Overheat protection circuit schematic diagram
Source: InternetPublisher:笑流年 Keywords: thermistor battery power overheating protection ptc Updated: 2021/01/15
For continuously operating electromechanical equipment such as automatic lathes, electric ovens, and ball mills used in production, as well as other unattended equipment, accidents often occur due to motor overheating or thermostat failure, and corresponding security measures need to be taken. The PTC thermistor overheat protection circuit can conveniently and effectively prevent the above accidents.
Principle circuit
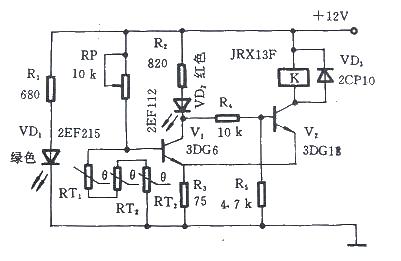
Taking the motor overheating protection as an example, it is a control circuit composed of a PTC thermistor and a Schmitt circuit. In the figure, RT1, RT2, and RT3 are three step-type PTC thermistors with consistent characteristics. They are buried in the windings of the motor stator. Under normal circumstances, PTC thermistors are at normal temperature and their total resistance value is less than 1KΩ. At this time, V1 is cut off, V2 is turned on, relay K is powered to close the normally open contact, and the motor is powered by the mains power supply.
When the motor locally overheats due to a fault, as long as one PTC thermistor is heated above the preset temperature, its resistance will exceed 10KΩ. So V1 is turned on, V2 is turned off, VD2 displays a red alarm, K is released when it loses power, and the motor stops running, achieving the purpose of protection.
Main component selection
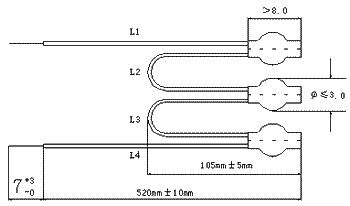
The selection of PTC thermistor depends on the insulation level of the motor. The standard dimensions of the components are shown in the figure. The Curie temperature of the PTC thermistor is usually selected in a range that is about 40°C lower than the limit temperature corresponding to the motor insulation grade. For example, for a motor with Class B1 insulation, whose limit temperature is 130°C, a PTC thermistor with a Curie temperature of 90°C should be selected. (PTC thermistor for overheating protection)
The selection of relay K depends on the capacity of the motor. The one in Figure 2.3.1 is JRX-13F with a contact load of 0.5A, which is suitable for small motors. RP should choose a potentiometer with a locking mechanism.
Installation and commissioning
The recommended installation method is to bury the PTC thermistors in the windings of the motor stator. The debugging method is: place the PTC thermistor in a constant temperature box, set the temperature to TK, and adjust RP so that when the PTC thermistor is at TK-5℃, VD2 does not light up and K does not act; when TK+5℃, The VD2 light is on and K moves. Just lock the RP.
- Build a simple buck-boost regulator and test it on a breadboard
- Energy-saving motorcycle rectifier regulator
- BA6104 five-digit LED level meter driver integrated circuit basic application circuit
- LED rechargeable flashlight circuit diagram
- Voltage-current converter constructed with XTR110
- Integrated regulated power supply with continuously adjustable output voltage
- UC3842 Electric Vehicle Charger
- Converting a lithium battery charging board into a constant voltage and current charger
- Practical constant current charger-----Constant current charger
- LM317T voltage regulation adjustable circuit diagram explanation
- Importance of Voltage Supervisors and Output Topology Selection
- Car battery charger circuit
- Overheat protection circuit schematic diagram
- Battery Monitor for Constant Boost Converter
- Basic circuit diagram of thermistor bridge measurement
- Schematic diagram of automatic battery charger
- DC 12V to AC 100V inverter power supply circuit design
- Solar power circuit
- Circuit 2 that uses thermistors to prevent relay contact competition
- Exhaust fan automatic control circuit (3)







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号