The key to wireless application design is to first select the right wireless connectivity technology based on the application requirements, which determines protocol, interoperability, range, robustness and application.
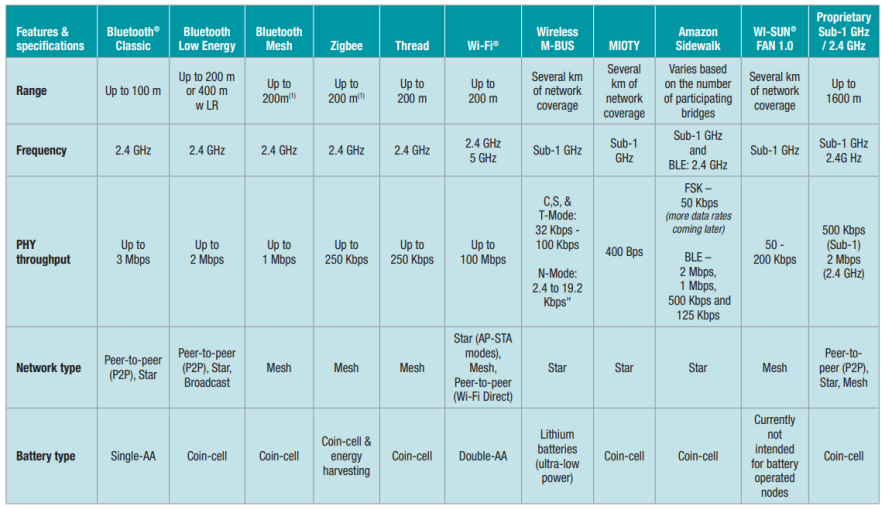
As shown in the figure, each different wireless standard has its advantages and disadvantages. The following is a detailed comparison of various wireless indicators (excerpted from TI's network protocol white paper).
Advantages of Classic Bluetooth:
• Network type: Classic Bluetooth is designed for short-range applications and supports network types such as point-to-point (P2P) and star network topologies.
• Throughput: Bluetooth Classic is designed for high data throughput applications, such as audio streaming, with data rates up to 3 Mbps.
• Target applications: Audio streaming through wireless headphones, speakers and soundbars.
Potential disadvantages of Bluetooth Classic:
• Power consumption: Classic Bluetooth is not optimized for low-power applications.
Advantages of Bluetooth Low Energy
• Network type: Bluetooth Low Energy is designed to support point-to-point (P2P), star and broadcast. Bluetooth Low Energy can be used in applications such as health monitors, personal electronics, asset trackers, and more. Bluetooth Low Energy is an excellent wireless technology medium that can quickly establish a connection and exchange data between two devices, such as smart car access.
• Power Consumption: Bluetooth Low Energy is designed for ultra-low-power wireless communications and is capable of operating for many years on a single coin-cell battery. The protocol is designed to be lightweight and can flexibly adjust various communication interval parameters, such as broadcasting at 1 second intervals.
• Throughput: The standard data rate for Bluetooth Low Energy 4.0 and newer is 1 Mbps, which is sufficient for most types of
communicate. Bluetooth 5 Low Energy now also supports data transfer speeds of up to 2 Mbps.
• Wireless Robustness: Bluetooth Low Energy uses the 2.4 GHz wireless band shared with other wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi, Zigbee and Thread. To alleviate conflicts in this crowded band, Bluetooth uses frequency hopping to find an open channel before communicating.
• Target applications: wireless keyboards, heart rate monitors, blood pressure monitors, smart car access control, etc. Bluetooth Low Energy is the most widely used wireless technology as it is ubiquitous in every smartphone or tablet.
Potential disadvantages of Bluetooth Low Energy:
• Range: Bluetooth is not designed for applications requiring long-distance connectivity. Bluetooth requires a gateway bridge to connect to the IP network.
