Analog oscilloscopes are better than digital oscilloscopes. This is indeed a question. Although analog oscilloscopes have been completely replaced by digital oscilloscopes, this does not mean that analog oscilloscopes will disappear. In fact, in some occasions, analog oscilloscopes still play an irreplaceable role for digital oscilloscopes.
Let's first take a brief look at the history of oscilloscopes.
In 1900, Karl Ferdinand Braun (also translated as Brown), a physics professor at the University of Strasbourg, invented the world's first cathode ray tube analog oscilloscope. Even Braun himself never thought that this crude device would not only evolve into a popular entertainment tool - television, but also become an essential instrument in the electronics industry and scientific research laboratories, and even a military equipment - radar. However, the oscilloscope really became an essential tool for engineers after Tektronix launched the 511 with trigger function in 1947. Before that, people could only view it qualitatively, but could not stably display the waveform on the screen for better measurement.
In fact, in the following decades, Tektronix almost led the development of oscilloscopes. Tektronix continued to improve the functionality and usability of analog oscilloscopes, and first established the concept of modularization in 1969, launching the 7000 series oscilloscopes, and reached its peak in 1979 with the launch of the 7104 with a bandwidth of 1GHz. In 1983, the 2465 series using integrated circuits was launched, and analog oscilloscopes reached a new height, realizing many functions similar to digital oscilloscopes. However, digital oscilloscopes have begun to appear and have realized some functions that cannot be achieved by analog, and slowly analog oscilloscopes have begun to give way to digital oscilloscopes. The
invention of the digital oscilloscope can be traced back to 1972, pioneered by Nicolet, but it was HP and Tektronix that really commercialized it. In the 1980s, digital oscilloscopes were still in the transition stage, and there were still many areas that needed to be improved. It was their contribution that made the performance of digital oscilloscopes surpass analog in the 1990s.
At this point, both types of oscilloscopes have entered the historical stage, and let's take a look at the difference between the two.
Structure
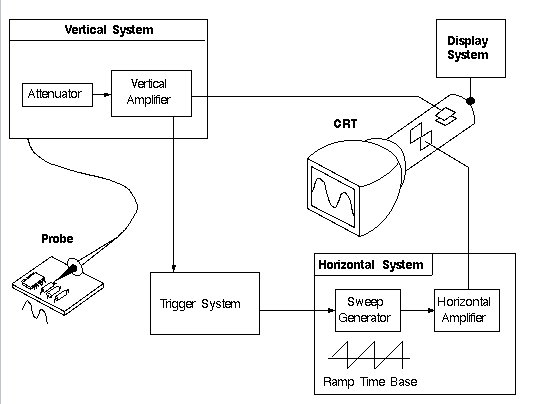
Typical structure of analog oscilloscope
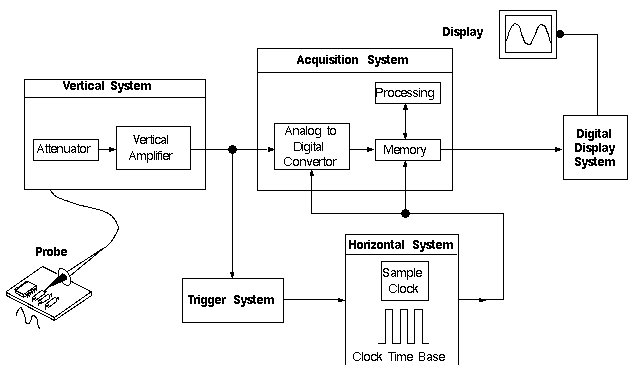
Typical structure of digital oscilloscope
From these two diagrams, we can see that the biggest difference between analog and digital is the waveform capture part. The analog oscilloscope is displayed directly on the CRT, while the digital oscilloscope drives the display for display after passing through the ADC sampling system. This is also the origin of the two names of analog and digital. The structure of the analog oscilloscope seems to be simpler than that of the digital oscilloscope, but in fact, the bandwidth requires oscilloscope tubes, vertical amplification and horizontal scanning to be fully promoted, while the digital oscilloscope only needs to improve the front-end amplifier and ADC. The development of oscilloscopes was very mature in the 1980s, and there was not much room for improvement. This directly restricted the development of analog oscilloscopes. After the 1GHz bandwidth was released, there was no qualitative breakthrough. The situation of digital oscilloscopes is exactly the opposite of analog. It happened to catch up with the great development of integrated circuits and digital circuits, although for quite a long time, the bandwidth did not break through the 1GHz mark.
Advantages of analog oscilloscopes
Simple operation - all operations are on the panel, the waveform responds promptly, what you see is what you get;
not easy to induce noise - the waveform is cleaner, without excessive noise coupling
Fast data update - hundreds of thousands of waveforms are captured per second, which corresponds to the waveform update rate of the digital oscilloscope;
