Introduction to Servo Drive
Servo drives, also known as "servo controllers" or "servo amplifiers", are controllers used to control servo motors. They function similarly to frequency converters acting on ordinary AC motors. They are part of the servo system and are mainly used in high-precision positioning systems. Generally, servo motors are controlled in three ways: position, speed, and torque to achieve high-precision transmission system positioning. They are currently high-end products in transmission technology.
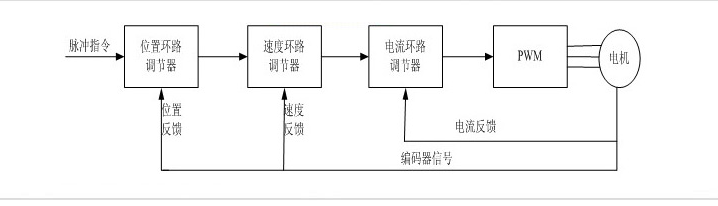
Figure 1 Principle block diagram of servo drive
Servo drive structure
Servo drives all use digital signal processors (DSP) as the control core, which can implement relatively complex control algorithms and realize digitalization, networking and intelligence. Power devices generally use drive circuits designed with intelligent power modules (IPM) as the core. The IPM integrates the drive circuit inside, and also has fault detection and protection circuits such as overvoltage, overcurrent, overheating, and undervoltage. A soft start circuit is also added to the main circuit to reduce the impact of the startup process on the drive.
Rectification section: The rectifier section converts the AC power into a DC power source, which is filtered by capacitors to generate a smooth and pulsating DC power source.
Inverter: The SPWM signal from the control unit drives the IGBT, converting the DC power supply into an SPWM waveform to drive the servo motor.
Control part: The servo unit adopts a fully digital structure, and realizes the software of closed-loop control through high-performance hardware support. Now all servos have adopted (DSP digital signal processing) chips, DSP, which can perform the functions of position, speed, torque and current controllers. Give PWM signal control signal to act on the power drive unit, and can receive and process position and current feedback, and has a communication interface.
Encoder: The servo motor is equipped with a high-performance angle measurement encoder that can accurately measure the position of the rotor and the speed of the motor.
At present, the output devices of servo control systems are increasingly using new power semiconductor devices with high switching frequencies, mainly including high-power transistors (GTR), power field-effect transistors (MOSFET) and insulated gate transistors (IGPT), etc. The application of these advanced devices significantly reduces the power consumption of the servo unit output circuit, improves the system's response speed, and reduces operating noise.
It is especially worth mentioning that the latest servo control systems have begun to use a new type of module that integrates control circuit functions and high-power electronic switching devices, called Intelligent Power Modules (IPM). This device integrates input isolation, energy consumption braking, over-temperature, over-voltage, over-current protection and fault diagnosis functions into a small module. Its input logic level is fully compatible with TTL signals and can be directly interfaced with the output of the microprocessor. Its application significantly simplifies the design of the servo unit and realizes the miniaturization and micro-miniaturization of the servo system.

Structural composition
The structure of mechatronic servo control system has various types, but from the perspective of automatic control theory, servo control system generally includes five parts: controller, controlled object, execution link, detection link, and comparison link.
Comparison
The comparison link is a link that compares the input command signal with the system's feedback signal to obtain the deviation signal between the output and the input. It is usually implemented by a special circuit or computer.
Controller
The controller is usually a computer or a PID control circuit. Its main task is to transform and process the deviation signal output by the comparison element to control the actuator to act as required.
Execution
The function of the execution link is to convert various forms of input energy into mechanical energy according to the requirements of the control signal to drive the controlled object to work. The actuators in the mechatronics system generally refer to various motors or hydraulic and pneumatic servo mechanisms.
Accused
Mechanical parameters include displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, and torque for the controlled object.
Testing
The detection link refers to a device that can measure the output and convert it into the dimension required by the comparison link, generally including sensors and conversion circuits.
Previous article:Requirements for servo feed systems
Next article:Working principle of servo drive
- Huawei's Strategic Department Director Gai Gang: The cumulative installed base of open source Euler operating system exceeds 10 million sets
- Analysis of the application of several common contact parts in high-voltage connectors of new energy vehicles
- Wiring harness durability test and contact voltage drop test method
- Sn-doped CuO nanostructure-based ethanol gas sensor for real-time drunk driving detection in vehicles
- Design considerations for automotive battery wiring harness
- Do you know all the various motors commonly used in automotive electronics?
- What are the functions of the Internet of Vehicles? What are the uses and benefits of the Internet of Vehicles?
- Power Inverter - A critical safety system for electric vehicles
- Analysis of the information security mechanism of AUTOSAR, the automotive embedded software framework
 Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
Professor at Beihang University, dedicated to promoting microcontrollers and embedded systems for over 20 years.
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Purgatory Legend-Battle of Doubler Circuits
- Bluetooth remote control serial port problem
- [Serial] [Starlight Lightning STM32F407 Development Board] Chapter 13 FLASH Data Storage Experiment
- DSP28335 serial port interruption problem
- How to make an echo on atmel/AVR microcontroller Atmega 128? Is there any relevant information?
- Download to get a gift | Collection of the best courseware: Tektronix Semiconductor Device Research Exchange and Keithley Test and Measurement Annual Seminar
- MSP430 Main Memory Bootloader Introduction
- I want to use POE to power some gadgets, but I don’t know what power chip to use?
- STM8L152 drives LCD experimental ultra-low power consumption code 7.2UA
- 5G and IoT will be the great equalizer

 Multimodal perception parameterized decision making for autonomous driving
Multimodal perception parameterized decision making for autonomous driving CVPR 2023 Paper Summary: Robotics
CVPR 2023 Paper Summary: Robotics
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号