circle into an ellipse
Possible cause: The two axes of the XY axis platform are not perpendicular
Cause analysis: XY axis structure, graphic deviation, for example, a circle becomes an ellipse, a square becomes a parallelogram. This problem occurs when the X-axis and Y-axis of the gantry structure are not perpendicular.
Solution: This problem can be solved by adjusting the verticality of the gantry X-axis and Y-axis.
Irregular deviation
Q: During operation, there is irregular deviation. The deviation is accidental and the amount of deviation is uncertain.
Possible cause ①: Interference causes the motor to be misaligned
Cause analysis: Most of the non-periodic deviations are caused by interference, and a small part is caused by narrow pulses emitted by the motion control card or loose mechanical structure.
Solution: If the interference occurs frequently, you can use an oscilloscope to monitor the pulse frequency to determine the time when the interference occurs and then determine the source of the interference. Removing or moving the pulse signal away from the interference source can solve some of the interference. If the interference occurs occasionally, or it is difficult to determine the location of the interference source or the electrical cabinet is fixed and difficult to move, you can consider taking the following measures to solve the problem:
① Driver grounding,
② Replace the pulse line with a twisted shielded pair line.
③ Connect 103 ceramic capacitors in parallel to the positive and negative ends of the pulse for filtering (pulse frequency is less than 54kHz).
④ Pulse signal magnetic ring,
⑤ Add filters to the front end of the driver and controller power supply.
Note: Common interference sources include transformers, coil relays, inverters, solenoid valves, high-voltage wires, etc. When planning electrical cabinets, avoid placing signal lines close to these interference sources, and signal lines and high-voltage power lines should be laid in different wire troughs.
Possible cause ②: Narrow pulses appear in the pulse train
Problem analysis: The duty cycle of the pulse train sent by the customer's motion control card is too small or too large, resulting in narrow pulses that the drive cannot recognize, causing deviation.
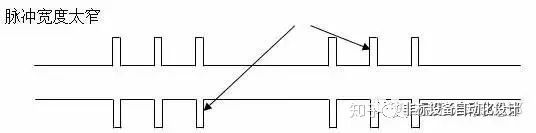
Solution: Find out why the controller has this problem, is it a pulse interface problem or a software algorithm problem?
Possible reason ③: Loose mechanical structure
Problem analysis: Couplings, synchronous wheels, reducers and other connectors that are fixed with jackscrews or clamped with screws may become loose after running for a period of time in fast impact situations, resulting in displacement. For synchronous wheels that are fixed with keys and keyways, pay attention to whether there is a gap between the key and the keyway, and for gear rack structures, pay attention to the matching gap between the two.
Solution: Use spring washers for key parts and structural screws with high stress, and apply screw glue to screws or top screws. Use keyways to connect the motor shaft and coupling as much as possible.
Possible reason ④: The filter capacitor is too large
Problem analysis: The filter capacitor is too large. The cutoff frequency of the ordinary RC filter is 1/2πRC. The larger the capacitance, the smaller the cutoff frequency. The pulse end resistance of the general driver is 270 ohms. The cutoff frequency of the RC filter circuit composed of 103 ceramic capacitors is 54khz. If the frequency is higher than this, the amplitude attenuation will be too large, resulting in some effective signals not being correctly detected by the driver, which will eventually lead to deviation.
Solution: When adding filter capacitors, it is necessary to calculate the pulse frequency and ensure that the maximum passing pulse frequency meets the requirements.
Possible reason ⑤: The maximum pulse frequency of the PLC or motion control card is not high enough
Cause analysis: Generally, the maximum pulse frequency allowed by PLC is 100kHz. Motion control cards vary greatly depending on the pulse chips they use. In particular, motion control cards developed with ordinary single-chip microcomputers may be misaligned because the pulse frequency is not high enough.
Solution: If the maximum pulse frequency of the host computer is limited, in order to ensure the speed, the driver subdivision can be appropriately reduced to ensure the motor speed.
Previous article:PLC ladder diagram of three-phase induction motor fault alarm control circuit
Next article:How much is the no-load loss of asynchronous motor? The calculation formula of no-load loss of asynchronous motor
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Keil C51 cracking problem
- AT32F425-Evaluation Report-CAN Communication Experiment 03
- [N32L43x Review] 1. Unboxing the N32L43XRL-STB Development Board
- [RVB2601 Creative Application Development] Temperature and Humidity Monitoring System Based on Alibaba Cloud
- Future Prospects of UWB Technology
- On the problem of value jump in PMT application
- Use of access/_access function in C language
- [Rvb2601 Creative Application Development] +02 Flowing Light
- Millimeter wave technology: key 5G technology
- "Date in Spring" + Factory Tour

 We address the problem of blind carrier frequency-offset (CFO) estimation in quadrature amplitude mo
We address the problem of blind carrier frequency-offset (CFO) estimation in quadrature amplitude mo LY530/LY530AL pdf datasheet
LY530/LY530AL pdf datasheet
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号