real-time bandwidth and real-time display - the bandwidth of the continuous waveform is the same as that of the single waveform. The bandwidth of the digital oscilloscope is closely related to the sampling rate. When the sampling rate is not high, it is necessary to use interpolation calculation, which is easy to cause confusion.
In short, the analog oscilloscope provides engineers and technicians with waveforms that they can see with their own eyes, and they can be tested with confidence within the specified bandwidth. Among the five senses of human beings, the eyes are very sensitive, and the screen waveform is instantly reflected to the brain to make judgments, and even subtle changes can be perceived. Therefore, analog oscilloscopes are very popular among users.
Advantages of digital oscilloscopes
Storage function - digital oscilloscopes have storage functions, which can not only store settings, but also waveforms. It really takes advantage of this feature that the analog oscilloscope does not have, resulting in many conveniences in application.
Powerful trigger function - not only the simple edge trigger function of simulation, but also the pulse width and single trigger are introduced for the first time. Almost all digital oscilloscopes have these three basic functions; trigger position setting, you can define the trigger point arbitrarily.
Powerful capture capability - optional sampling mode, peak, average, envelope, can easily capture burrs
Powerful computing power - not only can perform mathematical operations, but also FFT analysis
Uniform display - whether it is a high-speed signal or a low-speed signal, a single pulse or a repetitive waveform, the display brightness is uniform
Automatic measurement - can automatically measure voltage and time parameters, reducing reading errors
Self-calibration - self-check at power-on, no manual calibration of horizontal and vertical Connectivity
- convenient connection capability with computers, printers, and plotters
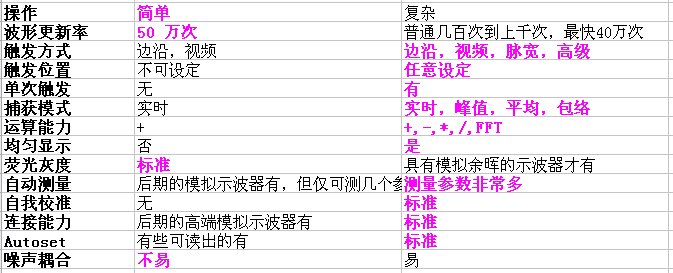
Table 1 Comparison of analog and digital oscilloscopes, only real-time oscilloscopes are compared here.
Keywords:Oscilloscope
Reference address:Let’s talk about oscilloscopes, part 1: analog or digital?
Let's first take a brief look at the history of oscilloscopes.
In 1900, Karl Ferdinand Braun (also translated as Brown), a physics professor at the University of Strasbourg, invented the world's first cathode ray tube analog oscilloscope. Even Braun himself never thought that this crude device would not only evolve into a popular entertainment tool - television, but also become an essential instrument in the electronics industry and scientific research laboratories, and even a military equipment - radar. However, the oscilloscope really became an essential tool for engineers after Tektronix launched the 511 with trigger function in 1947. Before that, people could only view it qualitatively, but could not stably display the waveform on the screen for better measurement.
In fact, in the following decades, Tektronix almost led the development of oscilloscopes. Tektronix continued to improve the functionality and usability of analog oscilloscopes, and first established the concept of modularization in 1969, launching the 7000 series oscilloscopes, and reached its peak in 1979 with the launch of the 7104 with a bandwidth of 1GHz. In 1983, the 2465 series using integrated circuits was launched, and analog oscilloscopes reached a new height, realizing many functions similar to digital oscilloscopes. However, digital oscilloscopes have begun to appear and have realized some functions that cannot be achieved by analog, and slowly analog oscilloscopes have begun to give way to digital oscilloscopes. The
invention of the digital oscilloscope can be traced back to 1972, pioneered by Nicolet, but it was HP and Tektronix that really commercialized it. In the 1980s, digital oscilloscopes were still in the transition stage, and there were still many areas that needed to be improved. It was their contribution that made the performance of digital oscilloscopes surpass analog in the 1990s.
At this point, both types of oscilloscopes have entered the historical stage, and let's take a look at the difference between the two.
Structure