Advantages of Bluetooth Mesh Network:
• Network type: Based on existing Bluetooth low energy technology, Bluetooth mesh networks extend the range of wireless networks. Communicating in a mesh network over multiple hops helps extend the range of your wireless connection. Supports up to 100 industrial-grade nodes from small to large while providing a self-healing multi-path network. There is no single point of failure. One device connects and communicates with another device, establishing a 1:1 relationship. Network devices can have a 1:1 relationship with multiple devices creating a central mesh network.
• Power consumption: Like Bluetooth Low Energy, Bluetooth mesh is designed for ultra-low-power wireless communications and is capable of operating on a single coin cell battery for many years. The device can stay on standby longer as long as the RF is on for longer intervals.
• Example applications: lighting, HVAC, wireless sensor networks, data collection, and more.
Potential disadvantages of Bluetooth Mesh:
• Throughput: Bluetooth mesh networks are not designed for high data throughput. This is a low latency application. For any high data throughput, Bluetooth Low Energy is recommended.
Advantages of Zigbee:
• Network Type: Zigbee technology is a mesh-based protocol that allows the network to grow with your application needs. It supports self-forming and self-healing meshes. There are four different Zigbee roles; coordinator, router, end device and green energy device (Zigbee Green Power). Zigbee is primarily used in building and home automation.
• Power consumption: Zigbee is a low-power wireless communication that enables long battery life in end applications. After executing low power, the end device wakes up periodically to send data and re-enters low power mode as soon as possible.
Zigbee Green Power Devices can even enable battery-less applications, such as using solar panels to collect energy.
• Wireless Robustness: Zigbee is a wireless stack based on IEEE 802.15.4 (as physical layer and MAC layer). Zigbee applications can select a specific channel to communicate with up to 16 channels. Zigbee is self-healing and can identify damaged nodes in the network and reroute as needed to protect the network.
• Range: Typical range for Zigbee applications is a single hop distance of up to 200 meters. However, Zigbee can achieve long-distance transmission through its mesh networking capabilities through multiple Zigbee routers in a daisy-chain network.
• Target Applications: You can find Zigbee networks in a variety of home automation controls, such as wireless light switches, thermostats, and many more. Zigbee certification also guarantees interoperability with Zigbee certified products from other vendors.
Potential disadvantages of Zigbee:
• Network type: Zigbee does not provide an easy way to connect to the cloud. Connecting to an IP network requires a gateway and address translation layer.
• Throughput: Zigbee is not designed for high data rate transmission. It is designed for applications with a maximum low data rate of 250 Kbps throughput.
Zigbee Sub-1GHz, which combines mature, safe and reliable low-power Zigbee with ultra-long-distance communication.
Advantages of Thread:
• Network type: Thread is designed for homes connected using a mesh network using an IP-based network. It is designed primarily for use in building automation to control lighting, thermostats and other products. Thread is self-healing and self-forming, meaning it automatically upgrades or downgrades nodes to ensure there is no single point of failure in the network. Additionally, Thread can be used with any IPv6 gateway, making it easy to commission new devices into the network.
• Power Consumption: Thread is designed to run in low-power sensing applications and connect your sensors to IPv6 networks. Thread End Devices can sleep for long periods of time, extending battery life.
• Range: For a single hop, thread range is typically up to 200 meters of line of sight. Thread is a mesh network with up to 32 hops, thus supporting wider range.
• Security: Inter-device communication is protected using AES-128 by default. Debugging uses standard DTLS with ECJ-PAKE.
• Target Applications: You will find Thread networks used in a variety of home automation devices such as light bulbs, electronic locks, and more. Thread is also designed to be controlled by any Thread certified device. It can be easily integrated with any existing application framework.
Potential disadvantages of Thread:
• Throughput: IPv6-based networks have the potential for high overhead, so Thread's 250 Kbps throughput may not be sufficient for existing IPv6 deployments.
• Application agnostic: Thread does not specify interoperable application frameworks; Thread verifies network interoperability and does not guarantee interoperability of application frameworks.