Typical structure of analog oscilloscope

Typical structure of digital oscilloscope
From these two diagrams, we can see that the biggest difference between analog and digital is the waveform capture part. The analog oscilloscope is displayed directly on the CRT, while the digital oscilloscope drives the display for display after passing through the ADC sampling system. This is also the origin of the two names of analog and digital. The structure of the analog oscilloscope seems to be simpler than that of the digital oscilloscope, but in fact, the bandwidth requires oscilloscope tubes, vertical amplification and horizontal scanning to be fully promoted, while the digital oscilloscope only needs to improve the front-end amplifier and ADC. The development of oscilloscopes was very mature in the 1980s, and there was not much room for improvement. This directly restricted the development of analog oscilloscopes. After the 1GHz bandwidth was released, there was no qualitative breakthrough. The situation of digital oscilloscopes is exactly the opposite of analog. It happened to catch up with the great development of integrated circuits and digital circuits, although for quite a long time, the bandwidth did not break through the 1GHz mark.
Advantages of analog oscilloscopes
Simple operation - all operations are on the panel, the waveform responds promptly, what you see is what you get;
not easy to induce noise - the waveform is cleaner, without excessive noise coupling
Fast data update - hundreds of thousands of waveforms are captured per second, which corresponds to the waveform update rate of the digital oscilloscope;
real-time bandwidth and real-time display - the bandwidth of the continuous waveform is the same as that of the single waveform. The bandwidth of the digital oscilloscope is closely related to the sampling rate. When the sampling rate is not high, it is necessary to use interpolation calculation, which is easy to cause confusion.
In short, the analog oscilloscope provides engineers and technicians with waveforms that they can see with their own eyes, and they can be tested with confidence within the specified bandwidth. Among the five senses of human beings, the eyes are very sensitive, and the screen waveform is instantly reflected to the brain to make judgments, and even subtle changes can be perceived. Therefore, analog oscilloscopes are very popular among users.
Advantages of digital oscilloscopes
Storage function - digital oscilloscopes have storage functions, which can not only store settings, but also waveforms. It really takes advantage of this feature that the analog oscilloscope does not have, resulting in many conveniences in application.
Powerful trigger function - not only the simple edge trigger function of simulation, but also the pulse width and single trigger are introduced for the first time. Almost all digital oscilloscopes have these three basic functions; trigger position setting, you can define the trigger point arbitrarily.
Powerful capture capability - optional sampling mode, peak, average, envelope, can easily capture burrs
Powerful computing power - not only can perform mathematical operations, but also FFT analysis
Uniform display - whether it is a high-speed signal or a low-speed signal, a single pulse or a repetitive waveform, the display brightness is uniform
Automatic measurement - can automatically measure voltage and time parameters, reducing reading errors
Self-calibration - self-check at power-on, no manual calibration of horizontal and vertical Connectivity
- convenient connection capability with computers, printers, and plotters
Table 1 Comparison of analog and digital oscilloscopes, only real-time oscilloscopes are compared here.

Previous article:Talking about oscilloscopes Part 2 - Specific performance of analog and digital oscilloscope test performance
Next article:Probe Advanced - Performance Differences Between Differential and Single-ended Active Probes
Recommended ReadingLatest update time:2024-11-16 13:46
Mouser Electronics Now Stocking Analog Devices AD9083 Analog-to-Digital Converter

Mouser Electronics Now Stocking Analog Devices AD9083 Analog-to-Digital Converter Providing low-power solutions for mmWave imaging and phased array radar applications May 19, 2021 – Mouser Electronics, Inc., the premier New Product Introduction (NPI) distributor with the widest selection of semiconductors and elect
[Analog Electronics]

Recommended Content
Latest Test Measurement Articles
- Keysight Technologies Helps Samsung Electronics Successfully Validate FiRa® 2.0 Safe Distance Measurement Test Case
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- Seizing the Opportunities in the Chinese Application Market: NI's Challenges and Answers
- Tektronix Launches Breakthrough Power Measurement Tools to Accelerate Innovation as Global Electrification Accelerates
- Not all oscilloscopes are created equal: Why ADCs and low noise floor matter
- Enable TekHSI high-speed interface function to accelerate the remote transmission of waveform data
- How to measure the quality of soft start thyristor
- How to use a multimeter to judge whether a soft starter is good or bad
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of non-contact temperature sensors?
MoreSelected Circuit Diagrams
MorePopular Articles
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
MoreDaily News
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
Guess you like
- Last day! Double 11 discount of 1,000 yuan for Tektronix oscilloscopes!
- [FM33LG0 series development board evaluation] 02. Basic engineering (LED, KEY, LPUART, LPTIM, SHELL)
- TMS320F28027F for power stage control
- Can anyone who knows about TSIP give me some advice?
- If anyone has photos of bulging lithium polymer batteries, please post them here.
- Adjust the brightness of the LED provided by Zigbee
- FPGA Design Flow
- Qorvo Launches First Smart Home Device Controller to Enable Simultaneous Wireless Communications
- [nRF52840 DK Review] +52840 NFC (Part 1)
- 【Beetle ESP32-C3】2. PWM breathing light (Arduino)

 Building real-time machine learning systems
Building real-time machine learning systems Digilent Vivado library
Digilent Vivado library















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号