Advantages of Wi-Fi:
• Network type: Wi-Fi can support star connections (stations with a central access point), point-to-point connections (Wi-Fi direct), and mesh networks. Wi-Fi is commonplace in most home and business environments, a technology that allows products with this capability to quickly connect to existing infrastructure.
• Wireless Robustness: Wi-Fi supports operation in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, allowing Wi-Fi products to make flexible decisions
Which frequency band do they want to support. Wi-Fi's ability to operate in the 5 GHz band enables products to benefit from less congestion on the channel for improved performance. In addition, the advanced PHY modulation scheme enables Wi-Fi to send data quickly, reducing time and collision probability.
• Security: Wi-Fi has an active ecosystem that is constantly improving its security to keep it up to date and resistant to hacker attacks.
Wi-Fi data can be encrypted before transmission using the latest WPA3 personal and enterprise-grade encryption. Wifi also has multiple layers of security thanks to its native IP (like TLS).
• Throughput: Wi-Fi protocols are designed to be scalable to support a variety of application throughput requirements, ranging from edge nodes to gateways. It supports fast over-the-air (OTA) updates and throughput up to MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) for typical IoT/edge node devices to 100Mbps applications.
• Power Consumption: Wi-Fi protocol flexibility results in extremely low average power consumption while connecting to the network for battery-powered applications. It is also the most energy efficient per bit of data transferred.
• Target Applications: Wi-Fi is commonly used in consumer, industrial, and enterprise applications to enable wireless connectivity between devices and the cloud. Wi-Fi can be found in controls in smart building products such as video surveillance, HVAC, access control, etc.; used in healthcare, such as patient monitors, medical equipment; used in smart meters, solar/renewable energy, electric vehicle charging; and More smart products require Internet connection and remote monitoring.
Note that Wi-Fi is one of the most widely used wireless communication standards between devices and the Internet.
Potential disadvantages of Wi-Fi:
• Power consumption: Wi-Fi networks include the overhead of additional transmit/receive cycles in addition to the application's requirements to maintain a Wi-Fi connection. Calibration and TX/RX current can be higher than other manufacturing Wi-Fi technology solutions that rely on AA batteries and have higher peak current draw.
Previous article:Nordic Semiconductor Announces nRF7002 Collaboration IC and nRF7002 Development Kit
Next article:Bluetooth SIG launches wireless standard for electronic shelf labels
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- e-Network Community and NXP launch Smart Space Building Automation Challenge
- The Internet of Things helps electric vehicle charging facilities move into the future
- Nordic Semiconductor Launches nRF54L15, nRF54L10 and nRF54L05 Next Generation Wireless SoCs
- Face detection based on camera capture video in OPENCV - Mir NXP i.MX93 development board
- The UK tests drones equipped with nervous systems: no need to frequently land for inspection
- The power of ultra-wideband: reshaping the automotive, mobile and industrial IoT experience
- STMicroelectronics launches highly adaptable and easy-to-connect dual-radio IoT module for metering and asset tracking applications
- This year, the number of IoT connections in my country is expected to exceed 3 billion
- Infineon Technologies SECORA™ Pay Bio Enhances Convenience and Trust in Contactless Biometric Payments
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- [Review of Arteli Development Board AT32F421] - Data Collection
- [2022 Digi-Key Innovation Design Competition] [Intelligent Garden Integrated Control System] TouchGFX displays Chinese menu
- Steering wheel direction sensing sensor selection
- Qorvo's new product makes it easier for 5G and Wi-Fi to work together
- msp430g2553-minimum system
- The pins of the components in the PADS self-made package library are missing
- Application of Keithley Source Meter in Electronic Thin Film Materials
- How can I hide certain items when printing in AD, such as the frequency mark of the crystal oscillator?
- Attenuator Specifications
- AD15 Help, help, help



 802.11® Wireless Networks: The Definitive Guide
802.11® Wireless Networks: The Definitive Guide
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号